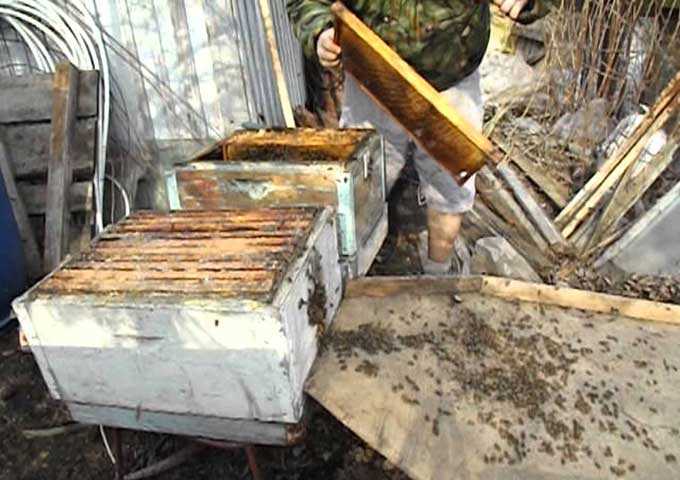
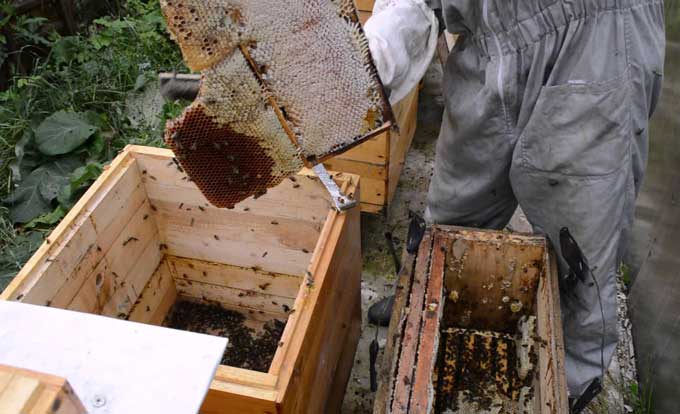
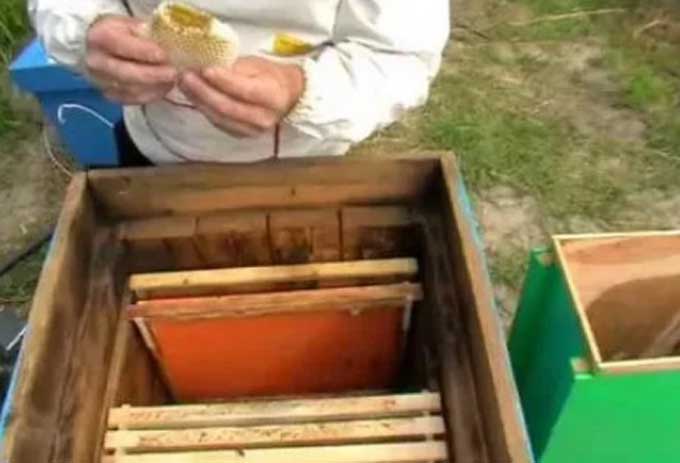
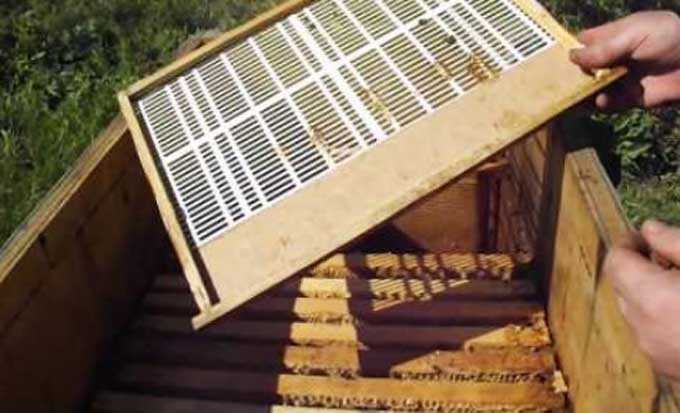
Transplanting bees into a clean hive in the spring is a common practice among experienced beekeepers. At least once every two years, all bee houses need disinfection and conservation. This is done as a preventive measure to combat various infections and bee parasites.
