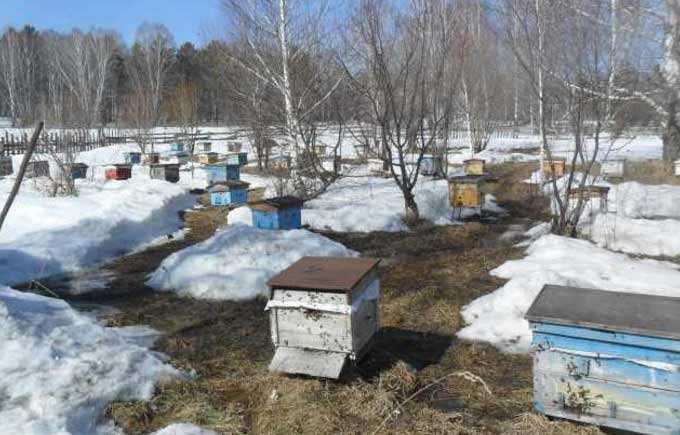
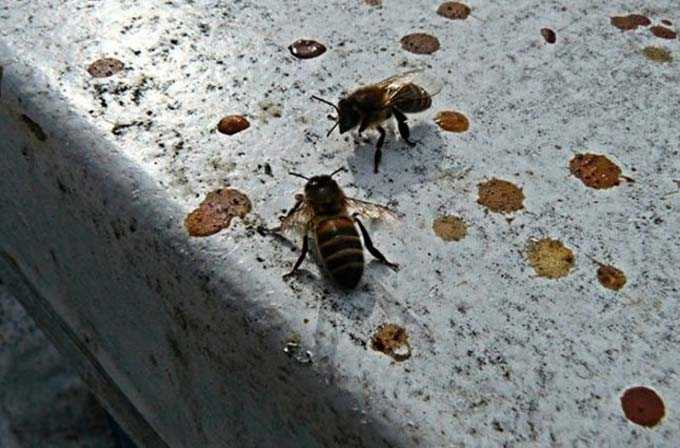
The summer period is the peak of the development of bee colonies. Summer can be called a real celebration of swarming and the time to receive the main profit from the apiary – any of the beekeepers has high hopes for the main bribe.
The work in the apiary in June is centered around keeping the colonies from awakening the swarm instinct. Providing insects with combs and additional hives, if multi-hive hives are used, is the main task of the beekeeper this month.
The content of the article
- 1 Brief overview of works
- 2 Swarming Prevention Techniques
- 3 What are the swarms
- 4 What can cause a swarm mood
- 5 What to do when a bribe occurs
Brief overview of works
In most climatic zones, June is a warm and sunny month, in which honey plants bloom en masse. The duration and strength of Vyatka can vary from year to year. With sufficient rainfall, plants produce nectar well.
The source of honey in June is acacia, linden and flowering meadow grasses such as alfalfa and sainfoin. The bribe encourages the queens to actively lay eggs. More than 2 fresh eggs are laid daily.
According to the state of families at this time, it is easy to predict income from the sale of honey:
- small families will be unprofitable – weakness will not allow the nest to prepare food even for wintering;
- average bee colonies are guaranteed to feed themselves and give a small amount of honey to the owners of the apiary;
- active strong families are the main source of income, they are able to provide an abundance of marketable honey.
Note: In June, it is no longer possible to use chemicals to combat the spread of Varroa mites. After all, chemicals can get into ready-made honey and affect the health of people who eat it.
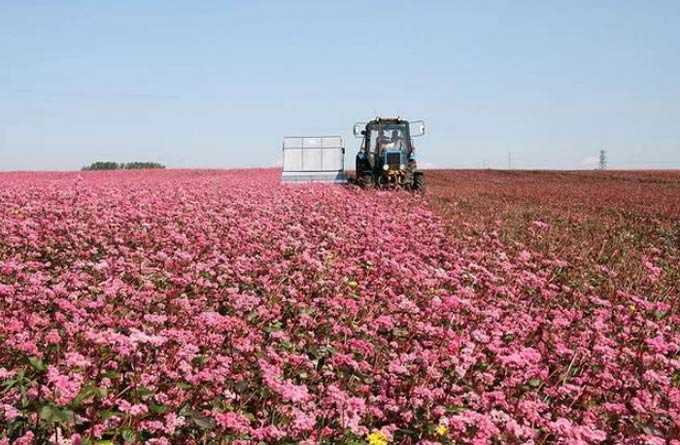
It is recommended to move the apiary to the points located near the massively flowering honey plants. Wandering is fully justified and pays for itself. For example, it will help strong bee colonies collect nectar from acacia. These trees bloom for about 1,5-2 weeks, providing a decent bribe.
