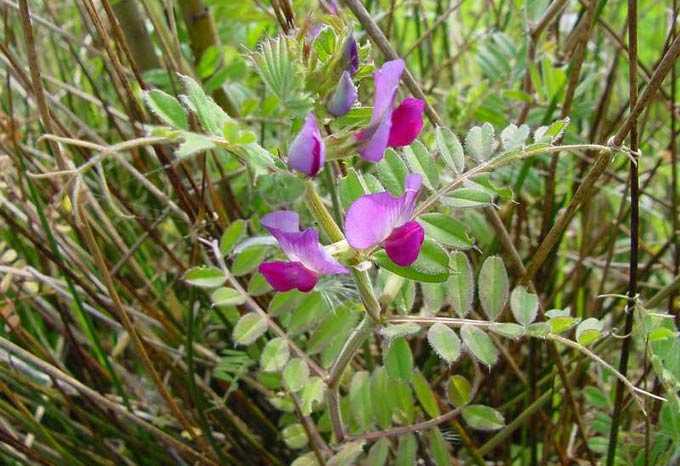
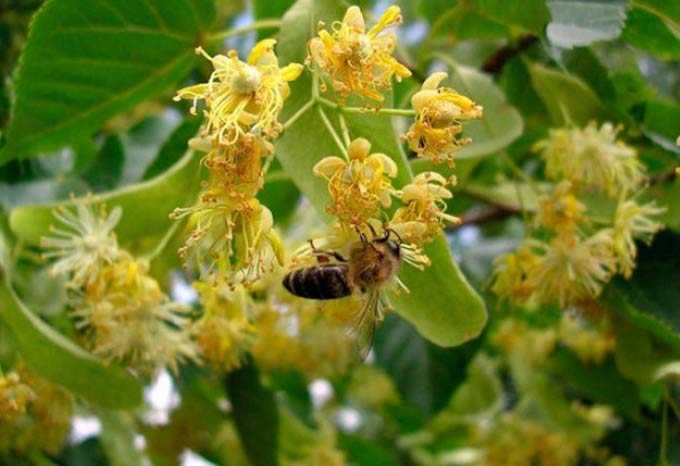
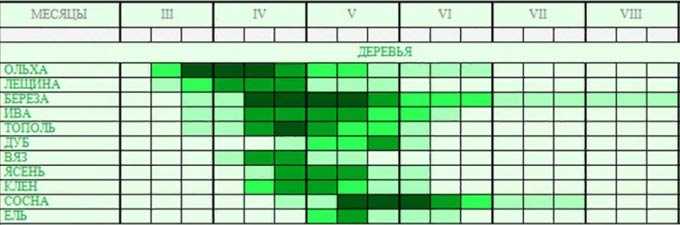
Spring honey plants are plants that bloom from the moment the snow melts until the end of the last decade of May. These include herbs, shrubs and trees, including fruits and berries.
The content of the article
- 1 What you need to know
- 2 Overview of early flowering plants
- 3 April plants overview
- 4 May plants overview
What you need to know
The flowering schedule of plants for each region should be compiled by the beekeeper individually. Since even within the same region, a significant difference can be observed. In addition, there is no year on year – no apiary is insured against weather whims.
Ideally, these are long-term observations recorded in a special notebook. For beginners in beekeeping, consultation with more experienced comrades in the shop will help.
How to draw up such a schedule can be found here:
Flowering calendar of melliferous plants
We remind you once again that the first honey plants in spring will be different for each climatic zone and region. For example, in the southern forest-steppe it is a mother-and-stepmother, in the Caucasus – some varieties of goose onions, real dogwood, snowdrops.
Overview of early flowering plants
Goose bow – a herbaceous plant found mainly in the Caucasus in woodlands. Blooms immediately after the snow melts. This large group includes several varieties of onions. Yellow goose onions are found, including in the vastness of Siberia, the Far East and the European part of our country. The herb is prized as a source of pollen, which stimulates the development of bee colonies, and a small amount of nectar. Visited by bees for two to three weeks. Nectar productivity is 8-12 kilograms per hectare of dense thickets.
Real dogwood – a tall bush or a small, highly branching tree. A typical inhabitant of the mountain forests of the Crimea and the Caucasus. Easily climbs up to 1,5 thousand meters above sea level. It can be used to form living fences, including in apiaries, and decorative decoration of gardens, parks. Its flowering dates are in March, April (approximately 15-25 days). Provides both nectar and pollen. Productivity for honey up to 30 kilograms.
Snowdrop – bulbous herbaceous inhabitant of the Don and the North Caucasus, also found in other regions. It blooms in the first forest clearings formed during the early melting of snow (February, March). Appears in Crimea in January. It is readily visited by flight bees. The exact honey production is unknown. Insects do not collect pollen from this plant.