Also, the reason for the resettlement may be the dampness in the nest detected in the spring, traces of the penetration of mice, martens and other pests. Sometimes the beekeeper wants to renovate the apiary and replaces outdated or worn out hives with new houses. Or it combines two hives into one. In each of these cases, a different technique is used.
We will tell you in more detail about the spring transplant, as well as touch on the different types of movement and relocation of bee colonies.
The content of the article
- 1 Disease control
- 1.1 Types of transplant for infections
- 1.2 Medical feeding
- 1.3 Processing and disinfection
- 2 Rodent and damp control
- 2.1 Once again about processing
- 3 Relocation to a different type of hive
- 4 About air temperature
- 5 Nucleus use
- 6 Transfer from a box house
Disease control
If a large number of bee colonies are infected, bee driving is practiced. This method involves relocation to new disinfected houses on frames with artificial foundation.
Distillation is carried out strictly to the main honey collection, but in the presence of a supporting bribe in nature. Work is done in the afternoon to avoid bee theft.
You will need:
- smoker and chisel;
- prepared clean, disinfected hives;
- frames with artificial foundation;
- a portable box for collecting infected frames taken from old hives;
- swarm for driving with fasting.
Types of transplant for infections
There are two types of haulage:
- the so-called double;
- with fasting.
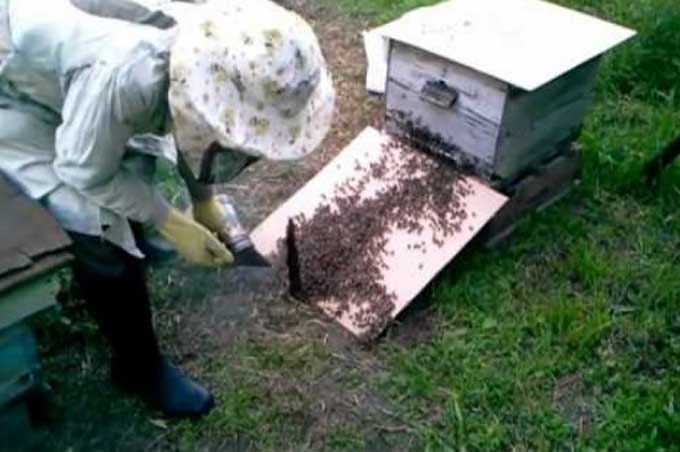
With a double run, the hive with a sick bee colony is removed from the place familiar to bees… Instead, a clean house is installed, in front of which a cover is placed – a kind of arrival board at the time of transfer.
Frames with artificial foundation are installed in the new hive. The cover, placed in front of the house, is covered with a piece of cloth or a sheet of blank paper. After that, insects are gently shaken off the infected honeycomb onto this attached platform. And then, with the help of smoke, they are directed in the right direction – to the tap hole.
After the procedure, the paper (fabric) is burned!
The entrance gap must be closed with a drone trap, that is, barred. This is done to prevent the rally or exit of the uterus. After a week, the distillation is repeated – hence the name of this method of combating diseases. At the same time, the queen bee is replaced by a young and productive one. Lattices are placed on the tap-holes.
Fasting distillation is performed using a swarm… The bees are shaken off onto the prepared surface and driven into the swarm. After that, she is carried away to a cool place for 2 days. At the end of the quarantine, the insects are shaken off into the prepared bee house.
Important points:
- Artificial foundation is issued at the rate of one frame per 300 grams of bees.
- Relocated nests are compulsorily reduced and insulated to prevent theft.
Medical feeding
While the resettled bee colonies are in quarantine, they are fed every 5-7 days until they are fully recovered. For preventive purposes, feeding is also given twice to all healthy families!
Feeding troughs are installed in the transplanted hives, into which feeding is poured at the rate of 200 ml for each street (the space between the frames is filled with adult insects).