Note: With the beginning of flowering of acacia or linden, there is a natural limitation of egg-laying. The instinct for the accumulation of feed is sharpened. Due to the reduction of the brood, a large number of insects that previously fed the young are released. They take the most active part in honey collection.
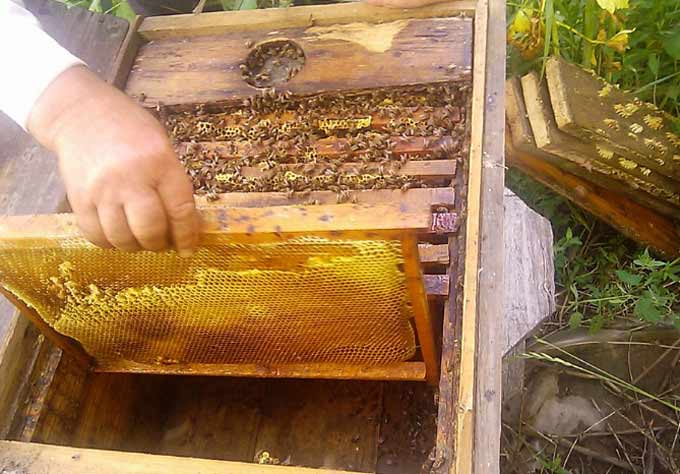
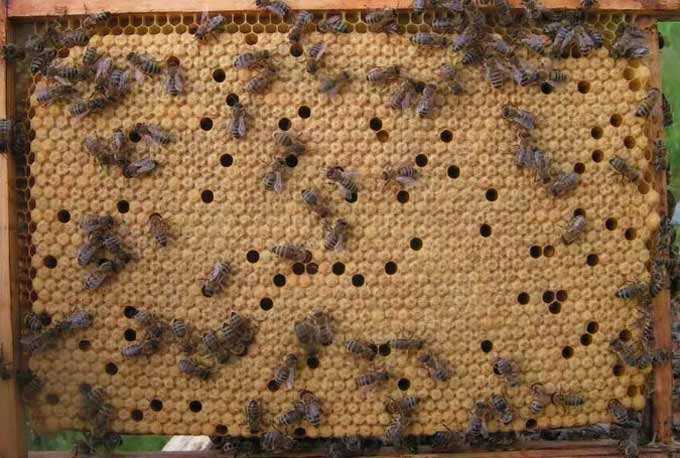
Bribes are a period of increased wax release. Bees willingly build new honeycombs, if they are given foundation in a timely manner (before the start of the bribe).
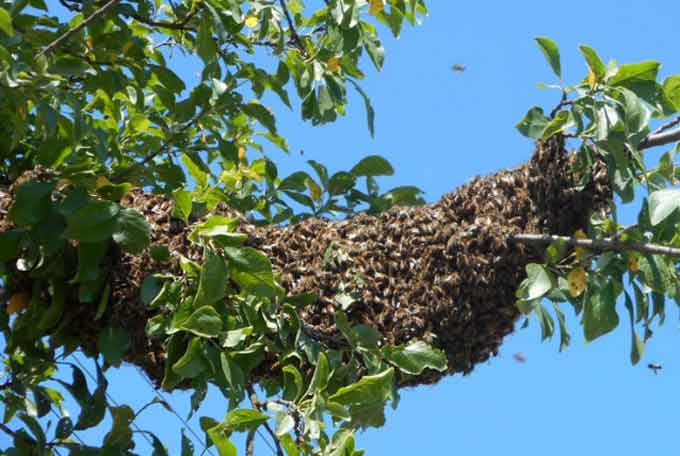
Note: Expansion of nests prevents early swarms from emerging, causing significant damage to beekeeping. But at the same time, swarms are an opportunity for additional breeding bee colonies. Swarms are more productive than farmed females.
