The infectious disease of poultry from the chicken chick pullulorosis order infects quite often, resulting in the death of young animals.
- Help on the nature of pullorosis
- Etiological picture of pullorosis
- Epizootology <
- Pathogenetic and clinical picture of typhoid fever
- Pathogenesis of infection
- Clinical signs
- The course of infection and pathological changes
- Acute development
- Subacute and chronic development
- Pathologies <
- Treatment and preventive measures

Pull chickens and poultry orosis
Pullorosis nature information
An infection called poultry infection refers to the intestinal infection of the parenchymal organs of chickens and causes it in an adult bird inflammatory processes in the ovaries, leading to vitelline peritonitis. Among other types of infectious diseases – dysentery, bacillary white diarrhea (diarrhea).
A distinctive feature of pullorosis in chickens is its asymptomatic course.
The first cases of mass-produced Pallorosis birds were observed in 18 89 year. Then English scientists called this disorder salmonellosis of birds . The causative agent of Pullorosis in poultry was identified in 1900.Typhoid fever, pullorosis, would have been recorded on European territory in 1913, intestinal infection appeared on Russian poultry farms in 1924, when chickens and turkey poults with signs of this disease were imported.
As a result of the effects of pullorosis on young animals the number of deaths among chickens reaches 70%. At the same time, the economic damage from it is also associated with a decrease in the productivity of adult chickens, a decrease in their egg production and the hatchability of a new generation due to the problem of embryonic development of the fetus. When Pullorosis develops, young chickens and turkey poults begin to lose weight, which directly affects the breeding characteristics of poultry.
The etiological picture of pullorosis
is caused by the pathogen belonging to the order salmonella, which is a stationary gram-negative bacillus that does not form either spores or capsules. Microbiology classifies the causative agent of typhoid fever as aerobes.
For the activity of an infectious bacillus, the most optimal temperature is 38 ° C with alkaline pH of 7.5.
In the usual nutrient medium, aerob develops sufficiently quickly, easily forming round forms, translucent colonies with clear outlines and a slightly protruding wet surface. pullorosis can multiply in a rough form, then it grows in dry colonies.
The causative agent of typhoid fever is significantly resistant to external factors.So, in bird droppings, pullorosis persists for 100 days, in conditions of non-flowing water – up to 200, in the soil layer – up to 400. At the same time, in conditions of bird litter that is not replaceable for 10 days, the pathogen of bird pullorosis dies.
Scientists noticed that aerobic pullorosis, which got into the gardening culture while maintaining the temperature within 18-20 ° C in the dried state, is able to live up to 7 years.
A long period of activity of the pullorosa infection is observed in freezing conditions up to 180-190 days. It is possible to inactivate the pullorosis virus when heated to 60 ° C for at least half an hour. At the boiling point, the aerob dies after only a minute, when the infected chicken egg is cooked – after 7-8 minutes.
Various drugs and solutions can lead to the death of the infection:
- 1% formalin is able to destroy Pullorosis in 5 minutes,
- for inactivation with carbolic acid, a concentration of 5% and half a minute is required,
- will cope with manganese, naphthazole, bleach in 15-20 minutes with active chlorine.
Scientists note the sensitivity of pullorous bacteria to drugs from a number of antibiotics, about Nako addictive infection observed when treatment is long-term use of the same medicament.
Epizootology
In addition to poultry (turkeys, turkeys, chickens, chickens, guinea fowl, pheasants and quail from the chicken squad) among other animals that are prone to pullosis, rabbits, decorative pigs, and mice emerge. A small resistance against bird pullorosis has been recorded among waterfowl.
Among broilers, typhoid fever mainly affects meat-bearing birds . The smallest cases of pallorosis in chickens were observed in those types of poultry that are hatched to receive eggs .
The main route of transmission of the disease is embryonic, when the infection passes through infected eggs to newborn young animals. Up to 50% of such cases are noted.
Pullorosis is observed in young animals depending on the age category:
- 5-7-day-old chickens suffer from pullorosis more often, the disease progresses in them over 20 days,
- upon reaching the age of 20 days and further, the number of cases in chickens decreases, passing into subacute forms of course or chronic development.
Transmission of intestinal infection occurs in different ways:
- as a source of transmission of the pathogen, sick young animals and adult hens carrying the bacte act AI, which together with the excrement is output to the environment pulloroza a large concentration of the pathogen.
- the penetration of pullorosis into chicken eggs occurs through the contents of the intestines of diseased individuals through the shell pores,
- bacteria, sources of fluff, waste, drinking water, food left after an infected brood,
- carriers of the disease are city birds (sparrows, pigeons, jackdaws).
Usually, only 25 to 50% of chickens hatch from pallorosis-infected eggs, the rest die during embryonic development.
Pathogenetic and clinical picture of typhoid fever
Among the factors that contribute to the appearance and development of pullorosis in chickens and chickens , many are related to the conditions of poultry and its quality of food:
- poor diet and non-compliance with the feeding schedule,
- crowded accommodation of birds in the house,
- overheating or hypothermia of individuals.
