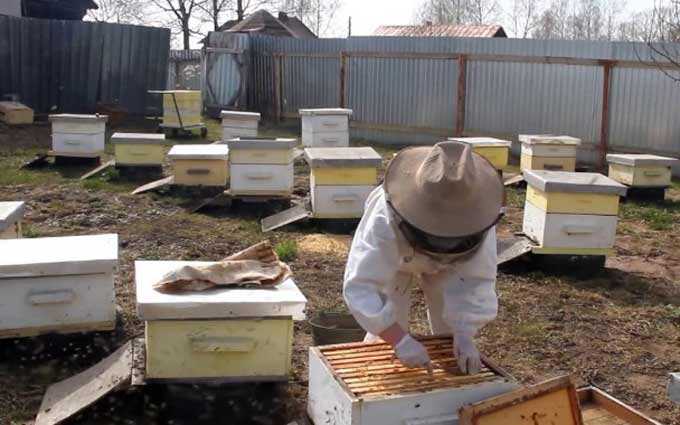
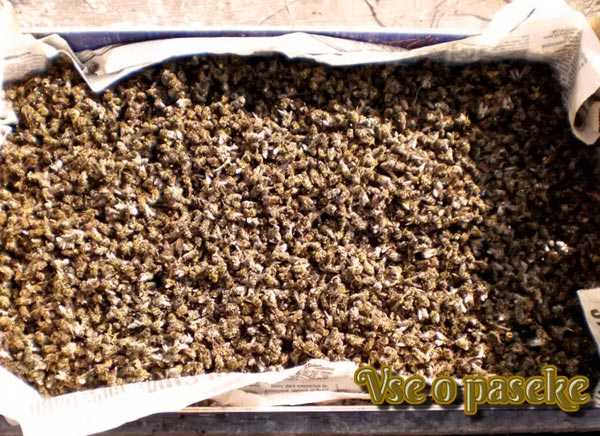
Bee packages are a great way to quickly expand your apiary in the spring. A package means a light plywood box in which bee layering is sent by mail.
In the CIS countries, two types of packets are sent: with and without cells. We will tell you more about the peculiarities of the development of the bee package after its transplantation into the hive.
The content of the article
- 1 What the package looks like
- 2 How much foundation is required
- 3 Features of the content
- 3.1 When and how to feed
What the package looks like
Depending on the configuration, the layering can be sent:
In plywood parallelepipeds (boxes measuring 430 x 155 x 250 mm) containing bees without frames. Such a package weighs up to 15 kilograms. The box has two holes for the feeder and the cage with the uterus. The loaded feed is enough for ten days.
In fiberboard boxes for 4 or 6 frames. There are brown honeycombs inside that can withstand transportation. Light frames are not used – they easily wrinkle and break off when shaken. The four-frame bag is formed from two feed and two brood combs. The size of the box is 475 by 200 by 390 millimeters. The six-frame package has a length of 475, a width of 290 and a height of 390 millimeters.
How much foundation is required
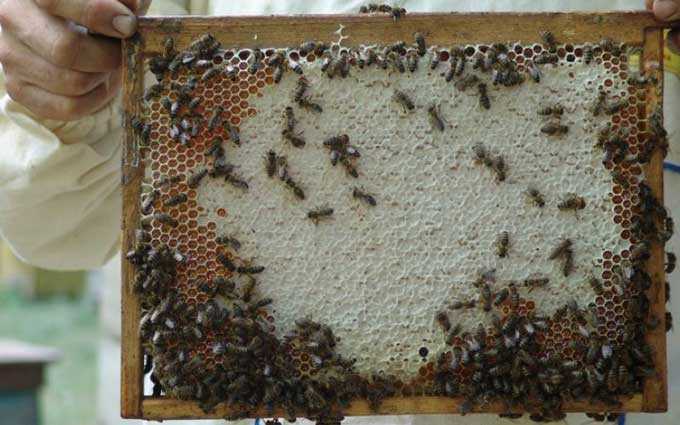
In the hives intended for the relocation of bee packages, 4-5 ready-made honeycombs and 2-3 frames with foundation should be installed.
In the future, the nest, as it develops, gradually expands due to the frames with honeycombs and artificial foundation.
Also, a one-time expansion has proven itself quite well, in which a 12-frame hive is completely filled with foundation.
When completing nests, it is recommended to adhere to the following algorithm:
- a full-copper frame is installed at the side wall;
- then honeycomb and foundation alternate;
- the seventh in a row is the aft low-copper frame – it serves to limit the nest;
- before the honey harvest, when there are up to 9 brood frames in the hive, a store filled with honeycomb frames and foundation is installed on top.
This technology allows insects to prepare well for honey harvest, that is, to stock up on fresh combs in sufficient quantities for storing the collected feed.
