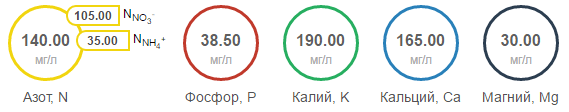
One of the most important conditions for making a good nutrient solution is choosing the right dose of nitrogen. Nitrogen is available to plants in two forms – in the form of nitrate ion (NO3–) or ammonium ion (NH4+). Nitrate ions are found in potassium nitrate, calcium and sodium. The latter salt should not be used as the only nitrogen source. It is best used as a supplement to other nitrogen salts. Sodium that is not absorbed by plants gradually accumulates in the solution and increases its alkalinity.
Ammonia nitrogen is found in ammonium sulfate and nitrate. For some unknown reason, ammonium nitrate does not grow well and therefore does not need to be included in nutritional mixes. Ammonia nitrogen is very easily absorbed by plants. Too high concentrations of it cause wild plant growth. Ammonia nitrogen should be no more than 25% of the total amount of nitrogen in the solution.
Carbamide (urea) is also considered a source of nitrogen.
In industrial hydroponicums, solutions are prepared in large quantities and each compound is added to the tank separately. Under these conditions, calcium nitrate is the best source of nitrogen and soluble calcium. However, retail packaged calcium nitrate is quite expensive. Moreover, it persists very poorly. If there are few pallets, purchased calcium nitrate should be used quickly. In small farms, it is better to use affordable and cheap potassium nitrate, but at the same time other sources of nitrogen must also be used, because potassium nitrate contains almost three times more potassium than nitrogen.
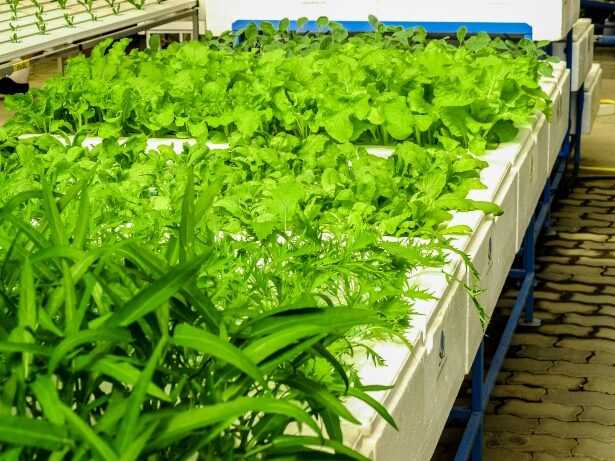
Nitrogen is needed to build leaf tissue. Vegetables such as lettuce, kale and spinach require nutrient solutions with a high percentage of nitrogen. However, an excess of nitrogen inhibits the development of flowers and fruits. Nitrogen is required for the formation of plant cell protoplasm. It plays an important role in all plant growth processes. Nitrogen is also required for the formation of chlorophyll. Lack of nitrogen quickly manifests itself in the form of a pale green color of the leaves.
Examples of nitrogen deficiency symptoms
From left to right: nitrogen deficiency in barley, cabbage, corn, cotton, legumes, wheat,.





Sources of
- IPNI Crop Nutrient Deficiency Image Collection.