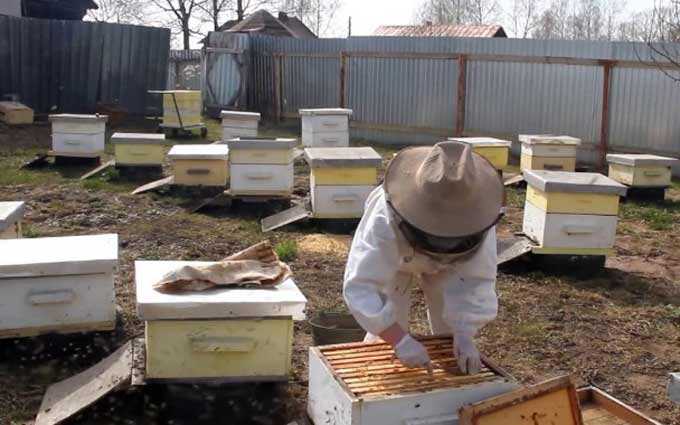
May is one of the most difficult periods in the life of a beekeeper. There is an active development of bee colonies, while there is a massive death of overwintered insects. The increase in the strength of families during this period directly depends on the amount of food and the availability of free cells for laying eggs.
The content of the article
- 1 What do we have to do
- 2 Spare uterus
- 3 How to plant a uterus
- 4 One of the ways to form layers
What do we have to do
Works on the apiary in May include the following activities:
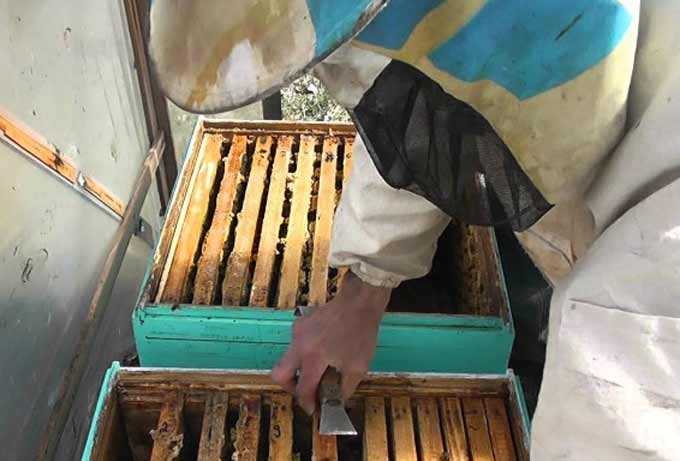
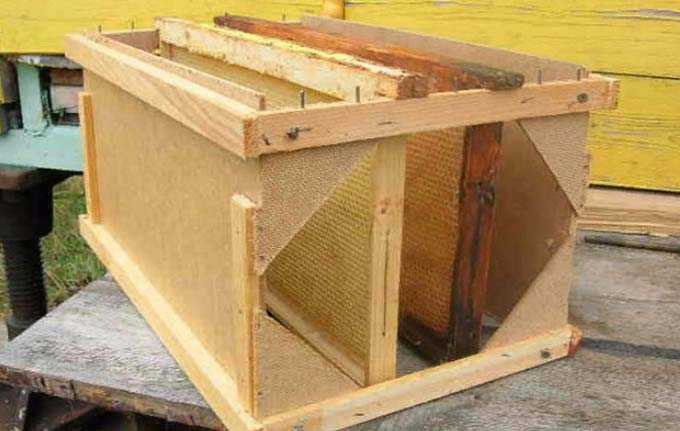
1. Expansion of nests in the first half of the month by installing light brown or brown high-quality honeycombs. It is recommended to use low-copper frames for this task, on which the caps are opened before being installed in the hive. The main task of the beekeeper is to ensure that the work of the bee “queen” does not stop due to the lack of empty cells.
Note: In multi-body designs, the dummy frames are placed so that they cover the passages of the lower ones (it is especially important to observe this above the center of the nest). In this case, the uterus will not mistakenly worm in the substituted store cases. The canvas between the bodies is removed!
2.Timely feeding… If there is a lack of natural bribe, each family is given 200-300 ml of sugar syrup, honey nourishment, or 1-2 honey-pepper frames are installed. The syrup is prepared on the basis of a part of sugar for two parts of water. Top dressing stimulates the development of bee colonies – the queen does not slow down the rate of worming, and the bees receive a sufficient amount of water for brood.
It is especially important to give bee bread in cool weather when there is not enough pollen on the plants. Bee bread made from pollen is vital for the growth of the young!
