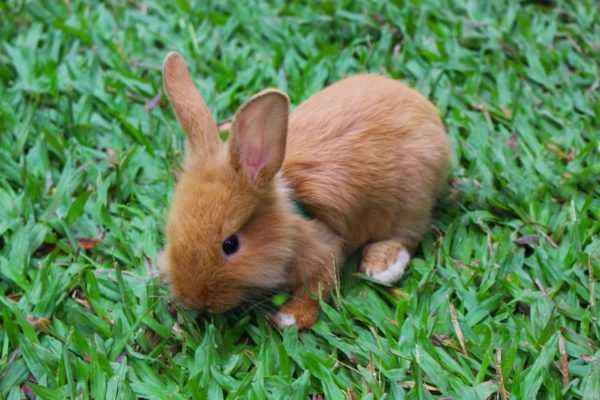
Brown hare, or in lat. Lepus europaeus, a hare-like mammal belonging to its large representatives.
- External attributes
- Geography of habitat
- Habits and role in human life
- Hare habits
- Gnats for humans
- Food ration and breeding

Brown hare
External signs
A hare in a hare family can be recognized by its large size, it often grows to 65-68 centimeters in length, and weighs from 4 to 6 kilograms. The largest individuals reaching Its masses of up to 7 kilograms are found in the northern and northeastern places of its habitat.
The description of the animal includes its main features of the appearance of the species:
- regardless of its large size, its constitution fragile,
- from the white hare differs in longer (up to 14 centimeters) ears and a larger (7-14 centimeters) tail in the form of a wedge, covered with black fur on top,
- hind legs grouse differ from the paws of the squirrels in the foot shorter than that of the squirrels, which is explained by the habitats of the grouse, where snow cover you are shallow and hard frozen crust.
Hare coat shiny, with swirls, painted on the belly white, flanked by a shade darker than on the dorsal section. External classification is clearly visible in the photo.The color of the animal depends on the season:
- during the summer, the hare is painted in shades of ocher – gray, brown, red or brown, with dark streaks folded with the tips of the undercoat,
- in winter, the animal changes its color to lighter, but unlike white, it is never white, their head and ears at the ends, and the front of the back are always dark.
When spring and autumn come, hares seasoned molting passes seasonal molting. In this case, the spring change of fur is delayed by 75-80 days, starting closer to the end of March and ending in May, and passes in the direction from the head to the tail section. Wools that have grown over the summer during the fall from September change to thicker winter fur, but unlike spring already in the opposite direction – from the thigh through the ridge to the front.
Geography
The main habitat inhabited by russians is the steppe, tundra thickets and forest-steppes. It can be found in the European steppe massifs, on the North African continent and in Asia.
The northern boundary of the range of habitat of the Rusak passes through the Irish and Scottish territories, in the range of Sweden and Finland. The southern border covers Turkey and Iran, the northern part of Arabia and Africa, the Transcaucasian region and the north of Kazakhstan.
In North America, European hare were settled artificially, introduced in 1893 through New York. In 1912, they tried to settle him in the Canadian province of Ontario.Having acclimatized in Australia and New Zealand, it was included in the list of animal pests.
In Russia, this species can be seen throughout European territory, they live right up to the Ladoga northern shores and Lake Onega, live along the river Northern Dvina. The boundary of the animal’s residence passes through the Kirov and Perm regions, capturing the regions of the Ural Mountains, then through the Caspian Sea and in the north to Karaganda. There are resettlement of grouse in southern Siberia and the Far East. Attempts by scientists to acclimatize a grouse on the squares of Buryatia ended in failure.
It happens that in the summer, grouse climb to mountain altitudes from 1.5 to 2.0 kilometers, descending from heights only when winter sets in.
Hare hare prefer outdoor areas for movement and life in the form of fields and meadows, clearings and large clearings. In deep coniferous forests, the animal lives extremely rarely, mostly live in deciduous forests and woodlands.
