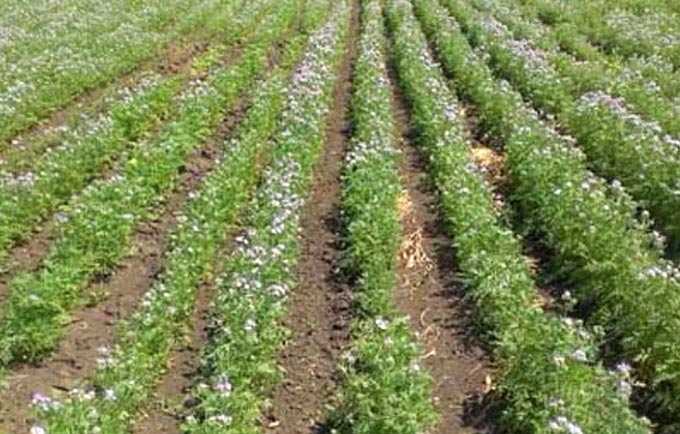
Peas as a honey plant are cultivated as part of a pea-phacelia mixture. Such crops are used to obtain pea grains and ensure honey harvest. The plant belongs to the legume family.
The content of the article
- 1 Appearance and distribution
- 1.1 Features of honey collection
- 2 Agrotechnics
- 3 Honey productivity
- 4 Closest wild relative
- 4.1 Mouse
- 4.2 Thin-leaved
- 5 Honey quality
- 6 Useful Properties
Appearance and distribution
In agriculture, peas, namely their garden variety, are valued as a good fodder plant. The culture is found everywhere except in arid regions.
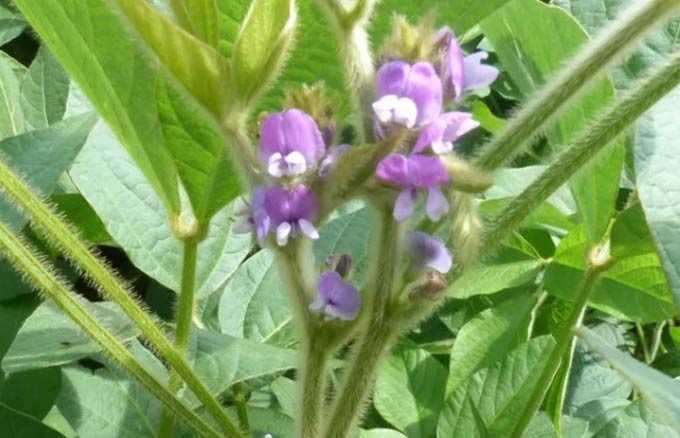
Peas have a long, weak, climbing-type stem, covered with feathery leaves and branched tendrils that provide anchoring (for example, on the phacelia). On closer inspection, it is noticeable that each leaf is covered with vegetable wax on top, which creates reliable protection against moisture evaporation.
The flowers are white with large stipules. There are varieties with purple flowers and purple wings. The culture is capable of self-pollination – its anthers develop before the flowers bloom. From them, pollen is freely poured onto the columnar brushes.
Features of honey collection
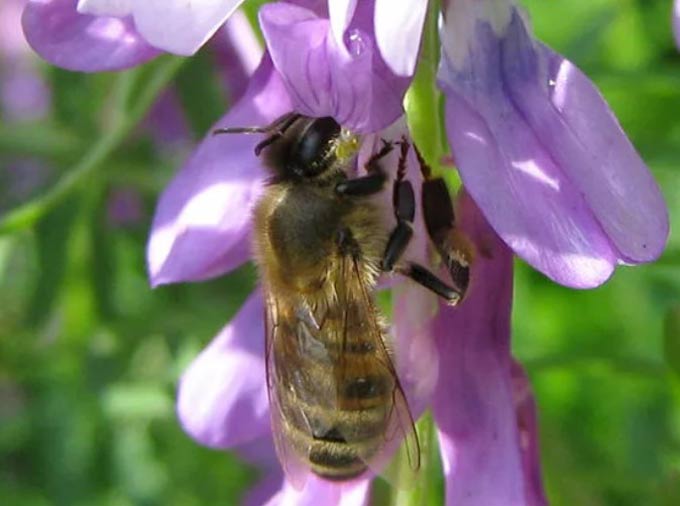
Such an unusual structure of petals is an important feature of peas. Its flowers are reliably protected from washing out nectar and pollen by rains.