3.Artificial formation of small bee colonies – layering… May cuttings are gaining momentum quickly and are profitable during the main summer honey harvest. This is a great way to grow your apiary for free.
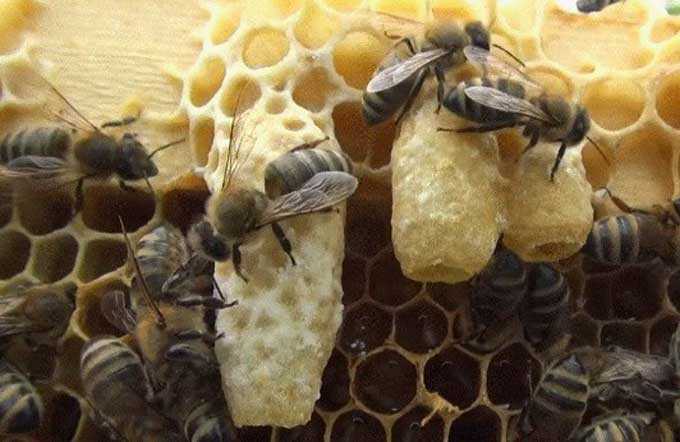
4. Self-hatching of queens easily produced in small apiaries if there are highly productive families. The best time for withdrawal is from early May to late June.
5 collecting pollen… The pollen is obtained with the help of special pollen traps installed on the entrances. By its composition, pollen processed by bees is a unique vitamin and mineral complex. After drying, the polish is used for treatment or handed over in bulk. In some cases, the share of income from the sale of pollen is 30-40%.
6. Issuance of frames with foundation begin from the moment nectar appears in nature. At this time, the wax glands are actively working in bees. If they are not occupied with useful work on building new honeycombs, insects begin to build wax structures in any place convenient for them – on the outpost boards, between the frames.
A strong family is able to build up to 8-10 hundred in the spring, if foundation is given to it on time.
7.Transportation of an apiary for pollination of gardens and fields… Working in an apiary in May implies active wandering, if natural conditions permit. With stable sunny weather during the May period, flower honey is highly valued in the market. To collect it, the hives are moved in an area where dandelions bloom profusely, clover, hawthorn, rape, buckthorn, mountain ash, honeysuckle, bird cherry, willow, acacia blossom (in the southern regions).
Bribes on May days are short-lived, but very strong. Therefore, during active honey collection it is not recommended to give out a lot of foundation. Better to set dry.
Rules for expanding nests during the May collection of honey:
- in 12-frame hives, only dry is issued;
- in hives-loungers and double-hull structures, six frames of land and two frames with foundation are installed.
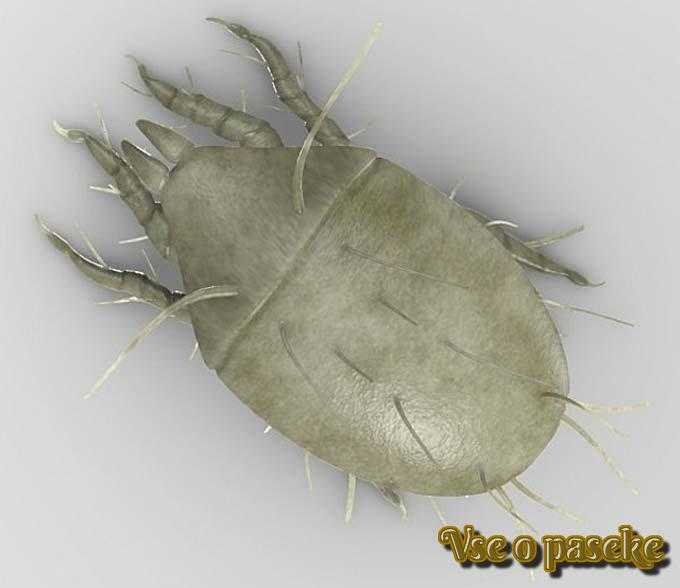
8.Prevention and, if necessary, treatment of varroatosis or foulbrood… To destroy ticks, plates containing acaricide are installed in advance (for example, “Fumisan”, “Varropol”, and others). With the beginning of the collection of honey, the drug is completely removed from all families.
You can read more about the treatment of varroatosis here: What you need to know about treating bees for varroatosis
Spare uterus
In case of loss of the queen bee colony or the need to replace the old female with a more productive individual, a young “queen” is placed in the nest.
There are two ways to raise queens:
- from two-day-old eggs;
- from larvae taken in a strong nest.