The medicine is prepared like this:
- two parts of sugar are taken for part of water;
- the water is heated, after which granulated sugar is poured into it;
- with constant stirring, the mixture is brought to a boil;
- then the syrup is cooled to about 30-35 degrees;
- one of the following drugs is added to it;
- the mixture is thoroughly mixed again and poured into the feeders.
Here are the most commonly used veterinary drugs (based on 1 liter of syrup): “Sulfanthrol” (1-2 grams); “Norsulfazol sodium” (0,5-1 gram); “Tetracycline”, “Neomycin”, “Erythromycin”, “Oxytetracycline” (400 units); “Biomycin” (000 units).
Processing and disinfection
When it comes to the prevention and control of an infectious agent, the disinfection of equipment, the hive and all its components is carried out with the utmost care!
Keep in mind – honey extracted from an infected hive is absolutely safe for humans. Accordingly, it can be pumped out and used for food.
Disinfection procedure:
- The extracted combs are stored in a closed room, inaccessible to worker bees, before pumping out and processing the frames.
- After pumping out, the honeycombs are reheated in the usual way. The resulting wax can be exchanged for foundation or taken to collection points.
- Then all wooden parts of the house are cleaned with a chisel from adhered wax, propolis particles, traces of bee excrement. This garbage must be incinerated.
- After that, the entire hive and its constituent elements are processed with a blowtorch. Team . for this purpose, he uses a tourist gas cartridge intended for cooking in field conditions. It is convenient and accessible even during a nomadic journey.
- A small inventory, laps and a beekeeper’s suit must be boiled for 10-15 minutes in a solution of ash lye or soda with a strength of 0,5%.
Inventory, dry, foundation and the houses themselves must be additionally treated with a mixture of gases:
- one part of ethylene oxide (by weight) is taken;
- and 2,5 parts of metal bromide.
Mixture consumption per cubic meter: 3 kilograms. After processing, everything is covered with a polyamide film and kept at a temperature of at least 15 degrees in a dark room. The inventory is in this condition for up to 10 days.
After disinfection, weathering is carried out at the same air temperature. To eliminate odor:
- dry, foundation wears out for at least two weeks;
- and the inventory – about 10 days.
Rodent and damp control
Moving bees from one hive to another due to the penetration of mice or the appearance of traces of dampness is easier to carry out.
Resettlement procedure:
- A clean hive is placed on a stand behind the problem house. The remaining gap is covered with a canvas – insects should not accidentally break loose and fall on the cold spring ground.
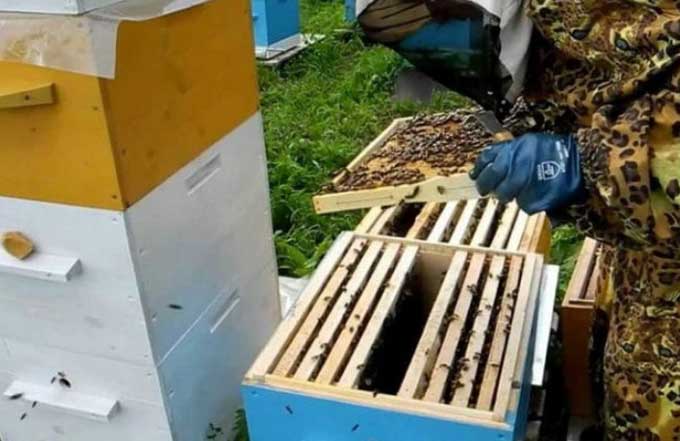
- Letkovye slots in the new house are tightly closed. A honey frame and a honeycomb for future brood are also placed here, pressing both frames against one of the side walls.
- Then the covers are removed from both hives. A little smoke is allowed into the problem house under the canvas. And they begin to transfer brood combs. They are immediately cleaned of adhering debris and obvious mold. This is done very quickly so as not to chill the young. And they clean it over the old nest – then the fallen adult bees will not die on the ground.
- If you need to remove the frame, the bees are swept from it into a clean house with a soft brush.
