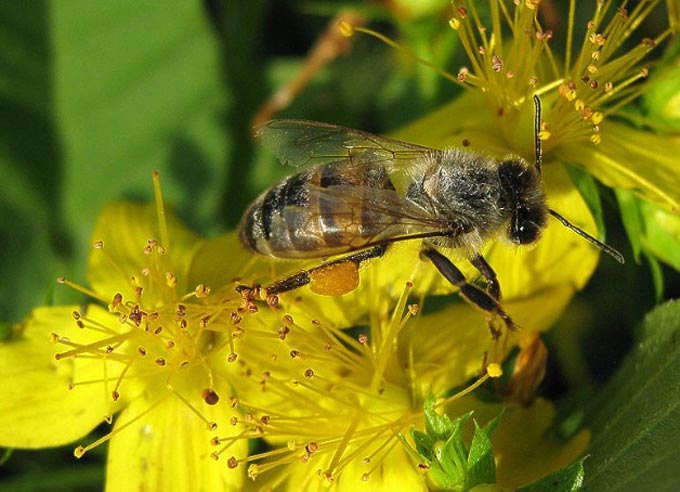
St. John’s wort is a herbaceous or shrubby perennial plant from the family of the same name. Medicinal varieties of the herb are widely used in folk and official medicine. In beekeeping, it is a summer source of pollen and nectar.
The content of the article
- 1 Distribution and Description
- 2 Significance for agriculture
- 2.1 The main varieties
- 3 Reproduction of dosage forms
- 4 Reproduction of garden forms
- 5 Honey productivity
Distribution and Description
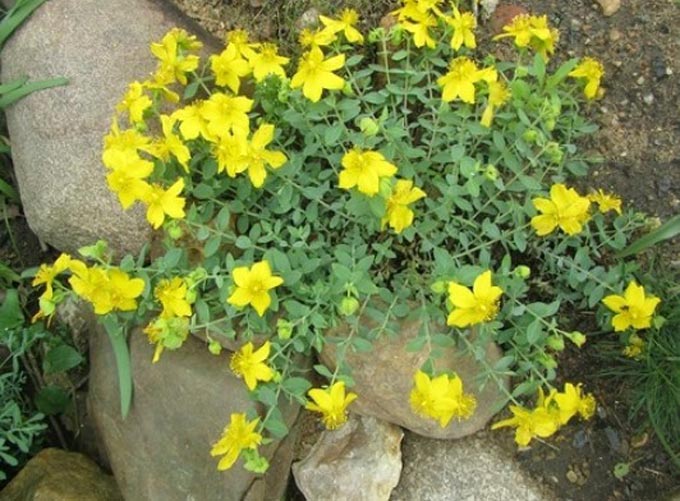
The plant can often be found in the wild. It does well in moderate climates. Distributed in the forest-steppe zone of the European part of the Russian Federation, in the mountainous areas of the Caucasus. And also in Central Asia, Kazakhstan, the western part of Siberia, where it grows in the same environment with representatives of the heather family. Thickets of St. John’s wort are found on the edges of forests, along the banks of small rivers, on lawns and the sides of country roads and paths.
The family consists mainly of herbaceous plants, most of which are precisely medicinal species. Some varieties are short shrubs or undersized ornamental trees. They have no medicinal properties, and are used on the farm to decorate the landscape.
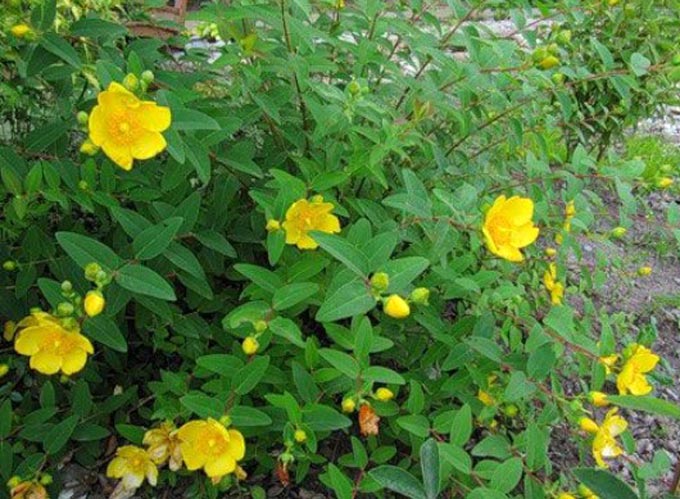
All types of shrubs have common features. They are distinguished by massive branchy shoots that form a spreading crown of a luxurious bush. Whole dark green leaves are ovoid, opposite, slightly elongated and pointed at the tips.