Crocus or saffron – herbaceous perennial, common in the steppes and mountainous regions of the Crimea, the Caucasus. There are several melliferous varieties of this plant: golden, Pallassa, beautiful, Crimean. However, their nectar productivity is low. But on the other hand, the grass serves as a good early spring source of pollen.
Two-leaved plank or “scilla” is widespread in the southern European part. It is an inhabitant of broad-leaved oak forests, providing a third of the nectar flow from the entire forest herbage. Blooms in late March, early April. The cuttings collected from this herb are dark blue in color. An average of 11-12 kilograms of pollen is collected from a hectare of grass stand. Nectar productivity is 10-12 kilograms.
Mother and stepmother – herbaceous perennial with beautiful bright yellow inflorescences. It blooms on slopes when there is still snow around. It is found everywhere in temperate climates. The collection of pollen is about 8-12 kilograms per hectare. The nectar productivity is low – 6-8 kilograms, and the nectar begins to be released abundantly only after the frost stops. But its value is extremely high – early honey harvest stimulates the rapid development of bee colonies.
Read: Mother and stepmother as a honey plant
lenses or hazelnut (hazel) grows in mixed forests, hollows, ravines and slopes. In the south, it blooms in the second or third decade of March, in the Crimea in February, and in other regions in April. It is considered an excellent pollen plant – bees bring up to 12% of the pollen per day from the bush. The plant has been successfully used to create hedges around apiaries, to strengthen slopes and slopes. The shrub begins to bear fruit in the third or fifth year of life, subject to reproduction through young shoots.
April plants overview
Spring honey plants in April are represented by the following plants:
Almonds ordinary – a nectar-bearing and pollen-bearing tree of the southern Crimea and the Caucasus. Blooms in late March, early April for 6-8 days. Nectar productivity is 6-10 kilograms. Basically, the plant supplies pollen to bee colonies. A shrub (European) variety of almonds blooms in late April for 10-12 days. Its honey productivity is noticeably higher – up to 30-35 kilograms.
Lungwort – a herbaceous perennial, which has taken a fancy to glades, clearings, forest roadsides. It can be grown near apiaries due to its unpretentiousness. In the southern regions it blooms in early April. It releases nectar for a month, and annually (bad weather almost does not affect the grass). Nectar productivity is about 70 kilograms per hectare of thickets.
Read: Lungwort as a honey plant
Crested crested – a biennial herb that blooms in the south from the beginning of April for 10-14 days. Other crested species – dense, Marshall, pallid, smoky-leaved, doubtful – are also excellent pollen. Nectar productivity is about 4,2-7,9 kilograms (indicators for the Ryazan region).
April is the time of flowering willows. Most valuable for apiaries willow bredina, willow (white), holly (red willow), Russian… They open their earrings in April, early May. Bribes due to erratic weather can be weak. Average nectar productivity is up to 150 kilograms.
Read more: Willow (willow) as a honey plant
In the second decade of April, another representative of the willow family blooms – aspen or a quivering poplar. It is planted as an ornamental plant. In the wild, the tree grows well on wet soils – in mixed forests, in clearings and swamps. In addition to the pollen, bees collect kidney glue from this plant for the production of propolis.
The end of April, beginning of May is the period of flowering of different maple species. Maples provide bribes of up to 200 kilograms per hectare of dense thickets. Other varieties – field, Tatar (chernoklen), white (sycamore), ash-leaved are also good honey plants.
Read: Maple as a honey plant
Apricot Is one of the earliest flowering fruit trees. The first flowers appear on it from mid-April, and in the warm conditions of the south – at the end of March. Apricots are extremely sensitive to spring frosts, but in favorable weather they provide bribes of up to 40 kilograms.
Dandelion – a wild-growing herb with bright yellow flowers, giving a lot of pollen in April, May (in the middle lane in May, June). It is found everywhere. On a day, bees can bring up to 3 kilograms of the same bright yellow pollen! Nectar productivity up to 50 kilograms.
Read: Dandelion as a honey plant
Currant – a shrub grown mainly in forest and steppe regions. In the climatic conditions of the south, it blooms in late April and early May. In other regions – in May, June. Depends on the variety, it shows good honey productivity. Especially valuable are red and golden currants with nectar productivity from 43 to 100 kilograms.
Alder in the middle lane it throws out hanging earrings in April, in the south it blooms a little earlier – in February, March. There are several types of wood: green, black, gray. There is a shrub form. They are all excellent sources of pollen. For a day, up to 17% of the pollen brought by bees to the hives is collected from different types of alder.
In subtropical regions, fragrant flowers of peaches, lemons, oranges and tangerines bloom in April. All of these fruit trees provide a supportive spring flow, comparable in volume to apricot nectar.