- After transplanting, the new nest is covered with a canvas. On the side of it, honey-beech frames warmed up at room temperature are installed at the rate of 8 kilograms of feed for a family of 3-5 honeycomb frames. Alternatively, you can install a four-liter feeder. The syrup will have to be added every 1,5-2 weeks.
- All bees remaining in the problem hive are carefully swept off the walls and shaken out into a new nest strictly on the frames under the canvas.
In order for the insects to move without problems, there must be transverse slats under the canvas!
Upon completion of the transplant, insulation is carried out using the upper and side mattresses, the lid is lowered. The holes open wide – the family must fly around, after which the gaps are reduced by two-thirds.
Honey can be pumped out of the discarded frames. Problematic honeycombs with traces of mold, which are too dark in color, twisted, deformed, are allowed to be melted. Dead insects are swept from the bottom together with the garbage and burned.
The problem hive is taken out of the apiary for disinfection and subsequent conservation. Letkovye slots should be closed tightly to avoid raids!
Once again about processing
Note: You can process the hive before planting the bees with a fire, using a gas can for tourists or a blowtorch (provided that this house has not previously contained sick insects).
All debris is preliminarily removed from it, propolis is purified as much as possible. The bottom and walls are washed with a rag dipped in a baking soda solution. This will prevent the beekeeper from breathing dust, possibly containing mite eggs or mold particles.
All prepared frames are also processed with a soda solution. They should not have traces of feces, adhered wax, propolis (especially in the area of the hanger – the dirt here makes it difficult to install the honeycomb in a new place).
Relocation to a different type of hive
Transplanting into a different type of hive is a more time-consuming process. Therefore, the most optimal period for this is the middle or second half of spring, depending on the region. The main thing is that the weather is warm.
When there are few adults in the nests, the work will be carried out promptly – hypothermia and bee theft are excluded.
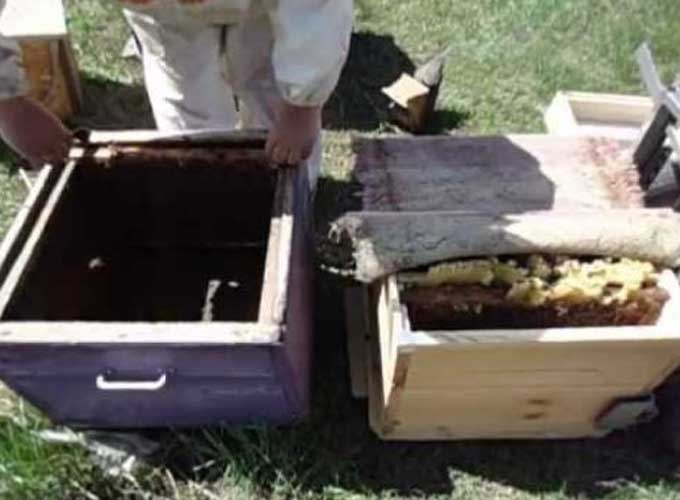
Only brood frames are transferred! The new house should be insulated, equipped with dry land and foundation. Insects are swept into it from all brood honeycombs (after each sweeping, the hive closes!)
Each freed frame must be cut in the workshop to the required size for the new bee dwelling. The honeycomb is additionally fastened with wires on both sides.
If the updated format is smaller, the brood honeycomb frame is cut so that it fills the new frame very tightly. Sometimes the combs are laid sideways, since the turning of the cells by 90 degrees does not prevent the young from emerging. This is much better than stitching together several cut pieces.
Note: all other frames are reduced not by cutting off empty cells, but by removing honey! And the remaining feed is positioned so that it adjoins the side bar. When placed on top, honey can crush the entire fragile structure (later the bees will “repair” new frames – the honeycomb will become reliable).
Please note that honey frames can only be repositioned if they are sealed and dark in color (that is, more durable)!
There is also one time-tested secret for stimulating the relocated colony. All trimmings with honey are given as a stimulating top dressing:
- they are placed in the lounger behind the shutter;
- and in multi-body structures – in an extension.
You can also feed the bee colonies 2 liters of syrup for 3-1,5 days, if there is no abundant natural bribe. The bees will like such a “treat” – they will willingly strengthen the new honeycomb frames and put the nest in proper order.
