Ascospherosis or pericystosis is better known among beekeepers as calcareous brood. The infection mainly affects drone larvae, gradually spreading to the embryos of worker bees and queens. The result of infection is the death of the larvae, followed by the liming of their corpses.
The content of the article
- 1 The causative agent and ways of infection
- 2 How does the disease proceed
- 3 Symptomatology and diagnosis
- 4 preventive measures
- 5 Treatment and methods of struggle
- 5.1 Preparations
- 5.2 disinfection
The causative agent and ways of infection
The causative agent of this disease is the marsupial mushroom (veterinary name Ascosphaera apia), the spores of which are highly viable in all conditions. The life span in empty hives, on inventory, frames (honeycombs), in stored bee bread and honey is more than fifteen years. At the same time, spores are resistant to many chemical compounds used for disinfection – formalin vapor, sulfur dioxide.
Honey obtained from a sick family can be used for food purposes. But it is not suitable for feeding other bee nests.
Ascospherosis is capable of causing sensitive damage to the beekeeping economy: the number of bees in the nests is reduced by 20-23%, and their ability to collect honey falls by 40-50%.
Honeycomb with signs of disease
The infection spreads quickly in wet weather and during cold weather. First of all, the drone brood, located at the bottom of the frames and on the outermost combs in the nest, gets sick, since it is cooler here.
The source of infection is the bodies of dead and sick larvae, as well as honey with bee bread containing fungal spores. Adult insects are immune to this fungus, but they easily spread its spores. Often the carriers of the infection are thief bees, wandering bees and various bee parasites. Failure to comply with sanitary standards by beekeepers also provokes outbreaks of mycosis of this type.
Care should be taken with acquired queens and bee packages. They should not be bought from non-laboratory controlled apiaries.
How does the disease proceed
Fungus infestation is observed from April to October, when fresh brood is constantly present in the nests. The peak of the development of a fungal infection occurs in the summer months, if the weather is humid. Weakened colonies with abundant drone brood are especially susceptible to infection. Also, poor insulation of nests in the spring can serve as a trigger.
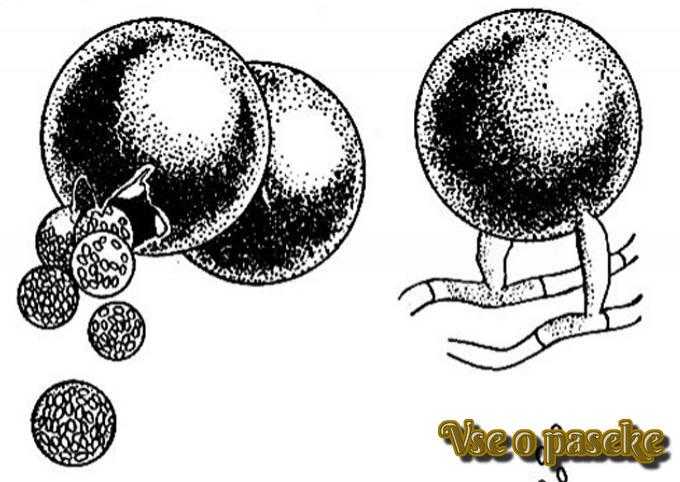
Spores and mycelium under a microscope
The disease takes two forms:
- latent, when the pathogen enters the intestines of the larvae, but does not cause their death;
- obvious (open), when most of the drone and bee larvae die.
This mycosis can also be a secondary infection, complicating the treatment of chilled, saccular brood, foulbrood.
3-4-day-old larvae are most sensitive to Ascosphaera apia. Spores, having penetrated into the intestinal tract of young animals, along with honey and bee bread, germinate into the mycelium. The filaments of the fungus penetrate the body of the insect through and through.
Symptomatology and diagnosis
Infected brood can be seen by its characteristic white color – fungal plaque covers the head end of diseased larvae. Then the body overgrows with it – the insects swell and fill the entire cell with themselves. If the brood is sealed, the fungus will grow through the comb lid.
Degree of defeat of the family
The cells themselves are covered with whitish or grayish mold. The individuals that died in them are completely mummified and can be easily removed outside. The bodies resemble bits of lime (hence the name of the disease). In the acute form, up to 50% of the brood becomes infected and sick.
The main symptoms are:
- dried-up corpses of larvae, painted in white (lime) color;
- from the head end on the corpses there is a thin layer of felt-like mycelium;
- faint mildew also appears on the lids of the sealed honeycomb.
To clarify the diagnosis, it is necessary to hand over the dead or sick young animals for analysis to the veterinary laboratory. Here, microscopy of the mycelium taken from the larvae will be performed.