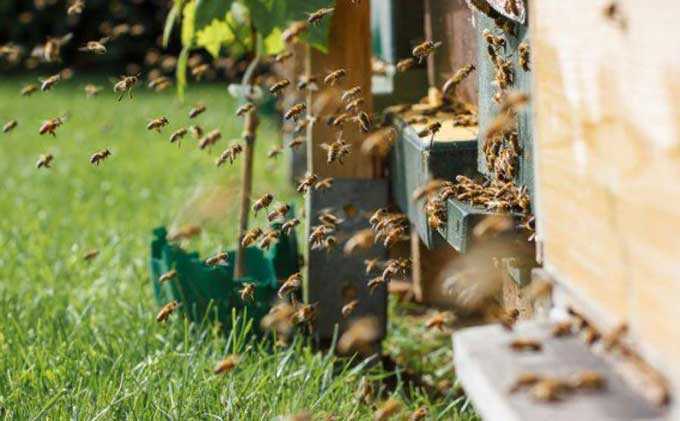
Bees work very unusual with this honey plant. In order to get nectar, insects are forced to “bite” the flowers.
And the pollen gets on the body of the bee during the extraction of nectar – sitting on a flower, the insect forces the “boat” from the petal to descend. In this case, the columnar brushes come out and touch the bee, transferring pollen to it. Pollination occurs by transferring a portion of pollen from one flower to the stigma of another.
Agrotechnics
Peas are sown mixed with phacelia in early spring. Both crops are resistant to low temperatures – they germinate well at 2 degrees Celsius. The first flowers appear 1,5 months after sowing – around the first decade of June.
The symbiosis of honey plants is very important! Peas enrich the soil with nitrogen, and the phacelia serves as a reliable support for pea stalks – pods with grains do not rot in a rainy summer.
After harvesting the grains, the green mass is used as silage – it is mixed with corn.
When sowing honey plants per hectare, you will need:
- 3 kg of phacelia seeds;
- 250 kg of pea seeds.
Sowing is carried out in rows with row spacings from 30 to 45 centimeters.
To read:
Phacelia and its value as a honey plant
Honey productivity
Peas are a honey plant, the productivity of which is extremely difficult to determine by nectar. But it is known that from 50 to 60 kilograms of marketable honey is obtained from a hectare of peas mixed with phacelia.
Fragrant honey with herbaceous notes, quite light and transparent.
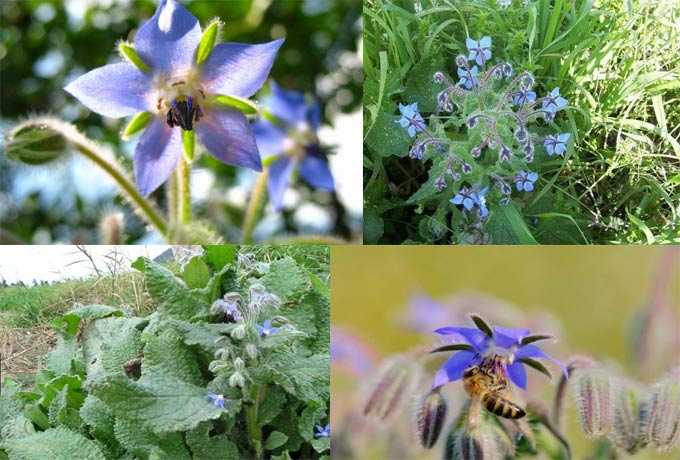
Closest wild relative
Garden peas have a relative from the same legume family in the wild called peas.
It is a perennial or annual forage grass found in almost all European regions. In nature, there are about ninety varieties of wild peas!
Here are the most famous of them that have value for apiaries:
- mouse;
- thin-leaved.
