The climate in most of Russia is characterized by short, hot, dry summers and long cold winters. But sometimes you really want young shoots to please you all year round. A winter garden or a greenhouse can help with this. And if there is no room in the apartment, then even an unheated balcony can be mastered. And the easiest way to do this is with a growbox.
Growing box heating
In order to grow plants in a grow box in winter, it will have to be well insulated, while simultaneously solving a number of very important tasks:
- create a sealed enclosure;
- choose the best thermal insulation material;
- choose a reflective material (it is needed to increase the effect of lighting lamps);
In addition, it is necessary to work out the irrigation and humidification system. On the one hand, the heating system contributes to overdrying the air, on the other hand, due to the complete tightness, the problem of root sticking and the formation of mold can arise.
As for the root system, when organizing heating in the greenhouse, overheating of the roots should not be allowed (for example, if a “warm floor” system is used). In the event of a sharp rise in temperature, you must immediately turn on the ventilation.
It is unacceptable to heat the growbox with a radiator from the inside or install convectors near the greenhouse.
These devices burn out oxygen and dry the air. Also, when using them, a sharp temperature drop is created: the farther from the heater, the colder. Radiators pose a risk of overheating the plants.
Some budding growers try to heat their greenhouse with light bulbs. With proper thermal insulation, the heat emitted by some types of lamps is quite enough, but the organization of this heating method is associated with other difficulties. In particular, the heating system has not been worked out at night when the lamps should be turned off. And in winter, such long breaks in heating can lead to disastrous results.
In addition, when using HPS or DRI lamps, you will need to install systems for regulating the start of the lamp (ECG / EMPRA) and removing excess heat.
It is best to carry out heating with an infrared heating film, the heat from which is evenly distributed throughout the space.
Such a film is relatively inexpensive, but it gives the maximum effect in the winter.
Thermal insulation
The most common material for insulating grow boxes is extruded polystyrene foam. Most often, sheets with a thickness of 20-25 mm are used. The box is sheathed with insulation from the inside, the joints are worked out with sealants.
Reflective material
The reflective surface amplifies the illumination several times and allows you to create a unique microclimate in the box. Most often, lavsan, foam sheets or special reflective paint are used as reflective surfaces. You can also install mirrors or sheathe the box with plain baking foil. The latter option is the cheapest and at the same time quite fireproof.
Humidity level
You can measure the moisture content in the air using a hygrometer (in winter, it is better to use models with a remote sensor).
The humidity level in winter should be the same as in summer.
At the beginning of germination of seedlings 80%, during active growth 70-75% and for adult seedlings about 50%.
Raise or increase the level of humidity with specialized humidifiers. In small boxes, it is permissible to use an artisanal method of humidification: containers with water, placed in the corners of the greenhouse.
Correct temperature regime
The comfort temperature is between 22 ° C and 27 ° C. During germination and active growth, the temperature must be kept at higher levels. As the seedlings grow, the thermometer can be lowered to the lower value.
You can regulate the temperature regime using ventilation. For the winter period, duct ventilation systems are used that allow mixing cold and warm air, preventing temperature extremes.
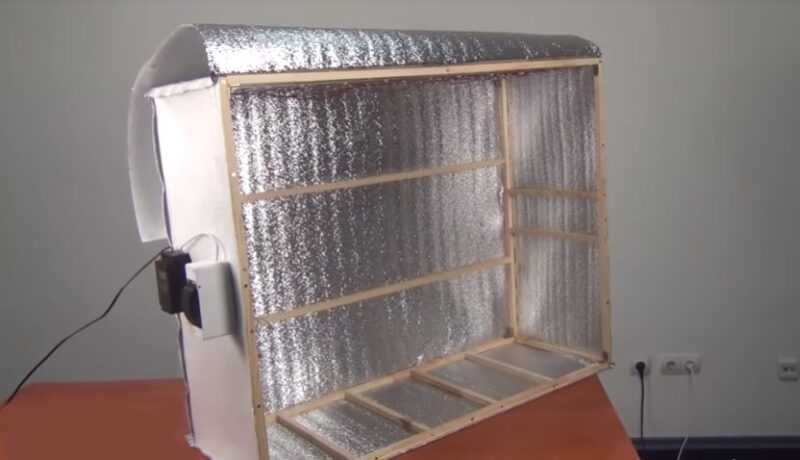
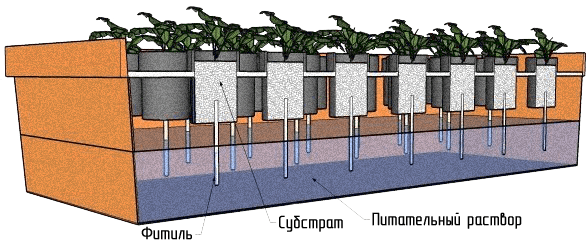
How to assemble a winter growbox?
The answer to this question is quite simple. Winter models differ from summer ones by the presence of insulation, which is used to sheathe the walls of the box from the inside.
Step-by-step instructions for assembling a winter grow box:
- Find the right size.
Before you start looking for schemes, you need to decide on the size of the future greenhouse. The standard version measures approximately 1 meter wide, 1 meter deep and 2 meters high. This option is ideal for growing tall varieties. For undersized flowers or small-sized exotic plants, you can build more compact models. Most often, a growbox is equipped in spent refrigerators or old cabinets.
- Organization of thermal insulation and heating
After the base of the future boxing has been chosen, it is sheathed with heat-insulating material. A heating part must be present in the winter configuration. If infrared film is chosen, it is mounted on top of the insulation, slightly rounding the corners. It is important to remember that you cannot bend the film at a right angle. The finished structure is covered with a reflective material.
- Installation of equipment
Then the grow box is supplemented with a lighting and ventilation system. It is better to think over and lay openings for duct ventilation at the initial stage. Then filters are installed, as a rule, for winter greenhouses these are coal models. And only then can shelves, pots, temperature sensors and humidifiers be installed. If possible, an automatic irrigation system can be installed in the grow box.
If all technical requirements are met in the grow box in winter, the temperature necessary for the growth of seedlings will always be maintained. And thanks to the ventilation system, excess heat will also heat the room in which the box is installed.