The gathering of bees in the autumn period is still a big mystery for both beekeepers and scientists. At first glance, there are no objective reasons for this phenomenon. This strange behavior is manifested mainly in strong colonies that do not show any signs of swarming. Having left the hive, the family, in fact, ceases to exist, that is, the gathering on the eve of wintering contradicts the basic bee instincts.
The content of the article
- 1 Signs of an autumn gathering
- 2 What is the cause of the anomaly
- 2.1 Poor honey harvest
- 2.2 Tick activity
- 2.3 Infections and viruses
- 2.4 Sugar syrup abuse
- 2.5 Bad uterus
- 2.6 Black honeycomb
- 2.7 Warm autumn
- 2.8 Influence padi
- 3 About the power of bee families
- 4 What to do
Signs of an autumn gathering
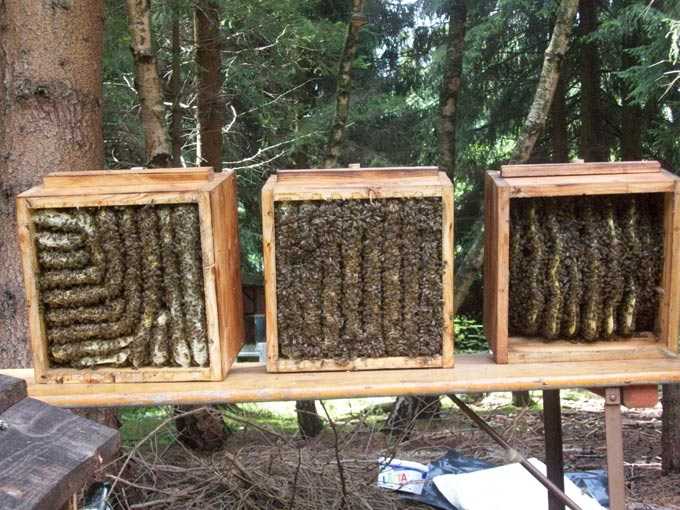
Bees leave the hive in the fall suddenly and most often unnoticed by the apiary owner – in the early morning. Sometimes several families fly away at once. Meetings of up to 70 percent of bee colonies from one point were recorded.
The following signs indicate an anomaly:
- the affected nests were fully prepared for wintering;
- after the departure of the family in the hive, there was practically no death;
- the established feeding frames are intact – in this case insects act in a completely different way than during traditional swarming;
- up to this point, there was no fatigue or any other symptoms of anxiety;
- neighboring hives do not react in any way to this behavior and calmly go into the winter;
- the analysis of the remaining dead disease does not record a single disease that is life-threatening to insects.
Bees leave the hive in autumn most often in early or mid-October, when the owner is fully confident in the health of all families and calmly prepares them for winter. Moreover, it is in the risk zone that there are strong promising nests.
What is the cause of the anomaly
An extremely comprehensive approach should be applied to the problem, taking into account all the conditions under which the rally occurs.
Usually, beekeepers look for the only cause of this difficult to explain phenomenon and cite it. The most common theories are:
- The flying insects suffered from melanosis or wing deformity virus.
- The autumn was too warm – there was a failure in the natural biology of the bee colony.
- In the hive there were low-quality combs – old, with deformed cells, not suitable for growing physically full-fledged individuals in the spring.
- A large percentage of honeydew, which in its composition and effect on the bee organism, is close to poison, has entered the fodder reserves.
- The uterus has grown decrepit due to the untimely change of the “queen”. For example, she is over two years old and unable to actively lay eggs.
