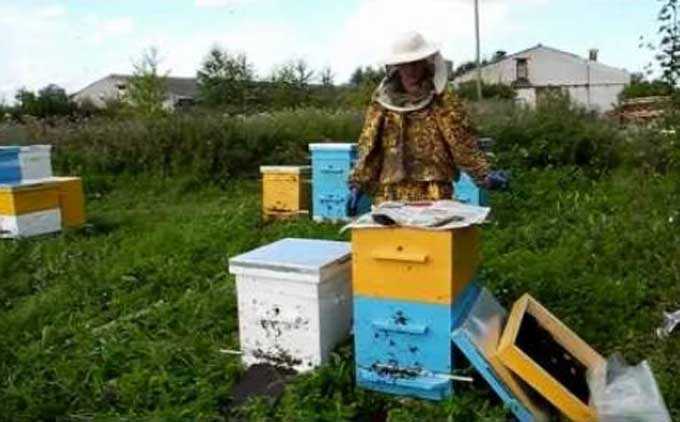
There is a constant debate about what kind of therapeutic measures should be carried out in the apiary in the spring. Each of the beekeepers has a special opinion on this matter.
Some have a hard-and-fast rule of dispensing antibiotics for prophylactic purposes. Others advocate treatment upon the discovery of a particular bee disease. What about beginner beekeepers? Those who experience the most excitement and concern about the health of bee colonies. The answer is simple – don’t panic ahead of time!
The content of the article
- 1 Prevention principles
- 2 Spring fight against varroatosis
- 3 Folk remedies
- 4 Spring fight against nosematosis
Prevention principles
Most often in the winter-spring period, bees suffer from diarrhea caused by nosematosis. You can read about this infectious and quite dangerous disease for the productivity of insects in our separate article:
How to cure bees in spring from nosematosis
And we will talk about the general principles in the approach to the prevention and treatment of bee colonies.
Spring inspection of hives is a mandatory annual procedure that helps to assess the health of bee colonies
You need to understand that if there is a disease, it must be treated. If the infection is not detected visually and, moreover, by laboratory means after passing the winter dead for analysis, the use of any medication will be an unjustified risk.
For the prevention of nosematosis, antibiotics are not used, for example “Nosemacid”! The same rule applies to the most common parasites, mites. They either exist – treatment is required, or they are not – in this case, there is no point in prevention.
This is supported by two obvious facts:
- There is a concept of “economically justified threshold of harm”. If it is exceeded, nest processing is started. Otherwise, the damage from processing will exceed the expected benefit.
- And in the case of infectious diseases, the use of any chemical preparations for prophylaxis will most likely lead to the emergence of pathogens resistant to the drug (after all, the dosage is also selected “prophylactic”).
Spring fight against varroatosis
The destruction of ticks in the spring is required only if the timely (autumn) processing of the hives has not been carried out.
The overwintered mite enters the brood – it is virtually impossible to kill it. At the same time, many drugs are indicated by manufacturers as “acting on Varroa mites at any stage of development.” Such promises are just advertising.
In spring, special plates (Amipol, Fumisan) can be installed in the hives. Plates are placed in the nest according to the instructions immediately after the spring flyby. And they stay there until the first bribe – that is, they work only in 1-1,5 months of the spring development of families.
However, the use of the same active substance leads to the appearance of generations of parasites that are resistant to its influence. Therefore, it is also recommended to use formic acid – one of the most environmentally friendly products. In liquid form, this substance can be dangerous to humans – when working with acid, the respiratory tract is irritated and burns occur on the skin.
The domestic drug “Muravyinka”, produced since 2001, is devoid of all of the above disadvantages. It has a wide spectrum of action and can be used prophylactically to combat varroatosis, nosematosis, acarapidosis, ascospherosis and rotten diseases. “Muravnka” also perfectly disinfects the honeycomb and the hive, destroys the wax moth.
Patriotic Muravyinka
But, as in the case of antibiotics, treatment with a formic acid-based preparation is advisable in the spring only when insects are strongly nibbled or when autumn processing is unsatisfactory (its absence).
Overdose is dangerous! You can not process hives with less than 5-6 streets… Overexcitation and pumping out of insects occurs, worker bees and old queens (more than two years old) die, since a small number of insects cannot provide sufficient ventilation to the nest.
