The raspberry honey plant is a branchy, thorny shrub that belongs to the Rosaceae family. The plant loves moist and mineral-rich soil. Prefers to grow in well-lit areas. In the wild, it is found in burnt-out areas and felling areas.
The content of the article
- 1 Appearance
- 2 Agrotechnics
- 3 Honey productivity
- 4 Useful Properties
Appearance
In the first year of life, shrub stems with thorns have a herbaceous shape. The rhizomes of the plant are long and creeping. In the first year, inflorescences are not formed, and the plant itself takes the form of a 1-2-meter shrub. The upper leaves are green, and the lower ones have a grayish tomentose shade.
In the second year, young raspberry shoots begin to bloom en masse, forming fruits, after which they dry up and die off. Up to 50 greenish-white inflorescences are formed on one stem.
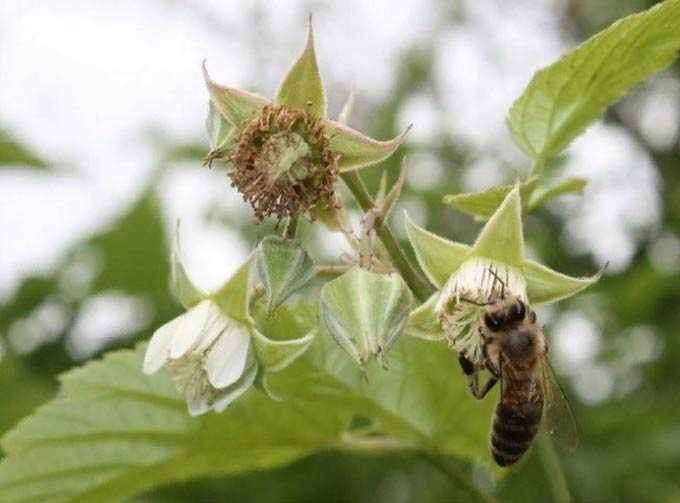
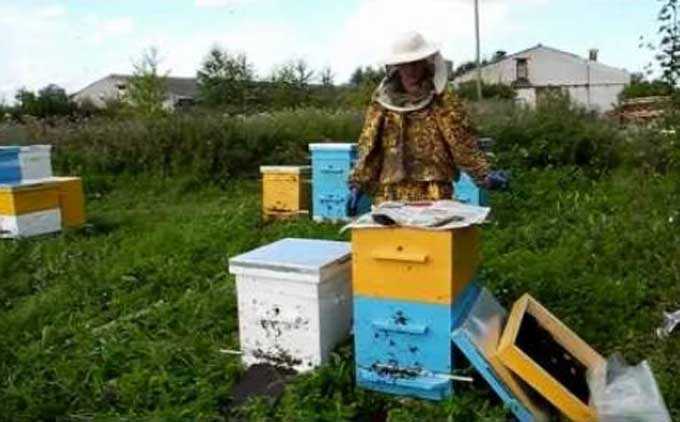
The flowers are capable of self-pollination, but since the plant’s pollen is heavy and sticky, bees cannot do without.
From observations: for full pollination of 2 hectares of raspberry plantation, only one strong bee colony is required.
Agrotechnics
Raspberries take root well on fertile, loose, sufficiently moist soils. Acidic soils require liming before planting crops.
You cannot choose elevated areas near apiaries – cold winds reign here in winter, and crimson shoots can freeze out. The ideal landing site is a sunny, wind-sheltered area.
Basal offspring serve as seedlings. For them, holes are dug at a distance of 70-90 cm, they are mulched with humus or peat. On sandy loam, holes can be dug deeper than 90 centimeters. Nitrogen is not used to fertilize this crop! The recommended row spacing is 1-1,5 meters.
Disembarkation is carried out in the spring or late autumn. All root shoots are carefully straightened (you must not bend upwards!), After which each seedling is carefully sprinkled with soil.
Note: Varietal raspberry bushes show the best nectar productivity.
Honey productivity
Raspberry honey plant blooming from May to June or July (depending on the weather conditions in the region). The peculiarity of this plant is that, on average, one flower lives for only one and a half days, and then dies off.
At the same time, beekeepers recognize raspberries as an excellent honey plant and try to plant them near their apiaries. Suitable varieties are determined by the abundant production of nectar. It is best to plant varietal or remontant raspberries. This will provide the bee colonies with abundant supplies of nectar and pollen.