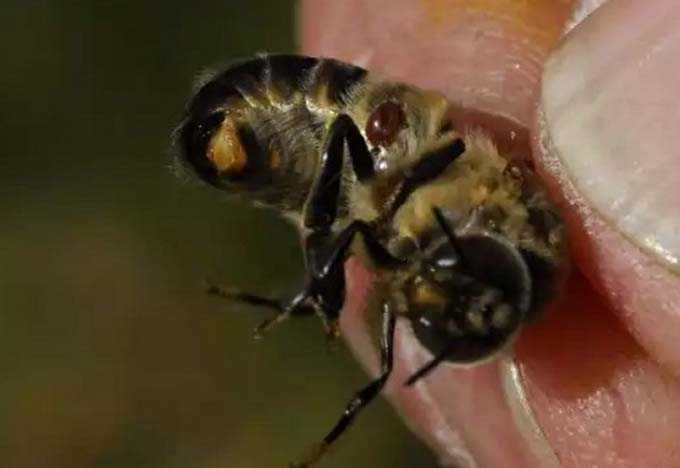
- A sharp increase in the population of Varroa mites in late summer and early autumn.
- Beekeeper abuse of sugar syrup and its delivery at the wrong time.
- Poor honey flow in the second half of summer – insects may not overwinter.
Let’s consider each of the above reasons in more detail in order to understand the mechanism of anomalous rally in all cases given as an example.
Poor honey harvest
Everyone knows that the biology of any bee colony is a complex self-regulating mechanism that depends on many factors. The food preferences of insects are directly related to the current season, as well as their age and the period of life of the bee colonies themselves. In summer, the natural food for honey bees is nectar and pollen.
A dry or bad summer leads to a sharp decrease in bribe. The bees are forced to switch to food that is unnatural for the season – honey collected earlier. And this, in turn, leads to a decrease or cessation of the laying of eggs by the uterus.
The activity of the bee colony immediately falls – the insects stop rebuilding the honeycomb. For another 21 days, the nest is replenished due to the remaining brood. But at the same time, the new generation is being grown in extreme conditions. Due to inadequate nutrition, insects are greatly weakened and, at best, live no longer than 40 days. Accordingly, by the end of summer, the nest noticeably loses its strength. Long-lived bees of the autumn generation will be completely absent or very few of them are found in the hive.
Such a bee colony is not viable – not ready for normal wintering, since it has lost the ability to regenerate and cannot build up strength. Around mid-October or early November, she commits an “act of suicide” – she leaves the hive on her own and dies.
All of these changes are almost invisible to the apiary owners! Only the disappearance of the printed brood three weeks after the beginning of the free period indicates the trouble.
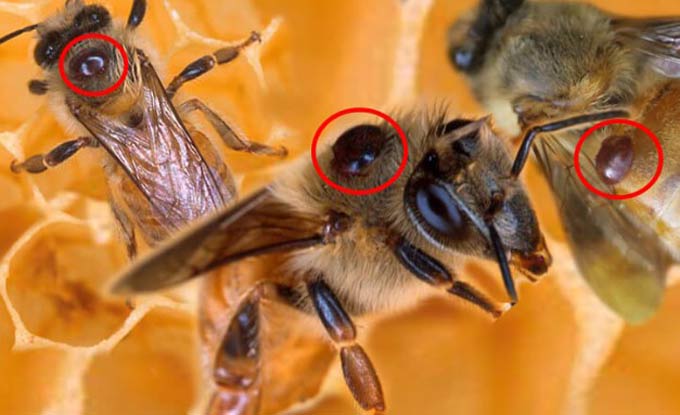
Tick activity
Anti-mite drugs are most effective at air temperatures of at least 15 degrees. However, beekeepers practice the processing of bee houses only after the entire brood has emerged.
This period (depending on the region) is from late September to early October. The ambient temperature ranges from negative values to +5 degrees. Therefore, anti-mite control has low efficiency.
Ticks fall from adult bees, having already drunk a sufficient amount of hemolymph and thereby weakening future brood breeders.
It should also be borne in mind that ticks have several generations. And the last one appears at the beginning of autumn. With the onset of the first cold weather, young mites are taken between the segments of the partitions of the bee abdomen, where it is impossible to get them with any drugs during the processing of the hive.
In bee colonies that have been mowed since spring, the development of parasites occurs so rapidly that no drugs are able to help them at the end of the warm season.