In forest-steppes and steppes, hares choose agricultural crops of grain, coppices and shrubs. Very often, animals tend to move closer to settlements and natural reservoirs.
The number of hares today is about several million. Their life expectancy and the number of individuals are primarily affected by weather and food factors.For many individuals, snowy winter seasons with blizzards, which do not allow animals to feed, become fatal. Adversely affect the size of the population of grouse and spring with alternating heat and frost, in which the early hatched broods die. Among the natural enemies of grouse hunters are wolves, foxes and lynxes.
Habits and role in human life
Hare habits
The habits of the grouse characterize them as settled animals living in a certain territory. They prefer not to leave the habitable area if there is a sufficient amount of feed in this place. In other regions, grouses move daily in search of food, covering tens of kilometers. Sometimes seasonal migrations towards settlements and less snowy to the fringes are observed.
The activity of the grouse begins at dusk and at night, and in the first part of the night and just before morning. During the day, they can be activated only during the rutting (mating).
In the summer period, the lying of the grouse looks like a shallow hole, hidden from prying eyes under the bush. At the same time, minks do not build permanent minks. On vacation, they dig in temporary shelters – daytime minks that save animals from the annoying heat. As a place of rest, hares can use other people’s burrows – badgers or foxes.
Hare hare run faster than the whites, developing a speed of up to 60 kilometers per hour, while tracking long jumps, confusing the tracks. They belong to good swimmers. The voice of the grouse cannot be heard only in danger, being caught or wounded, animals can make piercing sounds.
The female grouse calls to itself a bunny with a quiet cry, and the male only makes sounds when clicking with alarm with clicking teeth. As a communication between themselves, they often use paw percussion, the sound of which resembles playing a drum.
In spring, grouse birds lie on high surfaces warmed by the sun, and in winter hares move to deep snow with swarms of burrows up to two meters. Often, in the fall, animals lay in haystacks.
Mermaids for humans
In natural conditions, the males live for 6-7 years, with rare exceptions, life expectancy can be up to 12. It belongs to commercial animals and serves as an object of hunting with hounds and sports, being valuable for fur and meat. They also go for high-quality felt and for sewing some types of fur products.
In many countries these animals are classified as agricultural pests, since hares can damage winter crops and damage fruit trees, gnawing up to 15 plantings overnight.
In addition to the damage to agriculture, grouse are among the animals suffering from serious diseases, such as coccidiosis, pasteurrez, tularemia, brucellosis.
Food ration and reproduction
Among the main food for hare hares in summer Name – vegetation and twigs of trees. Animals prefer foliage and stems, but sometimes they can feast on the roots of shrubs. With the onset of the summer period, hares pass to seeds.
In summer, the feed ration becomes much richer and includes wild dandelions and tansy, alfalfa and clover, as well as cultivated buckwheat, cereals and sunflowers. Among the goodies for gourmets are vegetables and melons.
Not all seeds are completely digested by animal organisms, thus brown hares act as seed distributors along the path of their movement.
The basis of winter nutrition make up the same seeds and grass rags, the remaining garden crops that hares begin to look for and get from under the snow layer. In addition, animals feed on apple, maple and pear woods in winter, gnaw at willow and aspen.
The breeding season of grouse is directly dependent on their habitat.
Western European grouse in the period breeding from March to September have time to bring 4 hereditary broods, some even five. In a more favorable climate, rabbit breeding occurs throughout the calendar year.
On Russian territory, the hare runs from February to March, then from April to May and the third in June.
Pregnancy in females lasts 45 days, the brood can count from 1 to 9 rabbits. Such a difference in the number of offspring is associated with reproductive abilities – the fewer reproduction cycles, the more the female brings rabbits.
Rabbits of the roe are born sighted and with fur.
The weight of the average newborn rabbit is 80-150 grams. By the fifth day of life, rabbits begin to move actively, gain weight up to 400 grams at the age of two weeks, actively eating grass and become completely independent by the age of one month.