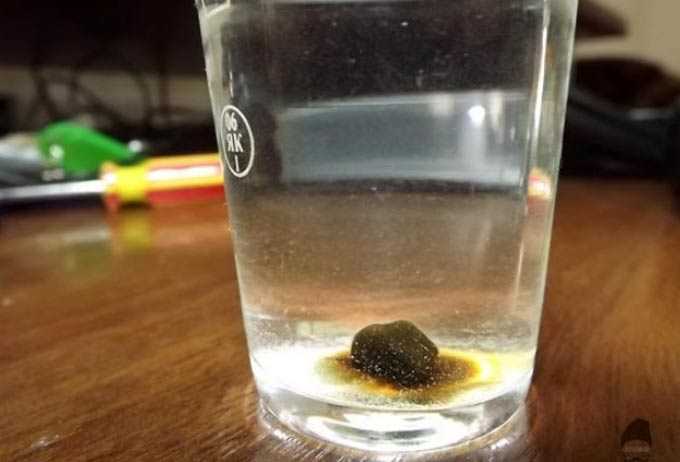
Counterfeit honey is a product that is not created by bees. It can be safely called fake or 100% artificial. Such honey does not possess any useful or medicinal qualities. And in some cases it can even harm human health.
There are also “partially artificial” varieties on the European and domestic market, in which small quantities of flower honey are found.
The content of the article
- 1 Counterfeit and unnatural product – differences
- 2 What is counterfeit made of (fake)
- 3 History of falsification
- 3.1 Three main ways to clean low varieties
- 4 Varieties of low-quality honey on the market
- 5 How to distinguish a fake
Counterfeit and unnatural product – differences
Let’s make a reservation right away that we distinguish an unnatural product from a completely artificial (falsified) one.
Unnatural varieties, although they do not contain flower nectar, are nevertheless processed by bees at an accelerated, rapid pace.
You can read about how these varieties are created here:
What is considered unnatural honey – characteristics, preparation
You can eat them. What can not be said about falsification.
What is counterfeit made of (fake)
Falsification is carried out by prolonged boiling of syrups with the addition of honey essence and acids. The artificial mass is boiled down. Outwardly, it resembles honey. Such a product is stored for a long time in a liquid state even in winter.
It is interesting that counterfeit products are sold quite legally in some countries (an excellent example is the Wol and Colreppa company, which specializes in its production). Their “honey” is prepared on the basis of cane sugar, for the inversion of which weak acids are used. The characteristic aroma and taste is imparted to the product using various chemical additives.
Laboratory analysis shows that the artificial product of this company contains:
- ash (0,12%);
- dextrose (36,06%);
- levulose (38,46%);
- dextrin-like additives (2,93%);
- nitrogenous substances (in small quantities);
- water (22,43%).
History of falsification
Approximately 200 years ago, unscrupulous traders developed technologies that made it possible to give lower grades of natural product the quality of higher and more expensive grades.
Traditionally, a high-quality bee product is obtained in a centrifuge (in a honey extractor) or by gravity, when honey flows out of the opened honeycomb under its own weight. And low grades are the result of melting honeycombs on a fire. They have an increased water content, and due to heating, the healing properties are partially lost, the taste and aroma have changed for the worse.
Any low grade needs “refinement” – cleaning and artificial aromatization. After that, its sales value increases.
Three main ways to clean low varieties
All of the above methods make it possible to create a conditionally artificial (falsified) variety, since natural honey was used as a basis, although of very low quality.
1)The easiest way to increase the value of the end product is to melt it and then pass it through filters.
2)Another method is dissolution in water with the addition of tannin or white clay, followed by prolonged boiling and filtration. Ideally, the resulting counterfeit should weigh the same as the previously low (unpeeled) grade taken for processing.
3)The third method is the most laborious, requiring several days of processing. First, low-quality honey is dissolved in warm water, adding alcohol to this mass. After that, settling is carried out for several days with repeated filtration. Thickening of the mass is achieved by evaporating the liquid over low heat.
If the final product has high acidity, chalk is added to it. For aromatization, an alcohol extract from flower petals, more often roses, is used. The commercial appearance and taste are achieved by adding flour or flour glue, starch or sugar molasses.
Sometimes substances that are completely unhealthy for humans, like clay and gypsum, get into the product!
In Switzerland, mixing starch sugar with flower varieties is a very common and legal phenomenon. Such a product is being sold under the name “Swiss (or table) honey”. It consists of 70 percent starch syrup and 30 percent of a natural bee product.
Varieties of low-quality honey on the market
On the domestic market, low-quality honey is presented in several varieties:
- Actually fake – that is, melted sugar with various additives (sometimes hazardous to human health) to add color, consistency, aroma.
- Partial falsification – a product made from molasses or sugar syrup with the addition of honey and decoction of herbs, for example, medicinal dandelion flowers.
