Among indoor plants, it is difficult to find a culture as popular in the design of modern interior styles (including offices, restaurants and cafes) as anthurium. Despite the status of a fashionable plant and the fact that in any flower shop anthurium will be the first to be offered both for a gift and for decorating a home, it would be a big mistake to call it a culture that is easy to grow. Anthuriums can only withstand minor care slips, otherwise they will definitely not bloom as long and brightly as they could. Growing them requires adherence to several strict rules, which are best never broken.
10 rules for growing anthurium for long flowering
1. Cleanliness and attention
Anthuriums are not plants that can be forgotten for a few weeks or abandoned on vacation without care. They suffer greatly not only with minor missed procedures for care, but also from lack of attention. To prevent any difficulties and start fighting problems in time, you need to inspect the plants weekly, paying special attention to the bases of the leaves, petioles, analyzing how young leaves differ from the old ones typical for this variety.
One of the most important nuances in growing this plant is the need for regular hygiene. Dust should not accumulate on the leaves of anthurium; it is better to gently wipe it with a damp sponge or cloth several times a week. Anthuriums grow well with the use of special polishes for leaves, but only professional formulations and high-quality preparations should be used.
2. Suitable lighting
One of the reasons for the popularity of anthurium among interior designers is its ability to grow in fully artificial lighting. But regardless of whether the light source is natural or not, special attention should be paid to the quality and intensity of illumination for this plant.
Anthuriums of all types grow best in soft, diffused lighting. They can be displayed at some distance from the southern windows, on the eastern and western windowsills; in the summer they feel good on the northern windows. Strong shading is unacceptable even for the most modest varieties and plants that have faded.
When placed in the interior, and not on the windowsill, if any signs of shrinking leaves or pale colors appear, it is better to rearrange the bushes in time.
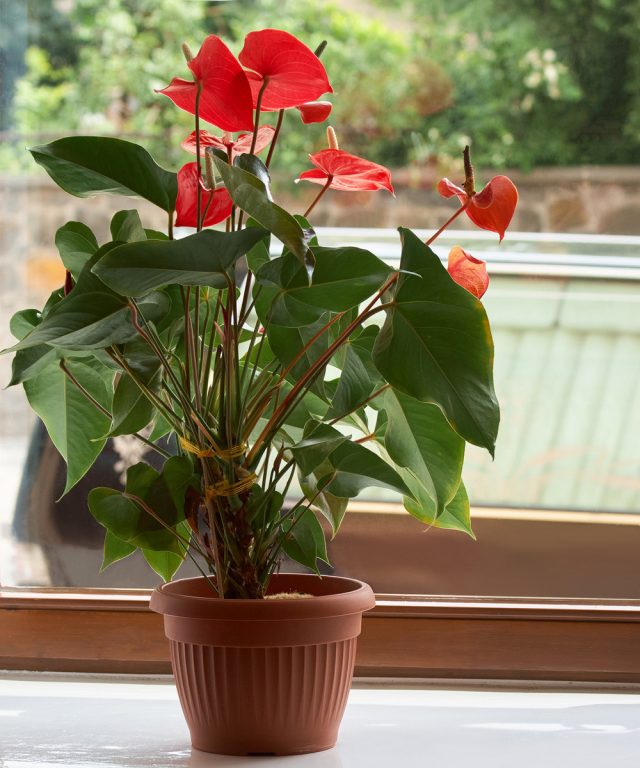

3. Stability is most important
For the anthurium, you need to find a permanent place with almost unchanging conditions – constant temperatures, soft ventilation, without any sudden changes in the conditions of detention. They do not like drafts, the influence of air conditioners or batteries, and moving to balconies. It is not worth taking them out into the fresh air in the summer “for the company” along with the rest of indoor crops, because their minimum temperature is quite high.
Anthuriums are thermophilic so much that even a cold snap to 18 degrees (for Scherzer’s anthurium – 15 degrees) will harm the plants. It is necessary to protect anthurium from hypothermia, especially an earthen coma, all year round. They endure heat only at high air humidity, ideal temperatures are from 18 to 25 degrees.
4. Constant moisture content of the substrate
Like the vast majority of indoor plants, anthurium does not like either dampness or drying out of the substrate. Complete drying of the soil should not be allowed, but overflows are dangerous. The more stable the soil moisture is, the better. The next watering is appropriate when a few top centimeters dry. In winter, it is better to dry the soil a little harder, limiting watering by the amount of water.
Water quality is also very important. Anthurium does not tolerate salting, it needs soft water, slightly warmer than the temperature in the room.
Read also our article Why do anthurium leaves turn yellow?
5. Air humidity plays an important role
Some types of anthurium (primarily, Scherzer’s anthurium) are less sensitive to dry air than others, but all anthuriums should be considered crops for which at least average indicators are needed. If the air humidity drops below 50%, it is better to immediately add spraying to the daily care or install trays with damp pebbles. The higher the temperatures, the higher the humidity should be.
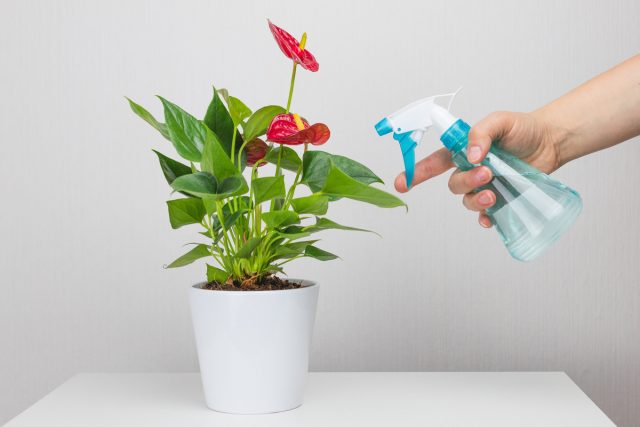