May plants overview
May honey plants become more diverse – with warming, gardens, berry fields bloom en masse, some agricultural crops join wild plants.
In May, early summer appear inflorescences on field mustard (not to be confused with the cultural species – white mustard blooming in summer!). You can meet this weed on wastelands, along roads, in crops of spring crops. Nectar productivity from 55 to 100 kilograms. The secretion of nectar lasts an average of one month.
Common rape or “rape” – a herbaceous inhabitant of the Caucasus and the European part. It is a field weed that blooms in late spring and early summer. Nectar productivity – from 40 to 100 kilograms per hectare.
Read: Rape as a honey plant
Loch – woody or shrub plant, found, including in the Caucasus. Blooms in May, early June for two weeks. There are two of its melliferous varieties: narrow-leaved (another name is “wild olive”) and silvery (eastern). Nectar productivity up to 100 kilograms.
Read: Loch as a honey plant
Irga – a short tree or deciduous bush. In the Caucasus and Crimea, there is an oval irga that blooms in April and May. Other plant varieties: the Canadian and spike varieties, are cultivated as fruit and ornamental plantings. Plants provide a supportive forage from pollen.
Read: Irga as a honey plant
Winter rapeseed variety also blooms in April, May, releasing nectar for a month. This oilseed crop is cultivated on Ukrainian and North Caucasian agricultural lands. Nectar productivity is about 80-120 kilograms.
Read about other varieties here: Rape as a melliferous plant
Common quince – a tree, less often a bush growing in forests and undergrowth in the Caucasus. In Ukraine, it is cultivated as a fruit plant. Blooms in late April, early May for two weeks. Average nectar productivity is 15-18 kilograms.
Barberry – a branched thorny bush, common in the Caucasus and throughout the European part. Both species known in beekeeping – common and Thunberg – are good honey plants. In the wild, they grow in coniferous-deciduous forests. Bloom for 20 days in May and June. Bribes reach 100 kilograms per hectare of dense thickets.
Read: Barberry as a honey plant
May is the time of mass flowering of late varieties of apple trees. This fruit tree is ubiquitous, providing bribes of 15-20 kilograms. In terms of volume, this is a small amount of honey, however, in combination with other May honey plants apple trees provide a good late spring honey harvest.
Read: Apple tree as a honey plant
Cherries – the most important garden plants that bloom earlier than apple trees. Honey productivity is largely determined by the timing of flowering and the variety, but it is higher than that of apple trees – about 30-40 kilograms. In the conditions of the southern regions, flowering is observed in the first decade of May.
Plum – another valuable garden tree, which differs from cherries in greater winter hardiness. This plant blooms for no longer than 10 days. Strong bee colonies bring up to 1,8 kg of nectar per day.
Pear depending on the variety, it can bloom from late April to early June. Both nectar and pollen are collected from this tree equally well. The average bribe is 20 kilograms of nectar per hectare of pear orchards.
gooseberries also applies to early flowering fruit and berry crops. Flowers on the shrub appear en masse in May. The duration of nectar secretion reaches 10-20 days. The plant can be used to form hedges. Nectar productivity, depending on the year, ranges from 10 to 75 kilograms.
Turner or prickly plum (blackthorn) – an inhabitant of black earth regions, in the wild, willingly inhabiting gullies, ravines, hills. Blooms in early May, releasing nectar for 7-10 days. Average nectar productivity is 25-30 kg.
Common bird cherry grows in forest and steppe zones, blooming in May and June. Releases nectar for 10-14 days. At the same time, the nectar productivity of the tree is average – from 20 to 35 kilograms.
Read: Bird cherry as a honey plant
Primula or spring primrose occurs throughout the forest and forest-steppe regions of the European part. Blooms in April, May for 20 days. Due to the elongated structure of the flower tube, it is quite difficult for insects to extract nectar from bright yellow flowers. But, nevertheless, bees bring up to 5-7 kilograms of honey from this herb.
Hawthorn ordinary, found everywhere, blooms in May, June for about two weeks. It is a source of pollen and nectar. True, the average nectar productivity of this thorny shrub is not impressive – 13-19 kilograms. Can be used to form living fences near apiaries.
Read more: Hawthorn as a honey plant
A special infusion is prepared from its fruits to stimulate the work of the queens. For a liter of boiling water, 50 grams of crushed dry raw materials are taken. The infusion is kept in a thermos for 4-5 hours, and then given out to bee colonies at the rate of 50-100 ml per liter of finished sugar syrup.
Gledicia – a drought-resistant tree that grows well in the steppes of the European part. Blooms in late May. Suitable for arranging hedges, shelter belts. The nectar productivity of continuous thickets is up to 200-250 kilograms per hectare.
Read more: Gledicia as a melliferous plant
Common blueberry – a small shrub growing in the forest zone, forest-tundra and mountains. It is found throughout the European part, in the Caucasus. Blooms for 15 days in May, June. Differs in good nectar productivity up to 100 kilograms.