- A quality product can also be given unnatural honey – syrup processed by bees with the addition of minerals, vitamins, medicinal substances. It is the safest for a potential buyer. But the trouble is that the consumer is being deceived – he overpays for the purchase. And in the end, it does not receive the expected healing effect. Such honey must be marked accordingly when sold!
The simplest and most harmless counterfeit is obtained by feeding sugar syrup to bee colonies. From a kilogram of sugar, would-be beekeepers get the same amount of honey, which significantly increases income from apiaries. Naturally, there are no vitamin and mineral supplements in the final product. Its use does not bring any benefit to the person.
Unripe natural honey cannot be called a quality product. It exceeded the standards for water content. If stored improperly, it may well ferment.
How to distinguish a fake
To assess the quality of sold honey, specialists consider over 40 parameters. GOSTs take into account ten of them. Without meeting these indicators, the bee product should not be marketed.
Unfortunately, only a few quick ways to identify a fake are available to the average buyer. In most cases, counterfeit can be detected exclusively by chemical analysis in the laboratory. Moreover, the folk method of “testing with a chemical pencil” will not work here.
It will help to recognize a falsified product:
- Weighing: one liter is 1,42-1,44 kilograms.
- Color: to light, the product must be transparent.
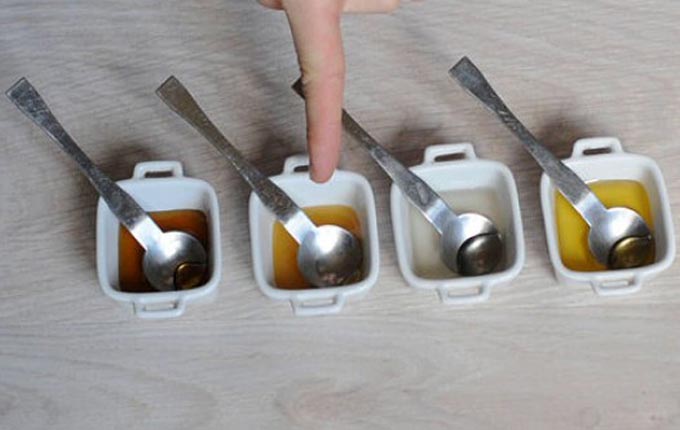
- Touch: A drop of quality bee product is easily rubbed between the fingers, and the fake rolls into lumps.
- Test on absorbent paper (blotter, napkin): the counterfeit spreads with the formation of damp spots, which indicate the presence of additives.
Read more: How to determine the natural origin of honey at home
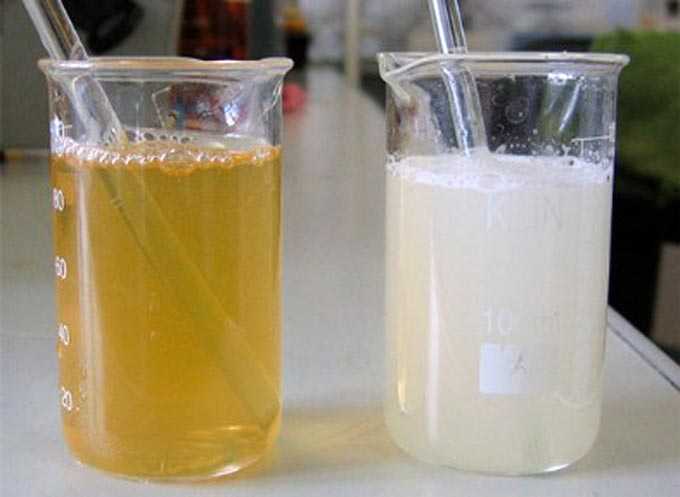
All other methods of checking the buyer cannot be applied directly on the market, since they include the dissolution of honey in water, followed by the use of various chemical solutions such as iodine, acetic acid, ammonia.
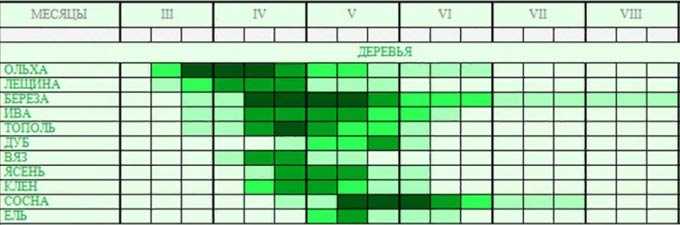
It will be useful to be aware of the flowering time of different melliferous plants, their honey productivity, as well as the differences between natural varieties in consistency, taste, aroma and color.
To read:
Various melliferous plants, their honey productivity, quality and useful properties of honey
Poisonous melliferous plants
Honey can be different – delicious and … very tasty
Monofloral (one-component) honey varieties
Polyfloral (multicomponent) honey
Special varieties of natural honey