Thanks to the work of people, bees, which have long been valued for the honey they bring, have become ubiquitous throughout the world. Other useful beekeeping products are also widely used in everyday life: pollen, royal jelly, wax, propolis. With the development of agriculture, the importance of bees for natural pollination of plants and for obtaining a bountiful harvest grew. Scientists have studied more than 20 thousand species of these insects, among which the honey bee, which is found in all corners of the world, stands out. Breeding them requires knowledge of their structure and keeping conditions, awareness and skills in caring for bee colonies.
What a honey bee looks like
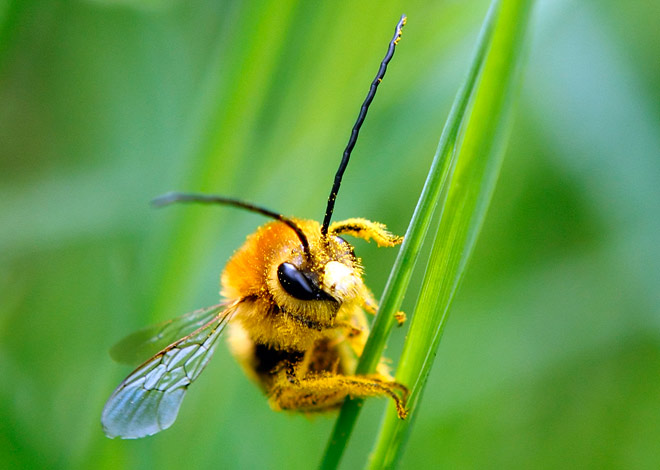
A characteristic external feature of the animal is a hairy body with alternating yellow and black stripes. According to the systematic position, biologists classify these insects as arthropods of the order of Hymenoptera. Usually, bees prefer to live in open places:
- in the steppe;
- in the meadows;
- in gardens;
- in the fields;
- in the clearings.
Honey bees are distinguished by good social organization and a high level of development. They have the basic necessary senses, feel warmth and temperature fluctuations. Differences in the size of the body of animals depend on their functions. Working bees reach a length of 16 mm, and the parameters of the queen are larger – up to 22 mm.
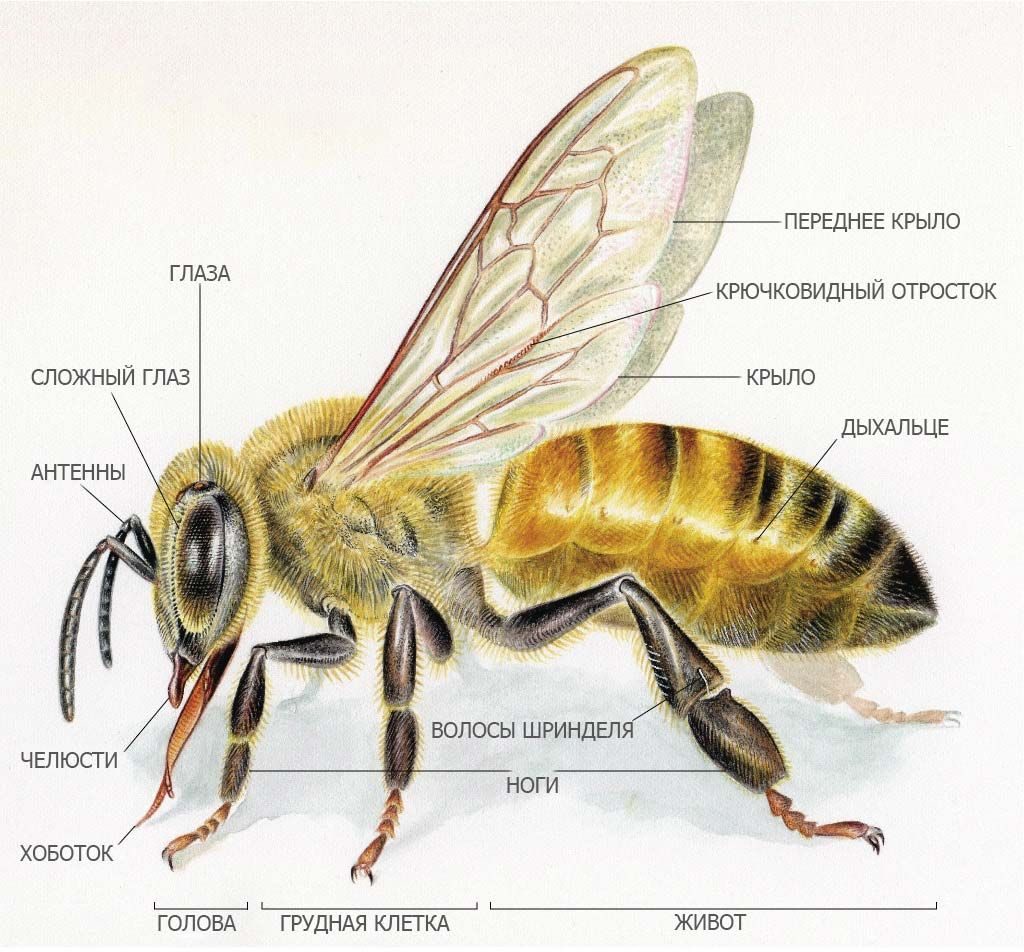
The structure of the body is perfectly adapted for the life of a bee. Outside, the honey bee is dressed with a hard cover that serves as a skeleton for the insect, protecting the internal organs from injury, temperature fluctuations and changes in environmental conditions. In addition, the body is shrouded in a large number of villi, many of which serve:
- to protect against dirt;
- for carrying plant pollen;
- for warming in the cold season.
