The question of the honey base is one of the most exciting topics for beekeepers engaged in stationary bee keeping. What can be sown from honey plants near the apiary, how to properly organize crop rotation? And is it worth doing this at all?
The content of the article
- 1 What to plant
- 2 Improvement of the honey base
- 3 Green spaces along the roads
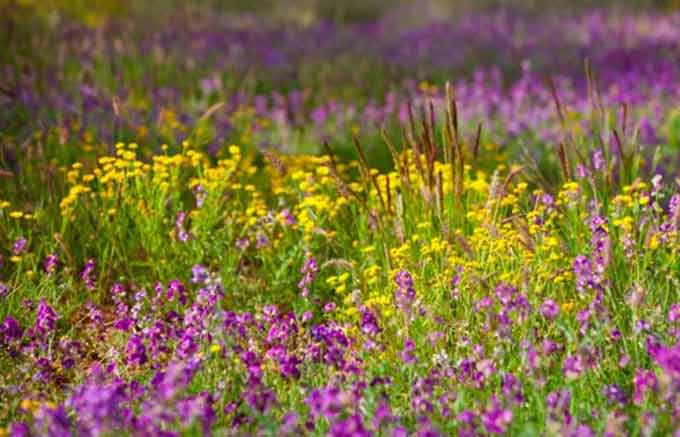
What to plant
Many people think about planting honey plants. This can only be realized if there is suitable land. Moreover, rather large areas of fields are taken for rent – from 10-20 and more hectares. Accordingly, it is necessary to have your own agricultural machinery for cultivating the land or to rent it. And these are additional costs.
For small private apiaries, land lease investments are not justified. After all, the main task of the beekeeper is making a profit.
A way out of this situation can be the unification of several beekeepers and the maintenance of common land. It is even easier to start migrating in conditions of a weak melliferous base. In this case, the profit will cover the cost of transporting the hives.
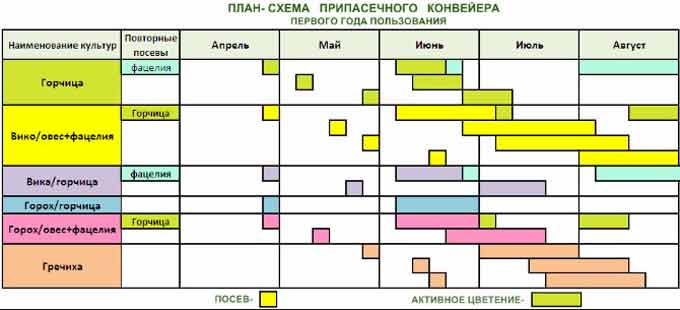
Example of crop rotation:
Some beekeepers practice planting melliferous grasses in abandoned plots and meadows occupied, for example, by a solid carpet of wheatgrass or other aggressive weed. To do this, in the spring, small bald spots are burned in the meadow, on which seeds of a suitable honey plant are scattered around the region.
However, the outcome of the struggle between plants is highly doubtful. Wild plants, well adapted to local conditions, quickly displace strangers from their territory.
Improvement of the honey base
Crop rotation in an apiary is possible only when planting honey plants on large areas of cultivated agricultural fields adjacent to the beekeeping farm (within 1,5-2 km).
Plants are selected depending on the region and climatic conditions. For example, for the middle lane, you can sow sainfoin, milk thistle.