If the swarm came out before the main honey collection, a nest is assembled for it from almost one foundation. For example, for 4 kg of insects, you can give nine frames with foundation, one with honey and two with dry. Place honey and dry in the center. Such a young family will quickly build new combs and be ready to actively collect nectar.
May and early June layers are formed according to a similar principle. In this way, the beekeeper significantly increases the income of the apiary and at the same time eliminates the need to catch swarms.
Note: Late swarms, which have already separated during honey collection, do not have time to quickly rebuild new cells. Therefore, they are given 50% of land and foundation in their nests.
Swarming Prevention Techniques
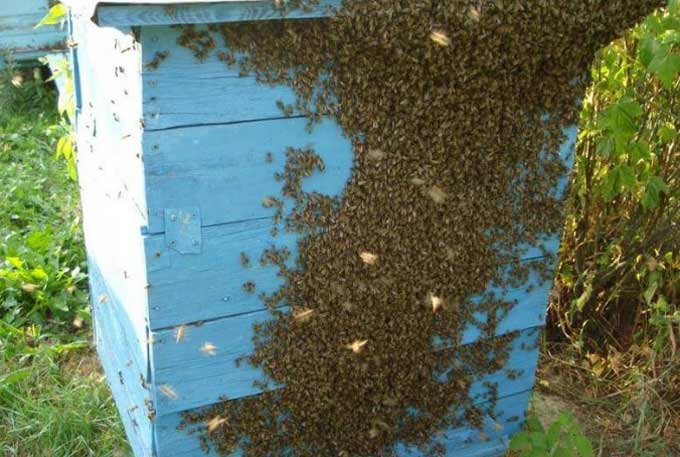
Many beekeepers consider the swarm state to be the result of oversight of the bee colonies. It is easier and more profitable to expand the apiary with layering.
The methods of dealing with uncontrolled departure of swarms include:
- Placement of bee houses in the shade of plantings. This will reduce the temperature in the nests.
- Protection of hives from heat if they are located in an open area. Green branches are used, cut grass – they are laid on the covers. In this case, the entrance slits are directed to the northeast.
- Enhanced ventilation – the upper and lower entrance slots are fully open.
- Expansion of strong nests by installing frames with foundation.
- Providing a good food supply. If there are no melliferous plants at the main location, the hives are transported to the melliferous massifs. Insects willingly collect nectar and pollen from grasses and shrubs: raspberries, viburnum, motherwort, clover, sweet clover, cornflowers.
Note: An external stimulus, whether it is the installation of foundation or the onset of a natural bribe, reliably suppresses the swarm instinct.
Work in the apiary in June necessarily includes the control of this complex biological process of reproduction of bee colonies. And a careless beekeeper runs the risk of being left without bees and income!
What are the swarms
Southern breeds swarm earlier, and Central Russian bees fall into this state a little later, finishing the process only by the beginning of July. It is extremely difficult to transfer insects back to working condition. As a rule, this is possible only with the onset of a powerful honey collection and the removal of all queen cells in the hive except for one – for a new queen, which is necessary to support the life of the family after the departure of the pervak swarm.
Note: Insects that have a young last year’s uterus do not come into a swarm mood. With the expansion of such nests, egg laying increases – the family does not have enough time to swarm.
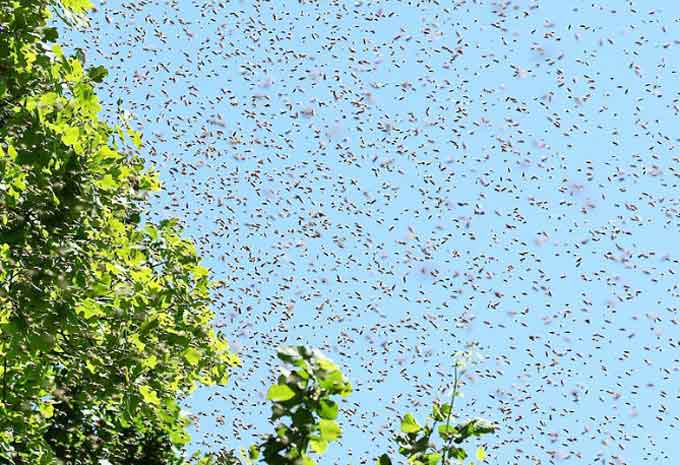
Swarms are divided into several types:
- Those flying out on the fourth day after sealing the queen cells together with the old queen are pervak.