A proboscis up to 7 mm long is located behind the oral cavity for collecting nectar, honey and water.
Interesting!
In winter, bees are crowded together to form a compact ball.
The most common breeds of honey plants
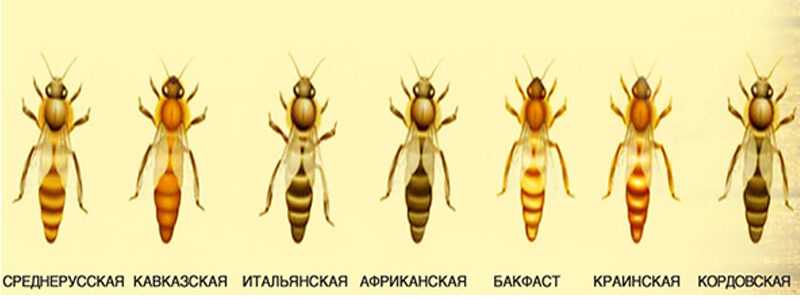
Not all types of these animals produce honey. For centuries, people have been engaged in the selection of the most useful honey bees, corresponding to the conditions of their habitat, in order to collect as much nectar as possible from local honey plants, pollinate them, and withstand regional climatic conditions. As a result, bee breeds have emerged, named after the territory where they come from. In addition to many specially bred breeds, in some apiaries there are varieties that have absorbed the properties of a number of species and adapted to the specifics of regional weather conditions. They differ in appearance, originality of evolution and life processes.
The most popular is the European dark, characterized by a large body and a shortened proboscis. By nature, these are rather angry bees. They produce honey that is light in color. This species is characterized by resistance to disease and bad weather.
The habitat of Central Russian honey bees, leading from dark forest bees, is the entire north and center of Russia, as well as more western regions:
- Belarus;
- Ukraine;
- Baltics and other countries.
Honey insects are perfectly adapted to the cold, they are distinguished by good resistance to frost, infections, and toxic substances. Individuals of this breed of bees in Russia are characterized by stability in the selection of honey plants, preference is given to linden, fireweed, buckwheat, but they are able to collect nectar and pollen before the first frosts. The productivity of a bee colony is up to 30 kg.
The Ukrainian steppe bee, with its outwardly small size, has a bright yellow color, sustained calm character, resistance to diseases and cool weather. The bee colony produces up to 40 kg of honey per season, which is advantageous in comparison with other breeds.
The parameters of the Caucasian insects resemble the previous variety, their colors are yellow-gray. Thanks to the elongated proboscis, they can extract nectar from the depths of the flowers. The breed is distinguished from other species by its high working capacity and immunity to diseases, however, manifestations of aggression are often found. One bee colony brings up to 40 kg of honey during the season.
The bees bred in Italy are distinguished by an elongated proboscis, a yellow abdomen, and a body surrounded by stripes. Calmness and cleanliness are considered the distinctive features of the species. Insects themselves carefully clean the hive and get rid of the moths that litter it, thereby increasing the quality of their products. In addition, the honey bee is disease resistant, but its productivity is lower than that of other animals.
The Carpathian variety has a gray body. Due to the lack of unfriendliness, good winter hardiness and excellent productivity, the breed is in great demand among beekeepers.
Wild honey bees
The difference between uncultivated insects and domestic ones is:
- in slightly reduced parameters;
- in less colorful colors;
- much more aggressive;
- in a powerful immunity to infection and temperature extremes.
They are characterized by solid endurance and are able to travel long distances to discover honey. Untamed honey plants are adapted to withstand severe frosts. Wild families usually settle in a crevice in a tree or mountains in vertically lined hives using wax as a bonding agent. Due to the lack of frames, the cells of the honeycomb have the shape of a tongue.