Golden or yellow flowers can be collected in large semi-umbellate inflorescences or grow singly. Sometimes they are grouped in panicles with small numerous flowers – it all depends on the type of ornamental plant. But all St. John’s wort during flowering form a lot of long yellow stamens, which give a special decorative effect to the bushes.
Herbaceous species have a well-developed thin root system and can reach up to 80 centimeters in height. Stems are many-branched, erect and ribbed. Leaves are oval in shape, up to three centimeters long, opposite. The flowers are small, always of the correct 5-petal shape, with long bundles of stamens.
Significance for agriculture
For people, it is the medicinal types of herbs that are of great value. They are used in various herbal mixtures and tinctures to treat and prevent many diseases.
Ornamental species of this plant are actively used by modern gardeners and flower growers to decorate the landscape.
The main varieties
The genus of St. John’s wort numbers about 300 species. There are 50-60 of them in Russia.
Among the medicinal species are:
Perforated (ordinary) grade St. John’s wort. It is distinguished by an unusual dihedral stem, and its leaves look as if pierced by needles. Only in this variety are yellow flowers capable of emitting red juice, which is considered the most healing in its family.
Among the ornamental plants of the family, the most popular are:
Great St. John’s wort – the most popular perennial among gardeners with powerful straight shoots up to 120 centimeters high. Leaves grow up to ten centimeters long. The flowers are very large, wavy at the edges.
Multileaf variety – a dwarf shrub reaching 35 centimeters in height. It has multiple densely leafy shoots that form a powerful crown. The flowers are large.
Cup-shaped variety – evergreen shrub with very large and long leaves. His flowers are huge, bright lemon color. The stamens can exceed the size of the flower itself.
Olympic grade – a semi-shrub with dense foliage. The leaves of the plant are narrow, small, dark green in color. The flowers are large, bloom in the second half of summer.
Coin (underdeveloped) grade – undersized herbaceous dwarf wild plant. Its maximum height is from 5 to 20 centimeters. The flowers are small and inconspicuous. The leaves are small, densely covering the stems. Used for beautiful landscaping of gardens.
Swamp sort used to decorate ponds, landscape transitions between plants. Its shoots are creeping, densely leafy. Small yellow flowers.
Spreading variety is the only semi-evergreen shrub that can withstand persistent winter frosts in the middle zone. Its leaves are quite large, changing color from ruby to green, depending on the season. Inflorescences are large, few in number.
Reproduction of dosage forms
It is customary to sow medicinal species in late autumn or early spring. The seeds can be purchased at gardening stores – there is no need to harvest them yourself. The soil is dug up in advance, for better development, mineral fertilizers can be applied.
Reproduction of garden forms
Ornamental bushes can be planted:
- in autumn or early spring by separating adult plants;
- in conditions of abundant humidity under a hood by cuttings;
- ordinary layering in the spring.
Also, plant seeds can be planted in open ground (but not for seedlings!) For better natural stratification.
The grass and bushes of St. John’s wort are unpretentious, develop rapidly and are able to bloom the next year after planting. They are not afraid of severe frosts.
It is recommended to water the young plantings in the first year, often weed and loosen the soil under them. In subsequent years, you can only dig up the soil between seasons.
Honey productivity
The mass flowering period of the plant falls on the period from June to August (much here depends on the climatic conditions of the area). On average, this is up to 30 days.
But only in warm, humid weather will the flowers release a little nectar. At the same time, St. John’s wort is moderately visited by bees to collect bright yellow pollen.
There is no monofloral variety of honey obtained from this plant. Since more honey-producing plants bloom en masse in summer, flight bees rarely visit St. John’s wort. Basically, only pollen is collected from it.