Pathogenesis of infection
When ingested the pathogen inside the bird’s body, at the site of penetration, for example, of the mucous membranes of the intestine, stomach, pulmonary system, begins to multiply and through the circulatory system begins to spread throughout all internal organs, leading to pathology of the heart, liver, kidneys, ovaries, spleen.
In the process of breeding, pullorosis releases toxins into the body, resulting in the death of the embryo.
When hatching, most chickens are already carriers of pullorosis, which is manifested with signs of acute intoxication. In the body of an adult bird, the pathogen glows in the egg-forming organs and from time to time is excreted along with egg laying.
Among the effects of bird transfer of pullorosis, when proper treatment is provided, is immunity to intestinal infection developed against intestinal infection due to the formation of antibodies in chickens that have undergone pullorosis. This feature formed the basis of breeding work when breeding chicken lines resistant to typhoid.
Clinical signs
The latent period of bird pullorosis can last from day to 20. Moreover secrete:
- congenital form, in which chickens already infected by hatching from infected eggs,
- postnatal form, when healthy individuals become infected from patients in the process of their joint content.
With a congenital form that develops in 3-5 days, the disease manifests itself in chickens in the form of general weakness and livyh states. Young animals lose their appetite and refuse to feed, moves with their wings down. Among the physiological symptoms is white liquid diarrhea. Similar clinical signs in those infected with a postnatal method that progresses from 2 to 5 days.
The course of the infection and pathological changes
The number of fatal cases with bird pululosis reaches 70% and depends on the form of the development of the disease.
The acute form of development
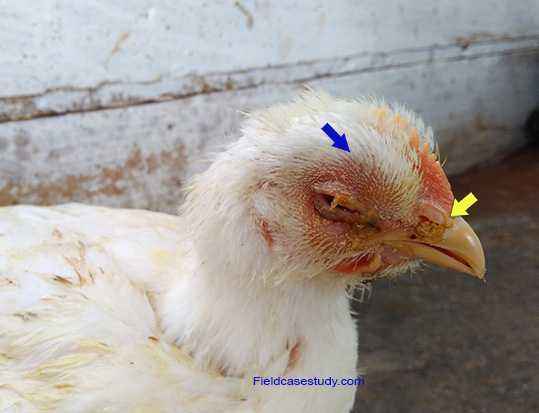
It is observed after 3 days-a week and is accompanied by shortness of breath, lack of coordinated movements of chickens, and bird immobility.Usually, diseased individuals freeze motionless with their eyes closed, legs wide apart, which veterinarians often demonstrate as a good example of a clinical picture in the photo. An increase in temperature to 44 ° C is noted. The main symptom of the acute development of pullorosis is profuse white diarrhea. The outcome of the acute course of typhoid in most cases is fatal, after 10-15 days.
Subacute and chronic development
Such forms of the course of the disease are characteristic for 2-3-week-old birds and adult chickens. Chickens begin to lose in the gain, become inactive, lag behind in development. If birds are treated with antibiotics , most chickens recover from the disease.
In adult broilers, no symptoms of pullorosis are observed, the disease proceeds without any special clinical signs. Only occasionally can a change in egg production be noted in the direction of decrease. Some individuals are characterized by lethargic conditions, decreased appetite. With exacerbation of bird typhus, cases of thirst and shortness of breath are recorded. Layers develop peritonitis. With the manifestation of pullorosis in broilers, lameness and the appearance of arthritis are noted, in the knee joints swell. Mortality rates among adult broilers are no more than 5% if they are treated on time.
Pathologies
Pathological changes in the internal organs are observed as a result of pullorosis developing in the body when the embryos, young animals and adults are opened:
- liver enlargement , spleen and gall bladder filled with dark green bile,
- accumulation of white uric acid salts in the rectum,
- the presence of foci of necrosis in the lung tissue, heart,
- inflammatory intestinal processes,
- the presence of follicular inflammation.
In accordance with the obtained epizootological data, the surgeons make a diagnosis taking into account the clinical signs, the age of the bird, the obtained pathological studies. The final diagnosis is made in the presence of bacteriological studies of fresh bird corpses or in vivo diagnosis of adults by the blood-drop reaction.
Medical and preventive measures
One of the most effective means for the prevention of pullorosis is bacteriophage used orally in a dosage of 2 ml. It is introduced twice with an interval of 2 days. On the third day, this drug is used as an injection subcutaneously in a volume of 0.5 ml.
Treatment of diseased individuals is carried out using antibiotic drugs, among which:
- furazolidone , mixed with feed at 0.04-0.06% for 15 days with repeated treatment after a 3-5 day break,
- less toxic furidine with a dosage of 200 mg per 1 kilogram of weight, added to the feed for 10 days,
- widely used as an additive to feed and drinking water sulfadimezin in a volume of up to 1% for 2 weeks with a repeat at intervals of 2-3 days,
- complex avidox and colimycin.
If detected and cases of typhoid typhoid fever and the final diagnosis made by the veterinary service, a decision is made by the executive branch of the region to declare an unfavorable situation and begin restrictive measures for breeding chickens and turkey poultry, comprehensive treatment and slaughter stripping are carried out.