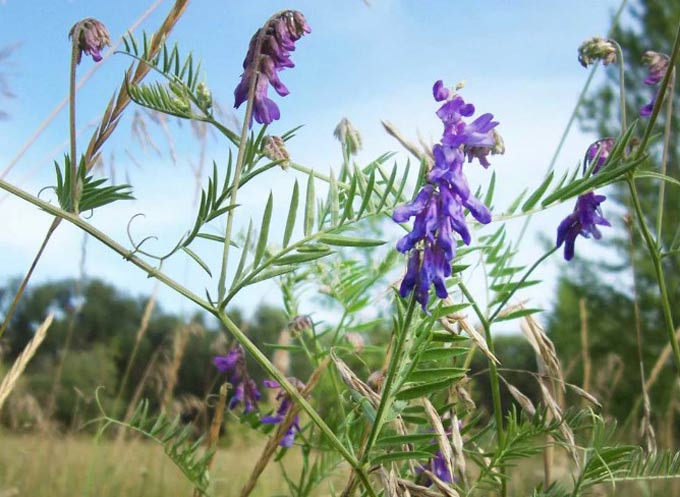
Mouse
This variety is a perennial herb with fallow leaves and antennae, reaching a length of 80 centimeters (when grown with support on other plants, the height can be up to 1,2 meters).
The flowers are collected in clusters, which are longer than the leaves. The flowers are purple or blue, rarely white.
Mouse peas provide the apiary with nectar and pollen from early June to September. This is a fairly long flowering, although the culture is a secondary honey plant.
The yield of marketable honey is up to 50 kilograms per hectare. In the intake variety – up to 10 kg.
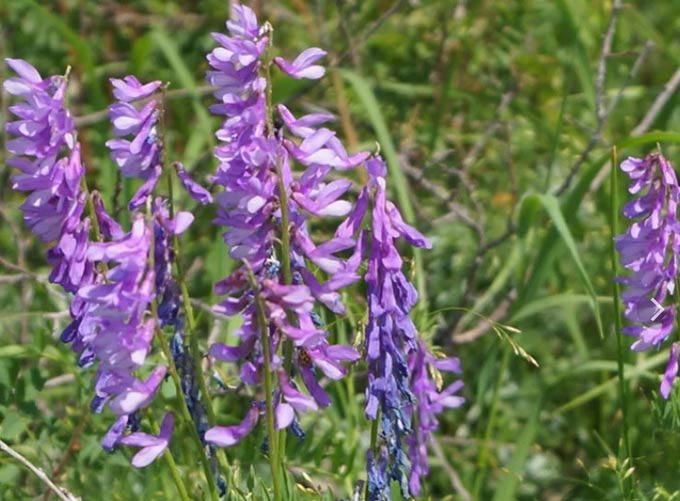
Thin-leaved
Fine-leaved peas are widespread in the steppe regions. It also possesses pair-pinned leaves and a creeping stem that is 30 to 120 centimeters long. Cultivated as a forage grass.
Inflorescences are very long – 1,5-2 more leaves. The flowers have a bluish-purple hue and a structure characteristic of peas.
The plant provides bees with nectar and pollen from June to early autumn. The average yield of marketable honey per hectare is from 40 to 50 kilograms.
Honey quality
Pure pea honey from a thin-leaved wild plant variety is obtained in Siberia.
It crystallizes slowly – within 3-4 months, and the crystals are unstable and easily melt at room temperature, and the former transparency returns.
Useful Properties
Peas and their closest relative, wild peas, produce a transparent marketable honey with a light aroma and delicate taste.
In folk medicine, it is recommended for the treatment of the digestive system.
Also, this bee product can be used like any other type of honey:
- for colds – to reduce high fever, treat a sore throat;
- as a prophylactic agent during periods of influenza or ARVI epidemics;
- as an antiseptic for the healing of wounds and abscesses;
- in home cosmetics to improve complexion, fight hair loss and breakage.
Inside, 1-2 tablespoons are taken per day half an hour before meals. You can drink it with a glass of warm clean water.