Laboratory analysis is a mandatory measure if bee brood is affected to a greater extent (mixed infection is possible).
preventive measures
Fortunately for beekeepers, treatment of bee ascospherosis is rarely required. This mycosis is not widespread. And when it appears in the apiary, only individual nests are sick. Moreover, the disease often stops by itself.
Issuance of medical feeding
Prevention is carried out through proper care of the apiary and compliance with sanitary recommendations (cleanliness of inventory, equipment, clothes, hands is observed).
To prevent infection, hives are placed in a sunny and dry place. Families should be strong, provided with adequate food, and well insulated during cool and rainy periods.
Treatment and methods of struggle
If infected young animals are found, the following steps must be taken:
- the diseased brood is removed from the nest, and the extra combs are removed from the hive;
- the infected family is moved to a clean hive, and the nest is well insulated;
- the bees are given medicated syrup and / or the frames are processed;
- infected empty hives and equipment are disinfected.
Preparations
Nystatin used together with top dressing in the spring and summer. For this, a 20% sugar syrup is prepared to which the medicine is added at the rate of 100 units per 000 milliliters.
The same syrup can be used to irrigate frames with honeycombs. Or spray powdered sugar with Nystatin powder (crushed tablets) in the hive in a ratio of 100: 0,5 and in a dosage of 10 grams per frame.
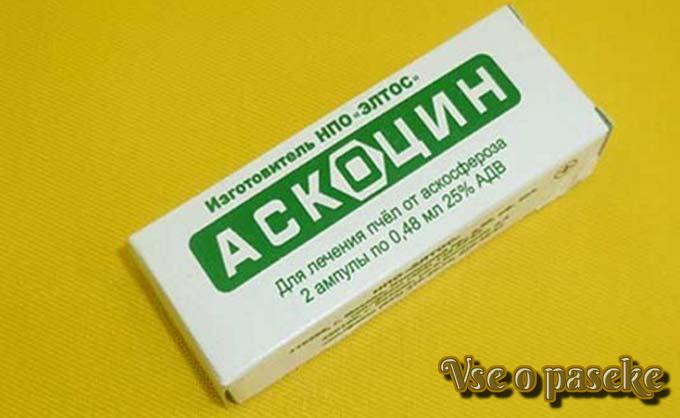
Askocin given at the rate of 60-70 ml for each frame fully occupied by bees. The medicine is added to syrup or kandy, pollen cakes (kneading the dough). The syrup can be poured into the cells of the lower part of the hive honeycomb, filling them by two thirds.
For irrigation, liquid sugar syrup (honey) is used in a ratio of 1: 5. Dose 10-15 ml for each frame. Processing is carried out two to three times with an interval of 3-5 days. It is necessary to work in personal protective equipment, including a respirator! Commercial honey from a sick family can be downloaded two weeks after the last treatment.
Askosan fed with sugar syrup (strength 1: 1) at the rate of 5 g per 2,5 liters. 250 ml of top dressing is dispensed per nest.
For dusting, 1 g of the drug is mixed with 100 grams of powdered sugar. The frames are powdered on both sides at the rate of 5-6 g of the mixture per piece. Treatment is performed 3-4 times with an interval of a week (until the clinical symptoms disappear completely).
“Askocid” applied as an emulsion for the treatment of nests. For this, 1 ml of the drug is dissolved in a liter of boiled and cooled to 40 degrees water. The solution is shaken thoroughly before use. Processing is carried out at the rate of 10 ml of emulsion per frame on both sides. Spraying is performed 3-4 times with an interval of one day. Honey can be used for food 20 days after the last treatment.
“Unisan” used to prepare medicinal syrup. To do this, prepare a syrup with a strength of 1: 1, then mix one liter with 1 ml of the drug. Each family is given 250 ml of top dressing.
For spraying, sugar syrup is prepared with a strength of 1: 4, in which the drug is dissolved at the rate of 1 ml per half liter. To process one frame on both sides, 10-12 ml of syrup is required. The treatment is repeated 3-4 times at weekly intervals.
Read about the use of folk remedies at the link:
Features of the use of celandine for the treatment of bees
disinfection
One of the following disinfectants is used to treat beekeeping equipment, frames, empty honeycombs and hives:
- an alkaline solution of formaldehyde (formaldehyde 15%, caustic soda 5%) – disinfection lasts six hours;
- 10% solution of iodine monochloride – five hours should pass from the moment of the first application;
- a mixture of 10% hydrogen peroxide and 5% formic acid – exposure for four hours.
Disinfectant is applied 2 times with a break of one hour (at the rate of 0,25 liters per square meter). After the completion of disinfection, all items are rinsed with clean water and dried.
An important point: antibiotics are not used for the prevention and treatment of ascospherosis in bees!
All medicinal products must be used strictly according to the instructions supplied by the manufacturer. At the same time, sufficient attention is paid to preventive measures and strengthening the immunity of bees.