Infection of bee colonies with viruses is a fairly common phenomenon in modern beekeeping. The first virus, the culprit for the emergence of saccular brood, was discovered at the beginning of the XNUMXth century.
And today there are already about twenty viral pathogens that can cause significant harm to beekeeping farms. One of the most common diseases of modern apiaries is viral paralysis.
The content of the article
- 1 How paralysis proceeds
- 2 Main symptoms
- 3 Diagnostics
- 4 preventive measures
- 5 Treatment
- 6 disinfection
- 7 Other viral infections
How paralysis proceeds
Viral paralysis of bees is an infectious disease that leads to the mass death of adult insects. Young and flying insects are sensitive to the virus, ensuring the productivity of any apiary.
The death of insects indicates that the hive is not well.
All routes of spread of the pathogen are still unknown. But it was found that the incidence of varroatosis contributes to its transmission. Dies within half an hour when heated to 93 degrees.
The infection is capable of taking on a chronic (latent) course. Periods of exacerbation occur in the spring and summer. Lack of bee bread (protein feed) and very hot, dry weather provokes the spread of the disease.
When infected, the nervous system is damaged. In an acute form, most of the affected insects die literally in a few days from the disease. The chronic form develops slowly. It is difficult to diagnose it – the number of dead insects does not exceed the threshold characteristic of the natural change of generations. The first bees die 30-40 days after the first contact with the pathogen.
Main symptoms
The disease is characterized by several stages of damage to the nervous system:
- At first, there is strong excitement – insects make noise, spin like a top, move quickly.
- At the second stage, infected individuals stop responding to external pathogens – they become lethargic and apathetic, and lose the ability to defend the hive.
- Then there is a refusal to fly and complete solidification in one place (when it touches an insect, it only weakly flaps its wings). At this stage, insects die.
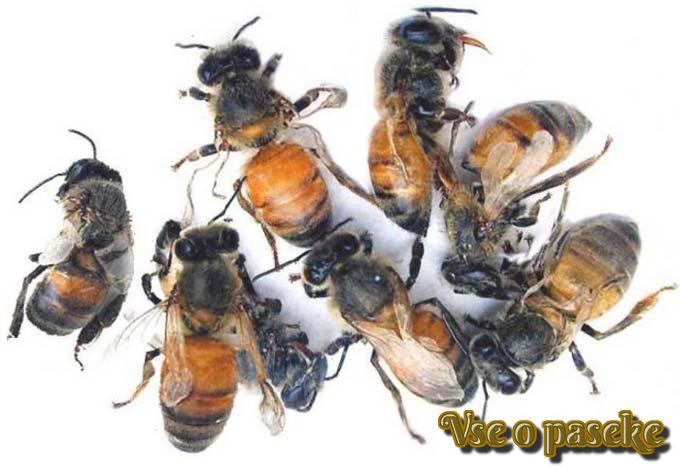
You can also notice the unhappiness of the family by the appearance of adult bees. Their abdomen color changes – a dark, oily-shiny shade appears. The scalp falls off. There is trembling of the whole body and wings.
Diagnostics
An accurate diagnosis can be established by passing the submortem for analysis to a veterinary laboratory.
At home, you will need to open the body of a dead insect. He will have watery feces in his hind intestine, and the honey crop will be full of sugary syrup. Such a podmor emits an unpleasant fishy odor.
Without laboratory tests, there is a risk of confusion with other infections such as acarapidosis or nosematosis.
preventive measures
The main preventive measure is the creation of favorable conditions for the development and life of families. Paralysis is a self-limiting disease. In strong hives, the focus of infection is eliminated on its own 10-14 days after the first contact with the pathogen.
In humans and animals, protection from viruses occurs due to the intake of interferon, which is able to activate its own production of endonucleases. The introduction of nucleases helps to turn on the antiviral defense faster. These enzymes are capable of interrupting the multiplication of viruses in a short time.
In beekeeping, viral paralysis of bees is also treated by the introduction of nucleases. With the help of these drugs, effective prevention of the disease is carried out.
The following enzymes are used:
Ribonuclease aqueous solution has been used since mid-May to process hives four times at intervals of ten days. Spraying is done through a spray bottle at the end of the day, when the active years stops. Dose per socket: 50 mg of the drug per 15 ml of water.
