general description
Medlar (Turkish muşmula) is a whole genus of plants, which
includes almost 30 species. However, there are two main cultivated
types of medlar: Germanic and Japanese.
The Germanic medlar was known to mankind for over 1000 years
BC. In the territories of Ancient Babylon, Mesopotamia, it was freely traded,
on ships it was transported west to Ancient Greece and Ancient Rome.
It was from here that the medlar came to European lands. Today
, the Germanic loquat grows in the Balkans, Asia Minor, the Crimean
mountains, Transcaucasia, Armenia, Algeria, Azerbaijan, Greece and northern
Iran. The tree is quite picky and grows well only in
dry, sunny places and on slightly acidic soil.
The German medlar has a round shape, slightly flattened along the axis
with expanded sepals at the end. The fruit is small in size
(2-3 cm in diameter), red-brown in color. The unripe fruit is quite
hard and sour. Medlar ripens only after the first autumn
frosts or after laying for a month. At the same time, the fruits lose
moisture, become wrinkled, but at the same time soft and sweet.
The homeland of the Japanese medlar is the subtropical territories of China.
It was from here that the plant got to Japan, and then in the 19th century. was brought
to Europe. Medlar is cultivated in Georgia, India, USA, Ukraine, Southeast
and South Asia and in the Himalayan mountains. This species is closest to quince,
pear and hawthorn. The plant begins to bloom in the fall, and the fruits ripen
in the spring between May and June. They have a pear-shaped shape with a diameter of
up to 10 cm. The color of the peel is orange-brown, the flesh is juicy, sweet and sour
in taste. Inside each Japanese medlar there are large dark brown
bones from 1 to 5 pcs.
Storage and use of medlar
The medlar should be stored in a dark, cool place, so
that the fruits do not come into contact with each other. Medlar is eaten mostly
fresh, but in the regions of growth, jam,
preserves, marmalade, marshmallow, juices, compotes, as well as wine and liqueur are prepared from it .
Useful properties of medlar
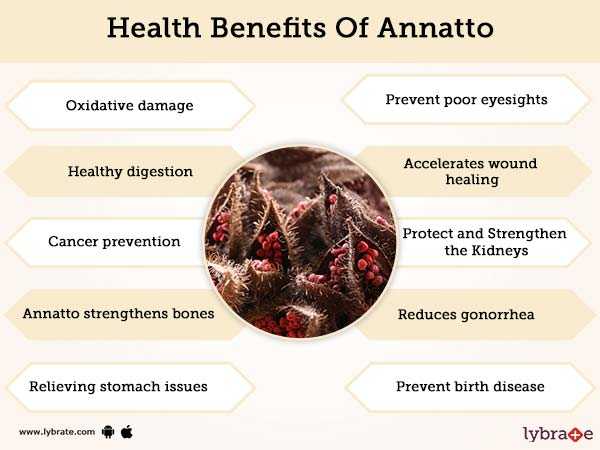
Composition and presence of nutrients
Fresh medlar contains (in 100 g):
Calories 47 Kcal
The fruits of medlar contain vitamins (C,
A,
V1,
V2,
V3,
V6,
B9),
minerals (potassium,
iron,
magnesium,
iodine,
calcium,
phosphorus,
sodium,
selenium,
zinc
and others), sugar (fructose, sucrose) and organic acids (citric,
malic). Phytoncides and tannins impart astringent
properties to fruits , which have a positive effect on the course of gastrointestinal
diseases, normalize intestinal function, and relieve pain in case of stone
deposits in the kidneys and urinary tract. Unripe medlar fruits
stop intestinal bleeding, relieve inflammation.
Useful and healing properties
From the pulp of ripe fruits, alcoholic tinctures are prepared for the treatment of
bronchial asthma and other respiratory diseases. To do this, the
medlar together with the seeds (5 pcs.) Are thoroughly ground,
honey (2 tbsp. L.) And sake
(100 ml) are added to them . All components are mixed and left to infuse
for a week in a sealed container. After that,
filter the tincture and take 30 g 3 times a day before meals. This
remedy relieves cough, binds and removes phlegm from the lungs,
improves the general condition of the body.
Dangerous properties of medlar
The unripe fruits of medlar should not be consumed by people with
gastrointestinal diseases , accompanied by an increased level of acidity of gastric
juice, ulcers, and inflammatory
processes in the pancreas.
Also, the fruits must be carefully introduced into the diet of children
and people prone to manifestations of allergic
reactions.
How and where the fruit grows on the trees and what it tastes like – in
our short video.