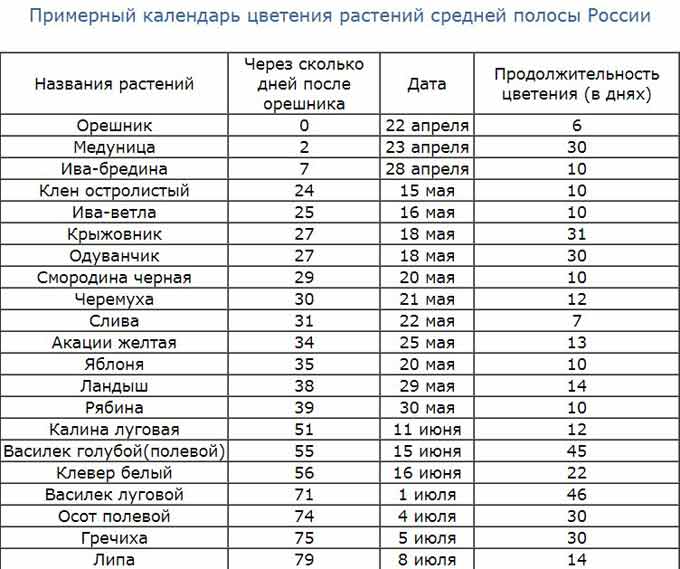
An approximate flowering calendar of plants, which can be guided by when sowing fields:
General recommendations for improving the honey base of small apiaries that do not use agricultural land are as follows:
Willow crops are of particular value for the development of bee colonies in the spring.… In the middle lane, their flowering lasts about a month. These are several dozen species of plants! The first to bloom is the holly willow or pussy willow. Then goat willow, willow, white willow bloom.
Note: Plants of this group are dioecious – they easily give hybrids. Therefore, it can be difficult, and not so important, to accurately determine the species before the foliage appears. The main thing to understand is that willow crops allow bees to quickly gain strength in the spring.
Willows are planted by cuttings or stakes along the banks of reservoirs, on wastelands and in the nearest ravines. The planting material is immersed in the ground 25-30 cm. The willow also successfully takes root on drier soils.
Acacia is one of the most important sources of May pollen and nectar… Propagated by seeds harvested in July. You can land them from April to the end of July, after soaking them thoroughly in water (keep for about 6 hours).
Bruise seeds are collected in autumn in leather mittens, and sown in spring half a kilometer from the apiary. The honey plant will gain strength in about two years. Mordovnik and sweet clover are planted in a similar way. Moreover, sweet clover can be sown directly on melting snow – it has excellent germination capacity.
Note: Melilot, bruise, mordovnik blooms every two years! Do not forget about this when expanding the honey base.
Unlike the listed herbs, fireweed blooms annually.… To plant it, it is necessary to cut the tops of the grass with testes, fix them in bunches on two-meter stakes and place them on the nearest wastelands, abandoned gardens and empty fields. The seeds themselves are carried by the wind.
The “cultural” cultivation of melliferous plants has proven itself well – first of all, the planting of hedges. As a rich source of nectar, you can use bushes of lilac, hawthorn, wild rose, red viburnum, honeysuckle, snowberry, hazel.
And decorative honey plants are planted on flower beds: marigolds (calendula), iris, purple mordovnik, Ivan da Marya, bells, white snowdrop, crocuses.
It is equally important to cultivate fruit trees and shrubs. With the bees in the neighborhood, their yields increase, and the collected pollen helps the insects in the spring build-up of the strength of the families.
Transplanting of various types of maple from the forest is practiced. These trees are unpretentious – they take root on any soil, grow quickly. Bloom in early spring. Linden is also an excellent honey plant. True, it is more demanding on the soil and watering. And it grows more slowly than maple. But the beekeeper will receive a nice bonus in the form of collected linden flowers. As you know, this is a time-tested remedy for colds.
Green spaces along the roads
And in conclusion, I would like to touch on the topic of honey plants growing as forest belts along highways. Bees also actively collect pollen and nectar from them. How useful is this honey?
Biology should be considered here. Flowers release nectar for a short time. The portion taken by the bee is formed in just a few hours. Many flowers release nectar only in the morning. Unlike nectar, pollen is formed for several days – its pollution with heavy metals is always higher.
All this is shown by laboratory analyzes of the contents of the honey craws of insects and the cuttings brought to the hives from the same plants. The fact is that honey bees process nectar, literally filtering off pollen grains.
Note: There are several times less heavy metals in mature honey than in bee bread or pollen!
With the help of laboratory analysis of podmore, propolis, pollen and bee bread, it is possible to accurately establish the ecological safety of the region by the level of heavy metals in them.
From which it follows that the keeping of bees in order to obtain marketable pollen (pollen) should be carried out with great care. Moving the hives at least 1 meters away from major motorways will reduce the lead content in the final product and make it safe for humans.