Blackroot (popular name “rat race”) is a perennial herbaceous melliferous plant growing in the Caucasus and throughout the European part. There are three known types of it, the most valuable for apiaries: medicinal, painted and mountainous. Blooms in the last decade of May, releasing nectar up to 1,5 months. Grass pollen is considered poisonous – bees take it reluctantly. Nectar productivity per hectare of solid grass stand is from 80 to 100 kilograms.
Eremurus – a steppe inhabitant of the Crimea and the Caucasus. All of its varieties are not distinguished by high honey productivity. However, a solid stand allows you to pump out a honey variety that has almost no aroma and is colored in a light amber hue. Bribes in the range of 10-20 kilograms.
Sainfoin – one of the most productive herbaceous plants in May, early summer. Grows in the Caucasus, in the central and southern regions of the European part. There are both cultivated and wild species with high honey productivity. Bribes are of the order of 40-150 kilograms.
Read more: Sainfoin as a honey plant
strawberry – short grass, widespread throughout mixed and deciduous forests. There are several varieties of it: forest, green, oriental, nutmeg (forest strawberry). They all bloom in May, early June. Average nectar productivity is from 13 to 40 kilograms.
Common mountain ash thrives in the undergrowth of coniferous and mixed woodlands. Also, a shrub or a low tree is used for landscaping settlements, creating protective forest belts. Blooms by the end of May for 15-18 days. Nectar productivity is 30-40 kg.
Read: Rowan as a honey plant
Swamp saber – an inhabitant of swampy meadows, river coasts in the Caucasus and in the European part. Blooms en masse in the second decade of May. This shrub is distinguished by long flowering (on average 55-65 days). Bribes per hectare from 100 to 200 kilograms.
Chingil silver – an inhabitant of salt marshes, sandy and rocky slopes in the Azov region, in the south of the European part, the Caucasus. Bribes from 150 to 200 kg of nectar. It is not recommended to leave honey for the winter because of the rapid crystallization in the combs.
May – the beginning of flowering of different varieties cleaver (deaf nettle)… This herb grows in the European and Caucasian regions, blooming from late May to August. The following varieties are most valuable for the apiary: white (in fact, it is called “dull nettles”), spotted, purple. Nectar productivity from 100 to 124 kilograms.
Yellow acacia or tree caragana – a bushy plant used for hedges, landscaping of settlements. In the wild, it occupies forest edges, clearings, hillsides. Shows the maximum honey yield in late spring seasons. Blooms in the second, third decade of May. Releases nectar for 10-14 days. Average nectar productivity is 50-60 kilograms. A variety of caragana known as dereza (chiliga) blooms a few days later. Its honey productivity is from 70 to 100 kilograms.
Horse chestnut (other names: “esculus”, “acorn”) is found everywhere as a decorative urban planting. Blooms in late May for 10-15 days. Nectar productivity is about 50-55 kilograms.
Read: Chestnut as a honey plant
White acacia together with chestnuts opens early summer honey harvest. It grows everywhere in city squares, parks, along cliffs, on inconvenient lands and as part of protective zones. Short flowering and dependence on the weather make this tree a capricious honey plant – the average bribe in the southern regions is 40-50 kg. In favorable years – from 300 to 600 kg and more (there is information about a record 1 kg; how true they are is not known).
Read: Acacia as a honey plant
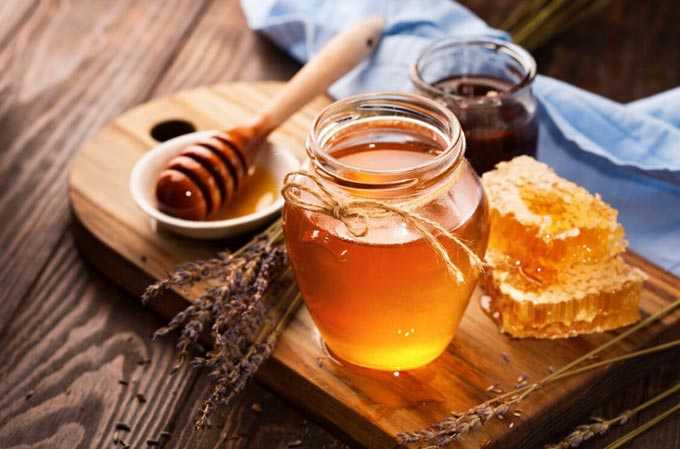
The first spring honey plants provide an exceptionally supportive flow for the development of bee colonies. And honey plants in May are able to provide marketable honey harvest. May honey is one of the most valuable varieties of this bee product. It has remarkable taste and healing characteristics, a fragrant aroma and a beautiful golden color.