A beehive in need of a “queen” is called a caretaker family.
When hatching from larvae take a frame filled with larvae, the age of which does not exceed ten hours. Previously, all frames filled with eggs and young brood are removed from the educator family. In a honeycomb with larvae, “windows” are made with a knife. Or they cut it from below and immediately above the cut, the cells are shortened, reducing them in this place almost to the bottom. Every third larva is left in a row, thinning out. The prepared frame is lowered into the nest at the place where the brood stood. The next day, a honeycomb with open brood of different ages is placed next to it. The family-educator, which does not have a queen, builds queen cells, at the same time feeding the young.
When hatching from eggs take a newly built honeycomb and install it in a high productivity family. Two days later, the frame is removed from there along with the laid testicles. After that, the honeycomb is cut at the bottom, making a horizontal cut, and then thinned out in the bottom row, leaving every third cell intact there. A family educator prepares in a week. There should be no young larvae in it! Only in this case, several bowls will be built in the thinned row and high-quality queen bees will be fed.
How to plant a uterus
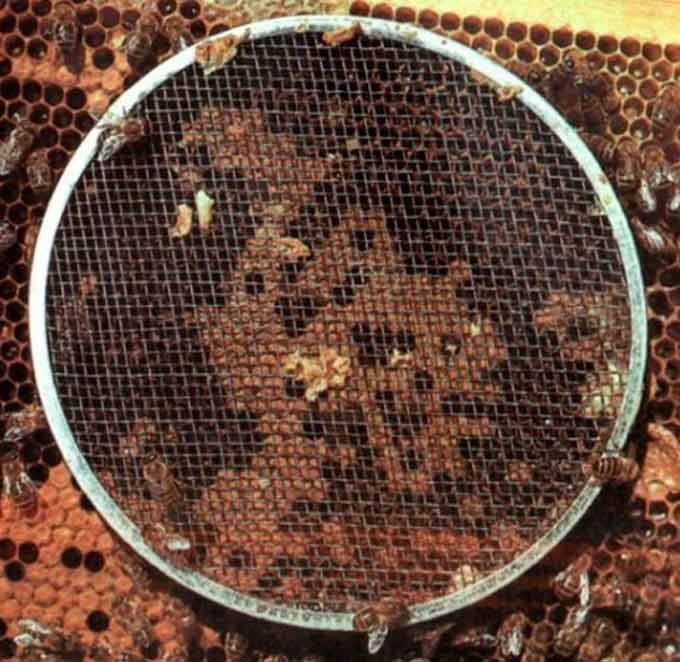
The queens received by mail or independently bred are planted in special caps or Titov’s cells.
The replacement is performed according to the following algorithm:
- The old uterus is removed from the hive and a honeycomb is selected for replanting a new individual. The honeycomb must have a supply of honey, a sealed brood and free cells that will be used for laying eggs.
- The uterine cap is positioned so that it covers part of the brood, empty cells and forage honey.
- The mesh of the cap and the bars of the frame are sprayed with a solution with a strong odor, for example, mint drops are suitable for processing.
- Three or four young bees and a queen are put under the cap. Then it is gently pressed into the honeycomb.
- Three days later, on the opposite side of the frame, make a hole with a pencil at the level of the cap and cover it with honey.
- The next day, the uterus should go to the other side of the frame and continue to lay. This means that the family has adopted a new “queen”. The cap can be removed even if the uterus is sitting underneath.
By mail, the queens are transported in cages ready for replanting. The stern compartment is pre-opened so that the female can freely pass between it and the cage wall. The hole is sealed with foundation, after which several holes are made in it with a needle. The cage is placed in a nest between frames with an open brood.
One of the ways to form layers
If the queens were replaced before the main collection of honey, the layers can be formed before nectar appears in nature. This allows young queen bees to start laying at the very beginning of the flow.
A new family is formed in the upper body of the hive on the mother or uterus. The nest is assembled as follows:
- three frames with printed brood, covered with insects, are installed in the center;
- honeycombs with bee bread and honey are placed along the edges;
- bees shake off two or three frames with open brood;
- the new family is separated from the lower housings by a horizontal diaphragm;
- in the body, inhabited by a layer, a tap hole is opened for the uterus to fly out for mating with drones;
- after 8 days, the diaphragm is removed so that the young “queen” can meet the old uterus and defeat her in the struggle for primacy.
From mid-May (at the time of flowering of currants, gooseberries), all winter insulation can be removed from the hives, leaving only scraps. To maintain optimal thermal conditions, a thinner mattress filled with dry moss is spread over the frames.