- Insects leaving the hive 9-10 days after the flight of the pervak along with the young infertile uterus are swarm-retora. The second swarm is followed in two or three days by the next, and so on. As a result, the maternal family may die!
- The united swarms of several hives are landfills, which have sat down in the same place.
What can cause a swarm mood
The apiary in June should be kept in such a way as to prevent the awakening of the swarm instinct. The beekeeper needs to remember that bees do not just fly away from their nests. This process is triggered by mistakes made during the exit:
- If not enough feed is left in the hives for the winter, in the spring the insects will “run away” from the negligent owner.
- A similar reaction will be caused by the spread of Varroa mites, if timely medical and preventive measures are not taken.
- If the entrances have not been completely open, insects become stressed due to the increased temperature in the house. After all, the process of converting nectar into honey requires a lot of heat. Bees need good ventilation!
- If expansion has not been carried out, all cells intended for larvae are filled with nectar. The queen stops worming – as a result, the number of inactive bees grows, which provokes the exit of the swarm.
- Sometimes the reason is the lack of natural bribe in a particular region. Without feeding, insects follow the instinct of preserving the genus – they fly out in search of a favorable area for life, because only food supplies guarantee survival in the winter.
- Insects do not like the presence of a sluggish old uterus, which slowly fills the cells with fresh egg-laying. As a result, young bees remain unemployed for a long time.
What to do when a bribe occurs
The time of mass flowering of honey plants requires utmost attention from beekeepers. Working insects actively fly from dawn to dusk, filling empty honeycombs with nectar.
Note: The task of the beekeeper is to constantly substitute fresh dryness and foundation, timely selecting frames completely filled with honey. If the honey is more than two-thirds sealed, the frame can be safely removed from the nest.
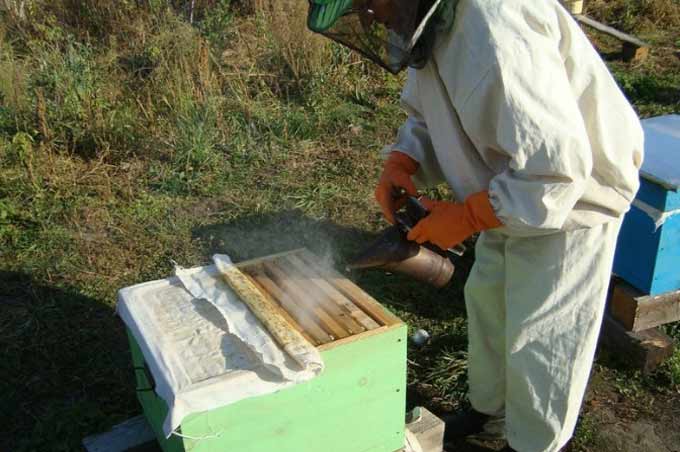
When selecting insects, they are shaken off into the hive using a soft brush made of natural hairs. And the frames are immediately placed in a portable box and tightly closed with a lid to avoid theft. The hive itself during operation is kept covered with a special canvas.
Note: You can bring the thief bees to their senses in the following way. If a hive with lovers of someone else’s honey is in the same apiary, the lid is removed from it, and an insulating layer and a canvas from the frames. Then two pieces of 10 × 10×60 cm are placed on the frames. And a lid is placed on top, and a gap of 8-10 cm is formed. The bees will be forced to huddle under the covers to protect their own nest from possible theft. Literally in a day they forget the “address” of the robbed hive and begin honest work in their own house.
Such exposure of the hive requires care and accuracy from the beekeeper. In itself, this is a rather risky undertaking. More often simpler methods of fighting theft are used. For example, fumigating a bee house with smoke. For this, a bucket of embers is placed in front of the entrance.
If the weather conditions are bad – there is a dry heat or constant rains, the first bribe may be weak. In this case, the nectar will be used exclusively for raising the brood. Bees will get it mainly from meadow grasses. This will be the so-called bribe support.