The result is the same – the bees leave their hives. Moreover, in standard designs without pallets, it is impossible to establish the true reason for the rally – there is no way to count the number of crumbling ticks.
Infections and viruses
Viral infections are still not well understood. If virosis occurs in a latent form, it is extremely difficult to diagnose it.
Diseases that can affect the viability of bee colonies and lead to their rally include:
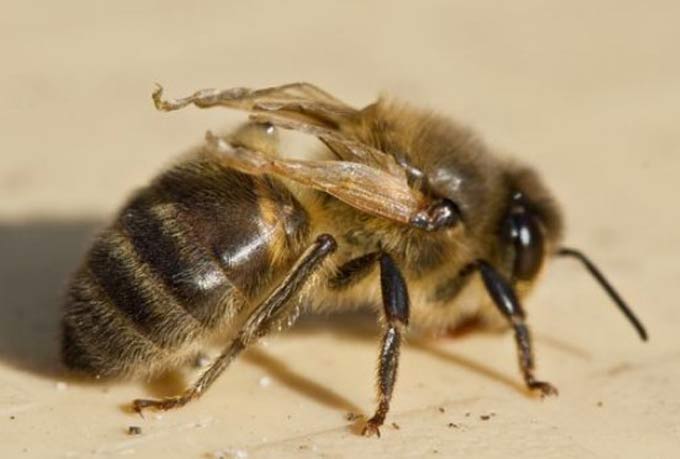
Wing warp virusdeveloping in dry summers. By autumn, the affected insects die en masse. For this reason, the gathering is indicated by the bodies of dead bees with characteristic signs of infection, which can be found near the hives. The wing deformity virus accounts for up to 30 percent of all cases of rally.
Melanosis, affecting queens, bees and drones, secretly flowing in the summer. With a change in the weather, the disease progresses.
The so-called “genetic lethality” – poorly studied brood disease caused by closely related breeding of honey bees. Affected brood does not differ in appearance from a healthy one, but at the same time it occupies from 30 to 70 percent of all cells. A genetic malfunction can be detected only when the lid is opened – a deformed larva is in the cell, filled with a white, opaque, odorless liquid. A problem family can be identified by poor performance during honey collection and the absence of young bees in the second half of the active season.
Sugar syrup abuse
By itself, the processing of bulk portions of syrup does not in any way affect the life span of insects. But here it is important to consider that an adequate supply of pollen is critical.
The timing of feeding is also important. The honey made from the syrup must mature and be sealed in time. That is, a lot depends on the air temperature and the presence of pollen in nature.
In addition, insects from the fall generation may begin to secrete wax. Due to the lack of pollen, the wax glands work at the expense of fat reserves intended for wintering. The bees become very weak and die immediately after the processing of the sugar syrup is completed.
It follows from this that it is impossible to feed bee nests from the end of September, when the plants are no longer blooming. Otherwise, the insects will use up most of the reserve substances stored for the winter, and then fly off.
The recommended timing for dispensing syrup in the middle lane is no later than the third decade of August! In this case, large doses are considered to be up to twenty liters per family.
The golden rule of any beekeeper: feed the nests exclusively in the warm season, when the pharyngeal glands of insects are still able to work actively and enrich the feeding with all the necessary enzymes.
Bad uterus
“Queen” is the center of the bee hive, providing balance and harmonious development of the family. The cessation of oviposition is always accompanied by a decrease in the amount of uterine substance. And this is a kind of signal of trouble, invariably leading to a shift in the balance in favor of adult bees:
- Workers are gradually turning into tinderpots, since they cannot lay queen cells due to the lack of full-fledged eggs and young larvae.
- A confrontation between the tinderpots and the inferior “queen” begins. The uterus is expelled or destroyed. But even her presence in the hive does not save from the gathering – some of the bees die, the other joins the bee colonies with young queens.
Timely change of old “queens” is a highly effective method of dealing with tinder fungus, varroatosis and abnormal gatherings.
Strong arguments in favor of this:
- Termination of masonry two weeks ahead of schedule. Observed at the “queens” at the age of two years.