Life span of a honey bee
The duration of the existence of honey insects is short, it is due to many reasons. How long a bee lives depends on the position that the animal occupies in its family. The lifespan of the queen, drones and workers is different.
Life cycle features
A large amount of resources are spent on pollen collection, honey production and nursing of the young generation. Due to the short life cycle in the honeybee family, there is a non-stop process of egg production (up to 2 thousand per day). In a healthy swarm, the life of animals usually lasts longer (up to 35 days), in a weak swarm – less (25 days).
The life span of insects is subject to the climatic conditions of the area. In summer, in warm favorable weather, the bees feel comfortable, therefore, their lifespan is maximally increased to 45 days. Individuals who survived the winter barely last up to a month. Specimens not rearing brood in summer and winter live up to 2 months. Those insects that left a lot of young animals in the fall die sooner. The lifespan of a worker bee depends on the energy it has expended. The August brood lives the longest. The life cycle of drones is the same as that of worker bees.
The queen, which plays an important role in brood and increase in the bee colony, does not expend energy on collecting honey. She is able to live up to 5 years thanks to a relaxed lifestyle and enhanced nutrition containing valuable substances. However, if in a swarm she produces large offspring, the uterus quickly grows old and dies after 2 years.
Territorial distribution
Nowadays, honey bees are common all over the world. The most important place among all species belongs to European insects, which in their development acquired the highest level of evolution, forming an optimal swarm structure, family lifestyle and development in the hive.
They have adapted to the conditions of a cool climate, which makes it possible to breed them even in the northern and Siberian regions. The placement of bees is done in a planned manner.
External structure
The three-piece trunk is supported by the external exoskeleton (cuticle). The hairs covering the top of the body serve both for touch and protection from dirt – there are the organs of perception and excretion. The body parts are connected by thin elastic membranes.
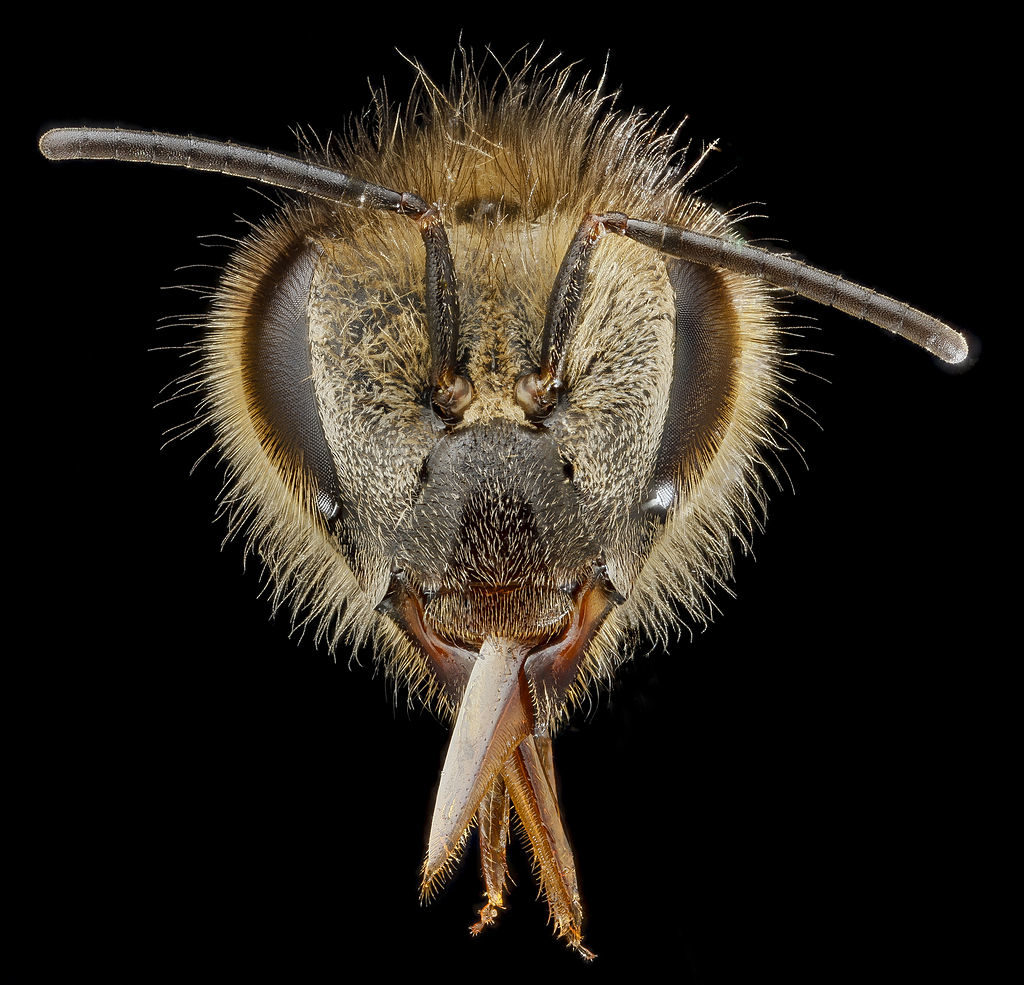
The bee’s body is symbolically delineated into three main fragments: head, breast and belly. The upper section contains the antennae, the oral cavity, and an intricate ocular structure consisting of two compound eyes and three simple eyes. In the chest part there are two rows of wings with membranes, which during flight mate with each other with the help of special devices on the lower wings. There are six legs on the abdomen, characterized by the presence of specific scrapers that allow the bee to shake off the pollen from the legs.