In the processed hive, the upper and lower entrances should be open for better ventilation. The bag “Ant” is placed on the bars of the frames under the canvas, based on the strength of a family of 5-12 streets. The treatment course is two to three sachets, set at intervals of one week. Complete evaporation of the acid occurs in 3-5 days. Already 40 days after the spring processing, the minimum content of formic acid is found in honey.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies are selected on an individual basis – in each area there is a practice of using certain herbs that can strengthen bee colonies and help them resist nosematosis and tick infestation.
Here are some recipes:
Fumigation of hives
Dried horseradish is placed in the smoker… Such smoke can reduce family clinging. At the same time, bees do not suffer from unnecessary exposure to chemicals. At the bottom of the hive, you can install cardboard greased with petroleum jelly. After fumigation with horseradish, the fallen mites are burned along with the cardboard.
They use decoctions of St. John’s wort and wormwood, which help to strengthen immunity and defeat nosematosis.
The recipe for the decoctions is simple: for three liters of boiling water, St. John’s wort herb (3 tbsp. L), wormwood herb (2 tbsp. L), mint herb (2 tbsp. L), yarrow herb (3 tbsp. L) are taken. The container is covered with a lid and the broth is allowed to brew for 50-60 minutes. After cooling, everything is filtered and diluted in 15 liters of water. This remedy is given every three days (you need to pour the medicine into the drinkers in the apiary). In this case, wormwood is responsible for the prevention of nosematosis, ascospherosis is treated with yarrow, the rest of the herbs are responsible for insect immunity.
Juniper leaves, spruce or pine needles are laid on the bottom of the hive… Evaporating essential oils cleanse the air in the nest from viruses and bacteria. Fern and eucalyptus leaves are used in the same way. This is a good prophylactic agent that ensures a healthy microclimate in the hive.
Spring fight against nosematosis
Apivir also has a natural origin. This extract includes several medicinal plants at once: garlic, St. John’s wort, Echinacea purpurea, eucalyptus, lemon balm, licorice, pine needles. The main direction for the use of this drug is the fight against viral infections (saccular brood, acute paralysis), fungal and bacterial infections (foulbrood, paratyphoid, ascospherosis), nosematosis.
“Apivir” is an effective natural medicine
In the spring, the balm is applied immediately after the first flight of insects. It has not only a therapeutic and prophylactic effect, but also helps in stimulating the development of families.
For the prevention and treatment of nosematosis, the following recipes are used:
Apivir with syrup – For ten liters of 50% sugar syrup, a bottle of extract is taken. Issued to bees in drinking bowls at the rate of 50 ml per frame completely covered with insects. For preventive purposes, one feeding is enough. And for treatment, it is required to issue it twice with an interval of 3 days.
“Apivir” with candy – a bottle of extract is taken for 5 grams of kandy. Candy is issued at the rate of 50 grams per frame. For prevention, a one-time dispensing of the medication is enough. For the treatment of nosematosis, the dose can be increased to 60 grams, but the Candy is given once.
Water solution used for spraying hives – the bottle of the extract should be dissolved in a liter of boiled water, cooled to 40 degrees. The solution is sprayed at the rate of 10 ml per frame. Moreover, its temperature should be room temperature (approximately 20-22 degrees). For processing, it is better to use a fine dispersion spray. Prevention is carried out with a single treatment. The treatment is carried out after two sprays with an interval of three days.
An important point: Antibiotics are used when indicated. However, it should be borne in mind that it is better to exclude nosematosis during the autumn formation of nests. During this period, it is appropriate to use “Nosemacid” or “Nosemat” – drugs based on tetracycline. Some beekeepers use Metronidazole (5 grams per 5 kilograms of Candy).
Treatment of bees in the spring is required only due to improper apiary care. A beekeeper who makes mistakes has to correct them urgently.
Experienced beekeepers consider the best spring prevention:
- keeping the nests clean and dry;
- the presence of complete feed (clean honey frames with bee bread);
- reduction of families in size.
If an autumn tick treatment has been carried out, its number will be reduced to a safe rate. In the spring, all that remains is to install plates with acaricide to control the parasite population. And families cured of nosematosis enter wintering completely healthy. If there are no traces of diarrhea in the hive, there is no point in using any chemical preparations in the spring. It is enough to use folk remedies that strengthen the immunity of insects.