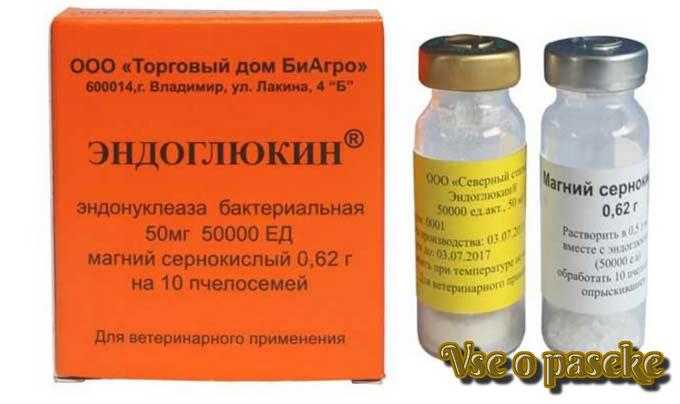
Endoglukin Treatment Kit
“Endoglukin” it is used in the spring and summer when the air temperature is not lower than 14 degrees Celsius. For prophylaxis or treatment, it is required to perform treatment 3-5 times at intervals of a week. The solution is sprayed with a fine aerosol device in the early morning or late evening (must not be active in years). The manufacturer produces kits for the treatment of two and ten families, including an enzyme in an amount of 50 mg (concentration 10 or 000 U) and an activator – magnesium chloride or sulfate. A vial of the enzyme, designed for 50 hepatofamilies, is dissolved in 000 ml of boiled chilled water and the activator is added from the second vial. “Endoglukin” for 2 families is diluted in 100 ml of water.
These drugs produce a stimulating effect by inhibiting latent viruses (circulating in a latent form). As a result, the productivity of the apiary increases. And in the treatment of the acute form of the disease, viral nucleic acids are cleaved and their reproduction is inhibited.
Treatment
Special treatments for paralysis have not yet been developed. Therefore, severely weakened nests are treated with broad-spectrum antibiotics:
«Biomycin» helps insects cope with the pathogenic microflora that develops simultaneously with the attack of the virus. At the beginning of summer, top dressing is performed three times with syrup with the addition of an antibiotic (400 IU per liter of syrup). The interval between feeding is 000-2 days. For one frame covered with bees, 3-50 g of syrup is given.
Oxytetracycline issued at the rate of 0,5 g per liter of syrup. Each sick family is fed 0,8-1 liter of top dressing three times with an interval of two days.
After using the antibiotic, insects recover completely. And sick individuals stop appearing in the nests after 5-6 days after the start of the treatment course.
Means created on the basis of herbal ingredients, which are designed to strengthen the immune system in bees, have also proven themselves well: “Apikur”, “ApiMaks”, “ApiVir”… In their composition, you can find echinacea, eucalyptus, garlic, St. John’s wort, coniferous extract and other medicinal plants that contribute to the destruction of viruses.
disinfection
To avoid the spread of the disease, it is necessary to adhere to the basic rules for disinfection and caring for bee nests:
- Old combs from an infected colony must be reheated. And the frames are disinfected with a blowtorch or by boiling for 30 minutes. Honey can be eaten – the virus is not dangerous for humans.
- After the brood emerges, it is recommended to transplant a sick colony into a clean hive on forage combs taken from a healthy nest.
- In the spring, families should be reduced and insulated with high quality.
- At each inspection, completely paralyzed bees can be removed from the nest. This is a laborious method, but it allows you to speed up the process of apiary health.
- All vacated hives and frames are disinfected annually, and the inventory is processed after each examination of infected families.
- A constant monitoring of the number of Varroa mites is carried out. The lower the nape, the more chances the bees have to avoid infection with dangerous viral infections (paralysis, wing deformation).
Other viral infections
Treatment of viral diseases of bees is carried out depending on the type of disease. There are virtually no antiviral drugs capable of destroying a particular virus.