Most people don’t know how many pairs of eyes a honey bee has. Placed on the side of the head, the compound eyes include thousands of facets. The peculiarity of vision lies in an ingenious mosaic structure, which gives her the opportunity to see sunlight through the clouds. Two types of organs of vision help to cover a large area during flight, although in a blurred form. Simple eyes can only see the intensity of the light. But a wide spectrum of color vision in a honey bee, consisting of five colors, makes it possible to distinguish between polarized rays, as well as volumetric shapes that resemble the outlines of a flower.
Internal device
The animal’s body is distinguished by a complex structure. The structure of the honeybee resembles the structure of the organism of higher animals, which have developed systems and senses. All her movements are run by quite powerful muscles.
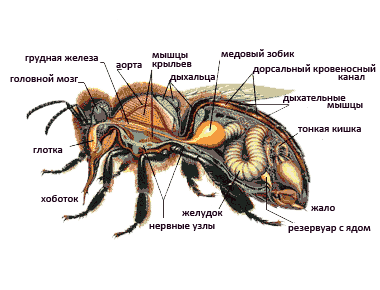
Digestion
The digestive system is divided into three sections. The first includes:
- oral cavity;
- swallowing organ;
- esophagus;
- goiter for honey.
The middle compartment includes the stomach, the lower part consists of the intestines. Absorption, assimilation, incomplete and complete transformation of nectar into honey are involved in the glands (salivary and subpharyngeal). From the pharynx, food enters the repeatedly expanding esophagus, which forms a goiter to accommodate honey, from where the content is expelled through the proboscis through the muscles. Digestion takes place in the stomach. The intestine is a thin and straight zone. In the latter, undigested food fragments are stored, from which the bee gets rid of through the corresponding glands.
Breath
The insect has an impressive respiratory system that includes a network of organs. Inhalation occurs through paired stomata on the trunk: six on the chest and twelve on the abdomen. Having penetrated through the hairs and cleared, the air fills in special bags and spreads throughout the body. Exhalation is carried out by the third pair of holes in the thoracic region.
Heartbeat
The five-chambered heart of a honey bee looks like an elongated tube running down the upper torso. Instead of blood, however, it is filled with hemolymph (plasma), which passes through the valves from the abdomen to the head. The uniformity of the current is regulated by the thoracic and dorsal diaphragm. The heart rate of a pacified insect is 100 beats per second, and immediately after the flight it rises to 150.
senses
The sight of bees allows them to see completely everything around them and simultaneously from above and below. Images from five eyes are combined into a single mosaic picture. Insects are able to determine the direction of light waves and even in cloudy weather know where the sun is.
With the help of the villi on the antennae, consisting of segments and flagella, bees use the sense of touch, which allows them to determine their place in the darkness of the hive. Antennae also serve bees to determine temperature and humidity. Thanks to the endings placed in the mouth, insects are able to determine the category of nectar. Bees have no ears, but they are able to hear: there are special auditory openings on the body. The endings responsible for gustatory sensations are located not only in the pharynx, but also on the proboscis, antennae, and even on the paws.
The value of bees in nature
The serious importance of honey bees lies in the production of honey and a host of valuable products that are important for humans in medicine. However, pollination of almost all flowering plants is much more significant. This work of the workers of gardens and fields contributes to an increase in yields by one and a half to two times:
- buckwheat;
- sunflower;
- alfalfa;
- apple trees;
- watermelons.
According to research, more than one and a half hundred agricultural crops on 20 million hectares require cross-pollination. The increase in productivity favors the expansion of the green cover of the planet, supplying living organisms with plant food and oxygen, purifying the air from carbon dioxide, preserving the ecology of the Earth.
It is difficult to assess the importance of honey bees in human life. They produce a lot of valuable products for health, containing biologically active substances, contribute to the development of agriculture, increasing yields by pollination of flower stalks and creating conditions for greening the planet.