The amount of foundation substituted for the entire time will directly depend on the design of the hive and the rate of development of the bee colony (its strength).
Note: When expanding the nests, the entrances open completely, as families need additional ventilation! With increasing strength, they are already able to protect themselves from the thief bees.
Features of the content
After the transplant, the so-called critical period begins in the life of the bee colony. It lasts on average up to three weeks.
The criticality of the situation is expressed in the imbalance between the number of adults and young animals. Many packet bees die when the larvae hatch. This imbalance in the family can lead to a quiet change of “queen”.
To avoid this, it is necessary, 14 days after transplanting, to strengthen the nest by means of brood printing combs, in which the young are already at the exit. Such frames are taken from strong and healthy nests in the apiary. And they are placed next to the extreme brood frames of the packages. This technique allows you to quickly build up the strength of bee packs.
Note: The longer the period before the main trickle, the more the power of new nests increases. For this reason, in the North, packaged families provide a good collection of honey in the very first season.
In other climatic conditions, bee colonies can be quickly strengthened by transplanting them onto ready-made honeycomb frames with abundant supplies of pollen and honey.
The main reasons for poor package development are:
- too frequent examinations;
- bad uterus;
- infection of the “queen” with nosematosis – for its prevention, the family must be fed with syrup with the addition of “Fumidil B” or another drug.
The problem with poorly sowing queens can be solved by using nuclei with fetal “queens” already available in the apiary. In general, it is recommended to have cores at every point. This helps to avoid interruption in brood rearing, and also allows you to change queens or effectively deal with their loss.
When and how to feed
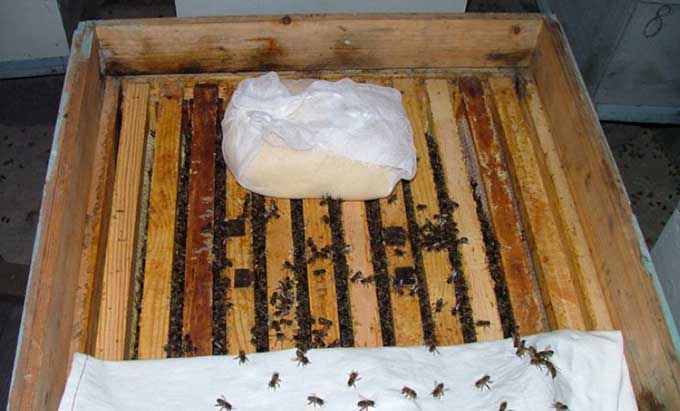
When transplanting to honeycomb frames without pollen or to frames with artificial foundation, pollen or its substitute must be added to the top dressing until a rich pollen flow is discovered in nature.
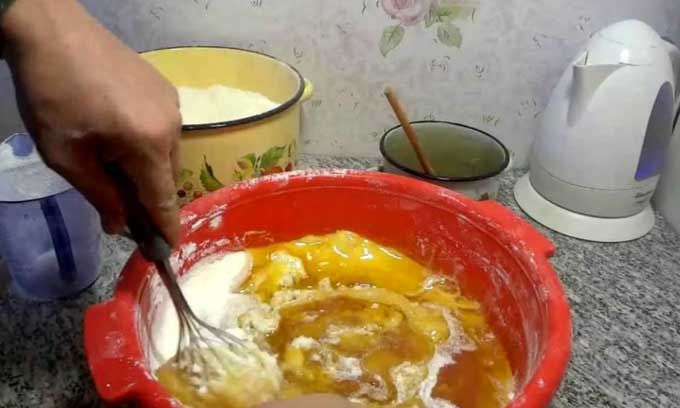
Here is one of the recipes for pollen substitute that came to us from the United States:
- For 3 parts of brewer’s yeast, six parts of finely ground soy flour are taken.
- The components are thoroughly mixed and moistened with 50% sugar syrup.
- A thick, soft paste is kneaded, from which cakes are formed.
- Top dressing is laid out in the hives on the upper bars of the honeycomb frames every 10 days until the insects willingly take it.
It is also allowed to issue honey-sugar cakes. They are prepared from honey and powdered sugar in a ratio of one to four.
When a pollen flow appears, feeding with a substitute is stopped completely!
To stimulate egg-laying, a common feeder is equipped under a canopy. 50% sugar syrup is poured here daily at the rate of 300 grams per bag.
For every 4,5 kg of stimulating feeding, you can add a quarter teaspoon of Sulfathiazole powder soluble in water. It is a good preventive measure against diseases of batch bees.
Note: During transplantation, up to 10% of the queens leave. For this reason, the packages must be checked on the 5th day in order to determine the quality of work of the “queen” and its presence in the nest for fresh egg-laying.