Oriental goat’s rue is a perennial plant from the legume family that is demanding on the quality of the soil. It is also known as the eastern galegi. It is a quality source of pollen and nectar for apiaries.
The content of the article
- 1 Agricultural value and description
- 2 Agrotechnics
- 3 Honey productivity
- 4 Useful Properties
Agricultural value and description
Goat’s rue honey plant used in agriculture as a fodder plant and an active reductant of atmospheric nitrogen molecules with their subsequent inclusion in the biomass of nodule bacteria (the so-called nitrogen fixer).
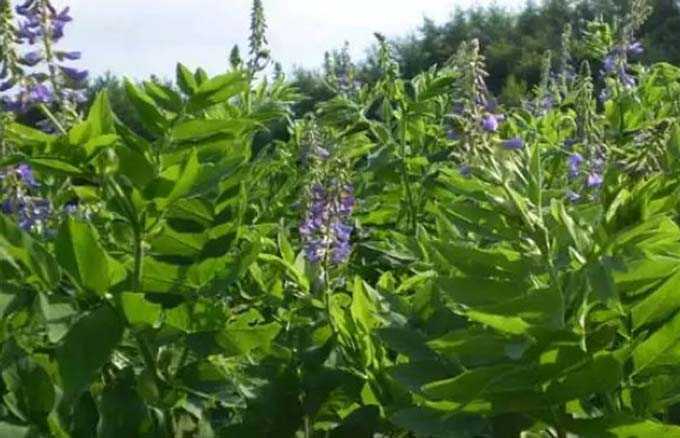
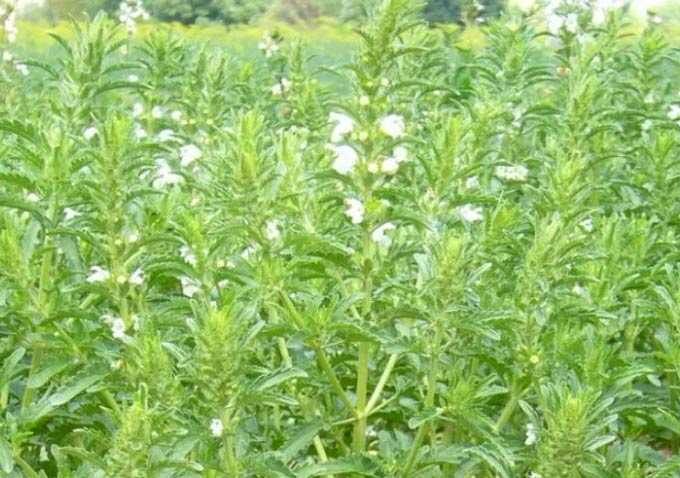
The grass is distinguished by high, erect, hollow stems, reaching a height of 1,5-2 meters. In the upper part, each of the stems branches into several branches covered with elongated pinnate leaves. The leaves are covered with fine hairs along the edges.
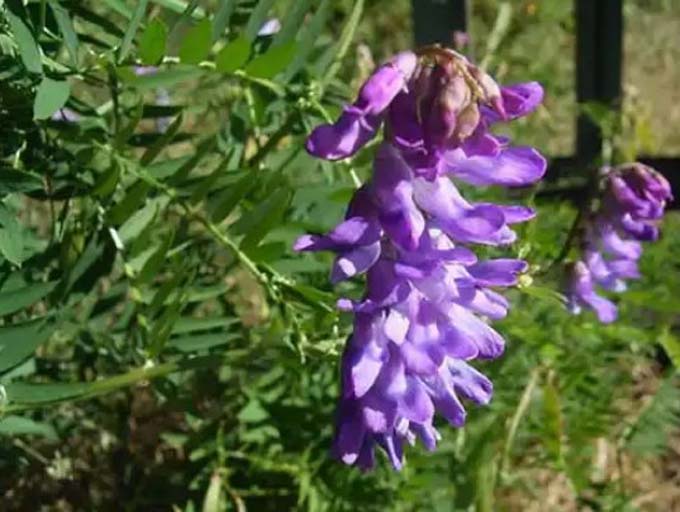
The number of inflorescences forming depends on the degree of development of the stem, and ranges from four to twenty pieces. Large purple moth-shaped flowers are collected in large brushes. A single flower blooms for 3-4 days, and the whole plant blooms within a month.
The grass is pollinated crosswise. Its nectaries are shallow – well accessible to bees of any breed.
At the end of flowering, small beans are formed, containing up to eight yellowish-yellow seeds. They are considerably larger than those of alfalfa or clover.
Agrotechnics
Grass goat’s rue as a honey plant can be cultivated on several types of soil. Chernozems, podzolic and calcareous soils, loams, clays, gray forest soils are suitable for her.
At the same time, acidic soils should be avoided, which impede the processes of nitrogen fixation and the correct development of the stems (the grass stand is weak in unfavorable conditions). The reaction of the medium should be close to neutral. Acidic soils are preliminarily limed!
The honey plant is sensitive to moisture – regular watering is required in arid regions or planting in an area suitable for the climate. Withstands short-term flooding, but does not tolerate swampy soils with high water occurrence.
For a successful sowing you need:
- pass dry seeds through a scarifier or seed grain;
- carry out inoculation (for this, bacteria that live exclusively on the tubers of this honey plant are used) or mix the seed with the soil on which the goat’s rue used to grow.
Embedding depth from 1 to 2 centimeters. Landing is carried out in rows with an inter-row distance of 45-70 centimeters. Sowing material consumption per hectare is 25-30 kilograms.
After the end of flowering, the green mass can not be removed from the site if it was not grown for livestock feed. The goat’s rue belongs to the green manure – it is used to enrich and improve the quality of the soil.
Honey productivity
Inflorescences bloom in the morning and release nectar until noon, attracting bees with a persistent aroma. Due to the convenient structure of flowers, bee colonies receive not only valuable pollen, but also nectar.
The goat’s rue is quite productive as a honey plant. The collection of honey per hectare of plantations is from 150 to 200 kilograms.
The flowering time from the end of May to the beginning of June allows obtaining pollen, which ensures the good development of bee colonies for the main summer honey harvest.
It is almost impossible to get monofloral honey from this herb! It always contains nectar collected from other spring honey plants.
Collected pollen is dark orange. Honey is light or dark yellow, depending on the impurities of other melliferous plants. With a delicate herbal aroma and rich taste.
Useful Properties
The medicinal properties of honey obtained from the goat’s rue are due to the substances that make up the herb. So the alkaloid galegin lowers blood sugar levels. Its main source is the green mass of the plant, but some part is present in pollen and nectar.
Nectar and flowers also contain 1,2 percent flavonoids, antioxidants that have antibacterial properties. In addition, they are saturated with mineral salts and vitamins that are important for humans.
In folk medicine, honey of this variety is recommended:
- to enhance immunity;
- as a tonic and anti-inflammatory agent;
- as a component of the diet for diabetes (consultation of the attending physician is required!);
- as a product that normalizes lactation in lactating women;
- as a diaphoretic for colds;
- as part of cosmetic masks and body wraps.
It is eaten with caution in case of individual intolerance. Testing is required – taking in the amount of a teaspoon, followed by monitoring the body’s response.