Under favorable weather conditions, one bee colony can bring up to 6 kilograms of nectar per day, and in less prosperous years – up to 40 kilograms for the entire period of a bribe.
If the concentration of sugar in the nectar reaches 60 percent, the work intensity of the bees decreases. Since the nectar in the inflorescence becomes very thick, which is why the bee needs to additionally liquefy the nectar with the secretion of its salivary glands.
Useful Properties
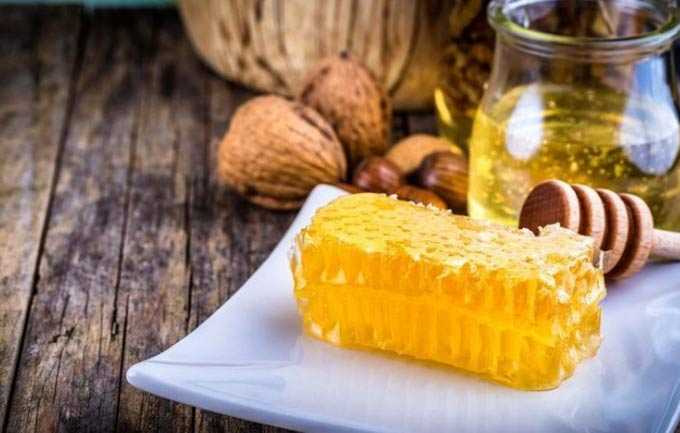
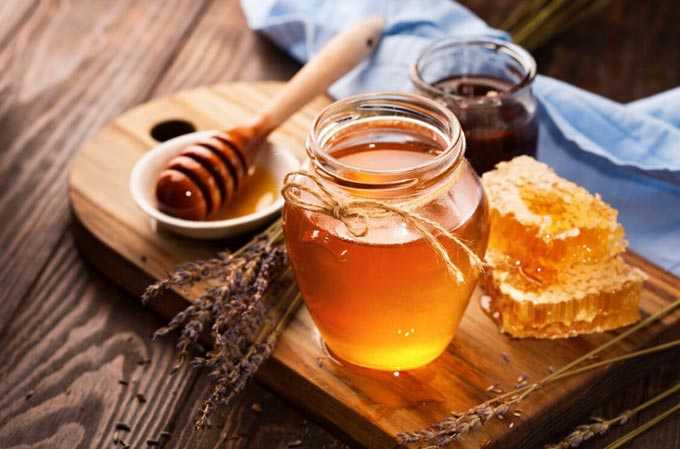
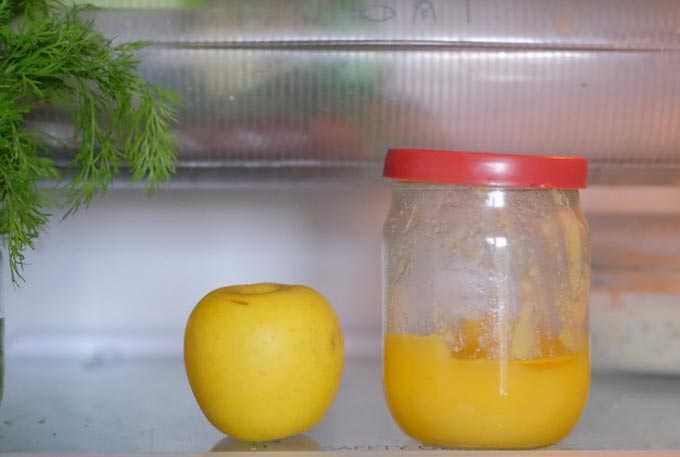
Raspberry honey belongs to light varieties with high quality. The product acquires a white-cream shade during storage. It has a pleasant taste without bitterness. It does not crystallize immediately, transforming into a fine-grained mass.
Due to the high content of glucose and levulose, this variety is known for its special energy and nutritional value.
The product is easily absorbed by the human body, regardless of age, and has a number of useful properties:
- it acts as a tonic recommended after prolonged physical exertion;
- able to relieve nervous tension and help cope with fatigue;
- and for colds, raspberry honey is used for prophylactic purposes.
Also, the variety is used to strengthen the immune system and treat various gastrointestinal ailments.