- Significant reduction in egg-laying volumes. In the third year of life, the uterus, after the main honey collection, will lay 2,5 times fewer eggs than the first year.
- Decrease in the amount of excreted uterine substance with age.
- Reduction of bees hatched by a family and an increase in the number of drones as the queen ages.
Black honeycomb
Low-quality old honeycombs are small in size. The larva in a too tight cell develops into a small and short individual – a gradual degeneration occurs.
Population conservation is at the heart of the honeybee’s biology. The queen is always trying to sow on new clean land. A hive in which there is no way to grow a full-fledged generation has no value in the eyes of insects. They have a natural disgust for such a house.
The presence of blackened honeycombs is one of the factors that, together with other reasons, can provoke a rally.
Warm autumn
The abnormally warm autumn weather in the middle lane means daytime air temperatures in September from +20 to +30 degrees.
Insects actively fly, consume all reserve substances harvested in the body and wear out quickly. As a rule, there is no natural bribe for this period in nature. As a result, families become weaker, there is a massive death of adults. A rally may occur.
Influence padi
Dry summers are always an increased risk of an increase in honeydew (low-quality honey) in nature. The lack of flowering plants makes flying bees look for other sources of bribe.
Even in the summer, honeydew honey is the worst food. This feed contains a lot of mineral salts, nitrogenous impurities and dextrins. When it is absorbed, bees develop toxicosis, accompanied by severe diarrhea.
The negative impact of honeydew honey is manifested in the violation of oviposition, a decrease in life expectancy and a gradual weakening of the nest.
About the power of bee families
First of all, I would like to note that bee colonies fly off, in which there were many adults by September. This is not the same as the power of the nest in the classical sense.
Unfortunately, the bees have no identifier. By eye, the beekeeper cannot determine who exactly fills the hive – the autumn or summer generation, which will soon cease to exist naturally.
Signs of a rally of such a supposedly strong bee colony:
- lack of submergence;
- untouched feed stocks;
- sometimes the queen is surrounded by a small number of bees.
A really strong nest dies due to the abundant summer harvest of pollen and nectar, especially if the insects are working on sunflowers.… A lot of honey was brought in such a hive. In this case, it only seems to the beekeeper that the bee colonies have flown away. In fact, the autumn brood did not cover the number of naturally leaving female workers. The colonies weakened and died by the fall.
What to do
To prevent a rally, you must take the following measures:
- Immediately after the end of the bribe (no later than two to three days), all nests are fed with 50% sugar syrup… The amount of feeding is calculated based on the weight of the insects. For example, about 20 kilograms of bees sit on 435 frames measuring 300 x 5 mm. They will need one tenth of their own weight of syrup, that is, 500 ml.
- If the bribe has stopped by the first decade of August, marketable honey is pumped out, extra frames are removed, tick strips are installed, syrup is fed every other day based on the assumption that by the beginning of autumn in each hive there should be at least 20 kg of honey. The production takes place in a 1: 1 ratio, that is, for every kilogram of honey, a kilogram of sugar is needed (not syrup!).
- In the second half of the active season, all low-producing uterus change.… By the beginning of next spring, they will enter the peak of egg production (at 7-8 months of life).
- Black and dark brown combs are removed from the hives immediately after the honey is pumped out..
- Tick containment activities are carried out throughout the season… The use of various aromatic substances is best suited for this purpose. Fifteen drops of aromatic oils are dripped onto a piece of fiberboard (for example, an extract from mint, eucalyptus leaves, fir is suitable). After that, the plank is laid over the frames, strictly in the center of the nest. After two days, the aroma changes. Herbs that emit a strong smell are also suitable: bunches of peppermint, thyme, calendula flowers, tansy, wormwood twigs, stems of homemade tomatoes.
All of the above measures give a complex effect, which allows avoiding not only the autumn gathering, but also the hard-to-explain weakening of bee nests during wintering.
Also, do not forget the common truth: the best preventive measure is the breeding of strong bee colonies.