6. What is the growth – such and feeding
When it comes to fertilization, it is better to rely not on recommendations and standards, but on how the plant develops. If the anthurium releases new leaves, blooms, it needs fertilizing. If there is no vegetation, it is better to stop them.
In spring and summer, half a portion of fertilizer for flowering plants or a portion of fertilizer for Aroids or orchids should be applied every 2-3 weeks, if the leaves continue to grow in autumn and winter – every 5-6 weeks (subject to lighting compensation).
7. Not special, but thoughtful wintering
Anthuriums are rare indoor crops that do not need a strict dormancy period and often continue to bloom in winter. It is better to lower temperatures, but only to about 18 degrees. This does not mean that you do not need to take any measures during the cold season. Changes in care and light correction of conditions will help maintain the high decorative effect of anthurium.
For the dormant period, the lighting for the anthurium must be increased. An option with a shift to a lighter place (from the interior to the window, from the northern window sill to the southern one, etc.), and additional supplementary lighting will also do. Daylight hours about 12 hours are a guarantee of the absence of problems, including with the health of the plant.
Watering for the dormant period will have to be reduced, on average, by half compared to the period of active growing season. And top dressing – completely stop.
Read also our article Scherzer’s Anthurium – the most unpretentious and compact species.
8. Cut off only faded parts
Anthurium should not be disturbed and try to cut unnecessarily, even with deformation of the bushes, the formation is not used and rejuvenation is possible only by separation. From a plant, you literally need to remove only those leaves and inflorescences that wither, dry up on their own. And it is better not to rush, waiting for complete wilting.

9. Soil and repotting method are critical
Anthuriums cannot be transplanted carelessly, often changing pots and trying to fix any problems by changing the substrate. Actually, plants cannot tolerate exposing the roots, completely replacing the soil and, in principle, it is better to simply transfer them, keeping the earthen lump intact. Of course, with the exception of an emergency transplant to save the plant from rot damage.
But it is possible to transship anthuriums not only in spring, but also in summer, if desired (and necessary) deepening a little for thickening, growth of lateral offspring, and compensation for aging.
There is no need to disturb anthuriums annually: for this plant it is quite enough to simply change the upper 4-5 cm of the substrate. And the transshipment itself should be carried out when the roots completely absorb the substrate and appear in the drainage holes – on average, once every 1-2 years for adult anthuriums.
Anthuriums grow better in a special substrate – for anthuriums, Aroids, Bromeliads or orchids, clean bark, sphagnum, inert soils than in conventional substrates. They need a rough texture, compaction resistance and a slightly acidic reaction. And a very high drainage layer.
Anthuriums have very few requirements for the pots themselves: the main thing is that the diameter exceeds the depth and there are drainage holes.
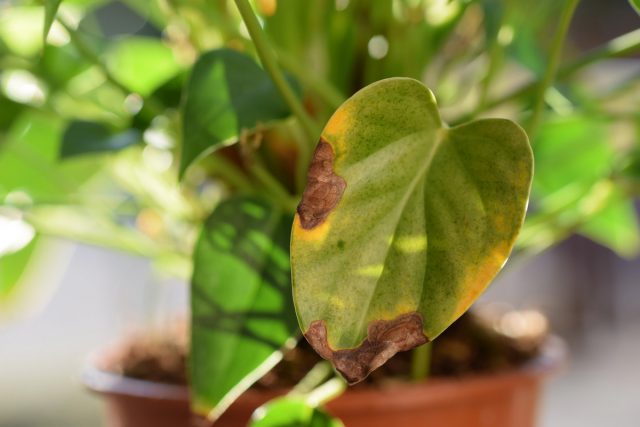
10. Any suspicion of infection requires immediate action
In general, anthuriums are considered very resistant plants for a reason. But if you make mistakes in watering, place the bushes in unfavorable conditions, it is easy to lose them from anthracnose and rot (especially sulfur). Of the pests on anthuriums in dry air, aphids, spider mites, and scale insects are not uncommon.
If any suspicious spots and damage are noticed on the leaves and inflorescences during regular inspection, there are growth disorders, it is better to immediately isolate the bushes and start treatment with systemic drugs, trying to correct the unfavorable factors and change the care as soon as possible. With anthurium, it is better to carry out unnecessary preventive treatments than to miss the moment of the initial stage of infection.