About air temperature
Compliance with the temperature regime is the key to a successful transplant of bee colonies.
In spring, work begins on fine days, when the air warms up during the day to at least +12 degrees. This is especially important when moving to a hive of a different format, which requires a lot of labor from the beekeeper.
In general, if it is necessary to relocate from one type of dwelling to another, it is better to wait for the period of active honey collection in order to avoid theft (the honeycomb frames have to be put out of the nest, which attracts other people’s bees). It is believed that the most ideal time to “solve the housing problem” is the time of flowering orchards.
With comfortable weather and temperatures, you can transplant bees into a clean hive without worrying too much about their condition.
Nucleus use
Transfer of bees to a new hive can be done using a nucleus. This is important when relocating nests from houses in which the honeycombs are built up with bends or criss-cross (for example, in logs or walls of houses, hollows of trees). The method is used not only in spring but also in summer.
The nucleus is formed:
- from two or three brood frames;
- from a new uterus;
- from adult bees.
A special shelf or stand is equipped on which the nucleus is placed. Its tap hole should be at right angles to the tap hole of the old house.
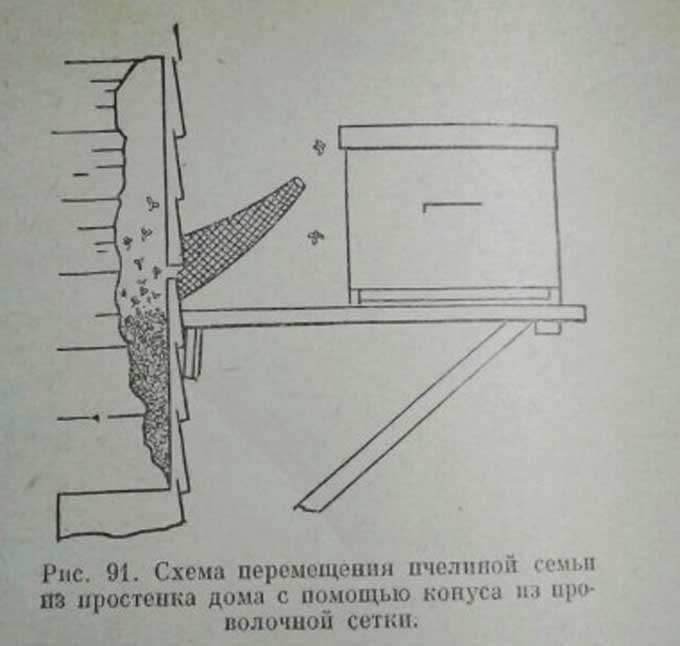
A cone is assembled from a mesh, which is attached with a wide end to the entrance of an old dwelling. The narrow end should have a small diameter suitable for the passage of only one insect.
Gradually, the whole family will gather in the nucleus. After that, the entrance gap is closed, and the new nest is transported to the place needed by the beekeeper. The old nest will be reduced to the limit by this time. If we are talking about the settlement of a swarm in the wall of a residential building, the bees remaining there can be killed with the help of cyanide.
Transfer from a box house
When relocating from a box (small plywood hive), you can follow this technique:
- The taphole is closed, the box is turned over and the bottom is removed from it.
- Immediately from above, a case is installed, filled with honeycomb frames or frames with artificial wax. All joints between the structural elements are carefully sealed – the bees must leave the hive exclusively through the entrance of the housing placed on top.
- Then the queen and the bees are forced to run upward – they tap on the sides of the old house. If possible, smoke a little.
- As soon as the uterus moves, a separating lattice is brought under the body, thereby keeping the “queen” in it. Within three weeks, the nest takes root in a new place.
- When young growth appears from below, the lattice is removed. Bees from the old hive are shaken out in front of the new one, which is installed on a standard bottom (the old honeycomb and part of the house is removed).
That’s all for the secrets of transplanting bees from one hive to another in the spring. Don’t forget about the optimal air temperature! Hypothermia destroys the brood.
Read about combining two nests into one and the reasons for such relocation here: When and why bees from different hives are combined