Insects with deformed wings
The main method of protection is to stimulate the production of enzymes in insects that can protect the body.… And, of course, the right care:
- giving high-quality feed frames and top dressing;
- keeping the nests clean and dry;
- timely identification of weakened and sick families;
- building up the strength of families;
- destruction of parasites, primarily Varroa mites.
If all of the above conditions are met, insects develop a sufficient level of protective forces that can withstand a viral attack.
List of common viral infections:
Cashmere virus (KBV) characterized by the absence of obvious symptoms. Genetically, the pathogen is close to paralysis. Insects die on the third day at any stage of development. The carrier of the infection is the Varroa mite. In healthy families, the infection remains latent.
Black queen cell (BQCV) affects larvae and pupae of queens. The disease develops in families infected with nosematosis. After sealing the mother liquor, the larvae die and take on a dark color.
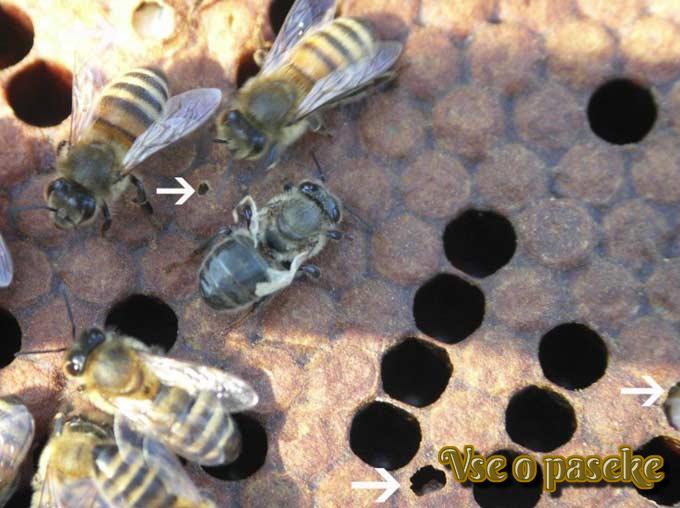
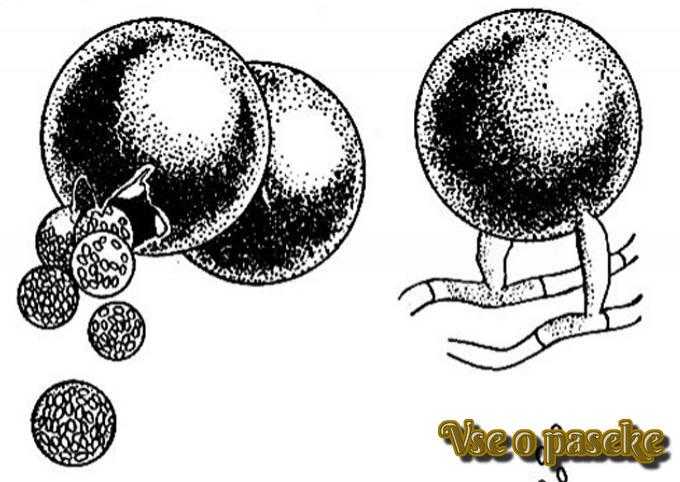
Cells with sick brood, opened by bees
Saccoid Brood Virus (SBV) affects mainly larvae. The source of infection is diseased uterus mites Varroa. In adult insects, infection leads to a shortened life span and refusal to feed the young. The virus spreads along with the bee bread. Infected larvae resemble watery sacs, within which millions of virus particles are found. The body color of the dead larva changes: the head becomes black, and the body dark brown. An outbreak of infection is observed during periods without incontinence in spring and summer. However, healthy colonies themselves cope with the removal of diseased larvae from the nest – the beekeeper does not even notice the presence of SBV. Virus in latent form can only be detected by laboratory testing if the host suspects foulbrood of the brood.
Wing deformation also occurs under the influence of a virus (DWV). The disease has a pronounced symptomatology: in insects, the body size decreases, and the wings look crumpled. The virus is found in 100% of varroa mites tested in laboratories. Sick insects lose the ability to learn, their life expectancy is reduced.
In completely healthy families, viruses are most often found only in a latent form – insects themselves resist infection. For this reason, measures to improve the apiary are a key moment in the successful prevention and treatment of viral infections.