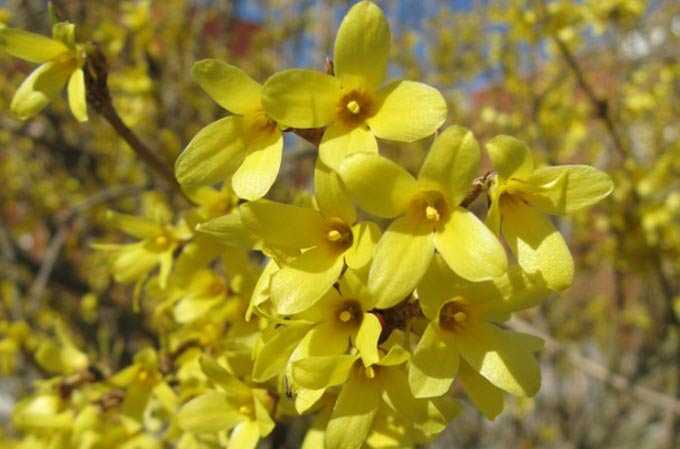
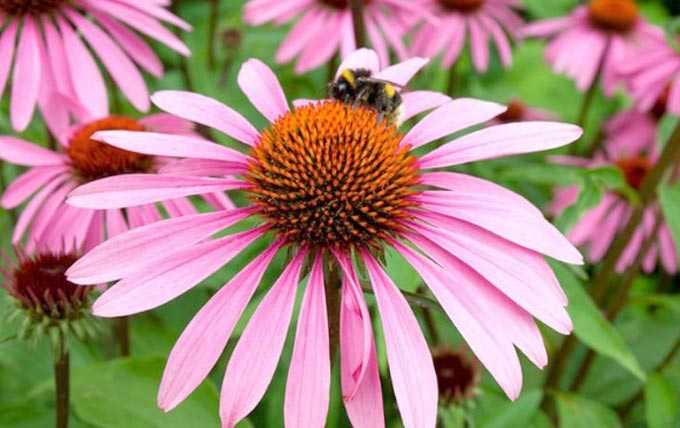
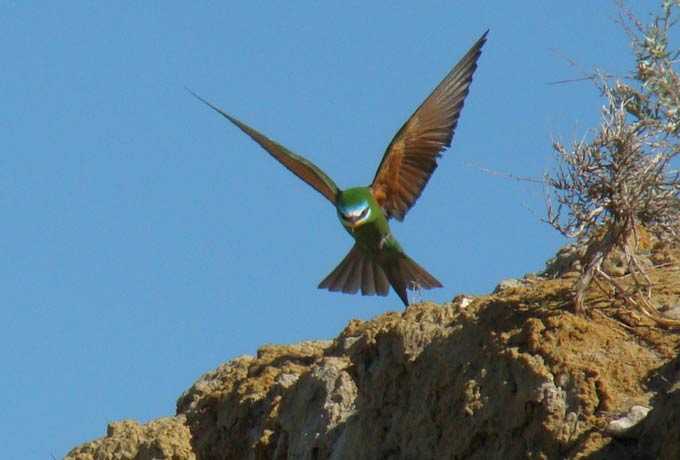
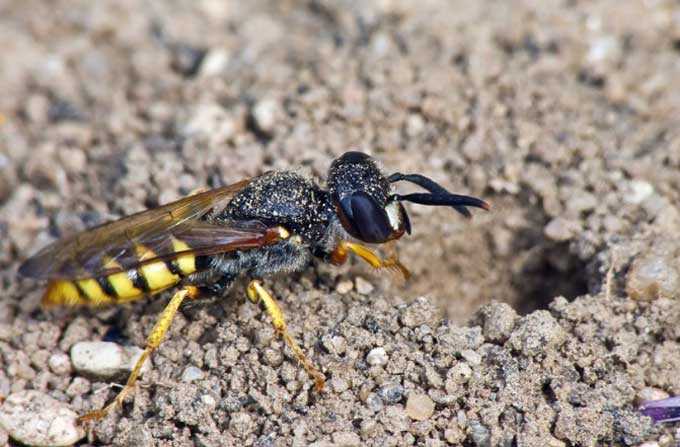
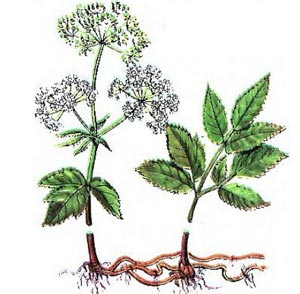
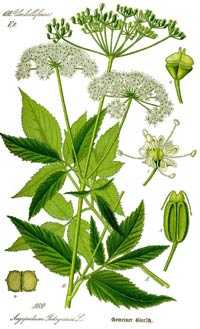
The herb honey is a plant that produces enough nectar and pollen for bees to collect. Herbaceous species do not have a tree trunk. At the end of the growing season, their entire ground part, consisting of leaves and stems, dies off. In spring, grasses grow back from overwintered roots or sprout from seeds.
The content of the article
- 1 Classification
- 2 Herbaceous forest vegetation
- 2.1 Forest pollen
- 2.2 Poisonous herbs of the forests
- 2.3 Minor honey plants of forests
- 3 Grassy vegetation of meadows
- 3.1 The most honey-producing species
- 3.2 Secondary honey plants
- 3.3 Pollen
- 4 Grassy vegetation of hayfields and pastures
- 4.1 Secondary honey plants and pollen plants
- 5 Herbaceous vegetation of swamps and reservoirs
- 5.1 Pollen
- 5.2 Secondary honey plants
- 6 Herbaceous vegetation of deserts and semi-deserts
- 6.1 Secondary honey plants and pollen plants
- 7 Herbaceous vegetation of fields (agricultural land)
- 7.1 Secondary honey plants and pollen plants
Classification
Distinguish between herbaceous annuals, biennials and perennials. Annuals live for a year. In biennials, flowering with the release of pollen and nectar is observed in the second season. Perennials grow in one place for three or more years.
The long-liver record holder can be called pierced-leaved sylphia. This herbaceous honey plant lives in one place for up to 45 years.
Read: Sylphia pierced-leaved as a melliferous plant
All herbs are conventionally divided into large groups, formed according to the place (area) of growth of certain species.
There is:
- forest;
- meadow;
- field;
- wetland;
- desert;
- pasture grasses.
On pastures and hayfields, grass is grown for livestock or hay production. Accordingly, the honey base in such an area may be weak – the grass will be mowed before budding or it will be eaten by livestock.
Alpine meadows are also not fully used. Due to the inaccessibility of honey plants, apiaries are rarely taken out here.
Herbaceous forest vegetation
There are forest herbs known for their high nectar productivity. Such species are extremely valuable for apiaries. They are listed below.
Siberian Hogweed – a powerful herb with small leaves and white multi-rayed inflorescences. It blooms in summer, in June-August, releasing from 180 to 200 kilograms of nectar per hectare of dense thickets.
You can read about its differences from poisonous species here: Hogweed as a honey plant
Forest angelica (angelica) – a perennial growing everywhere, including in meadow forbs. Blooms in the middle of summer. Up to 350 kilograms of honey can be obtained from this herb.
About other varieties of angelica: Angelica as a honey plant
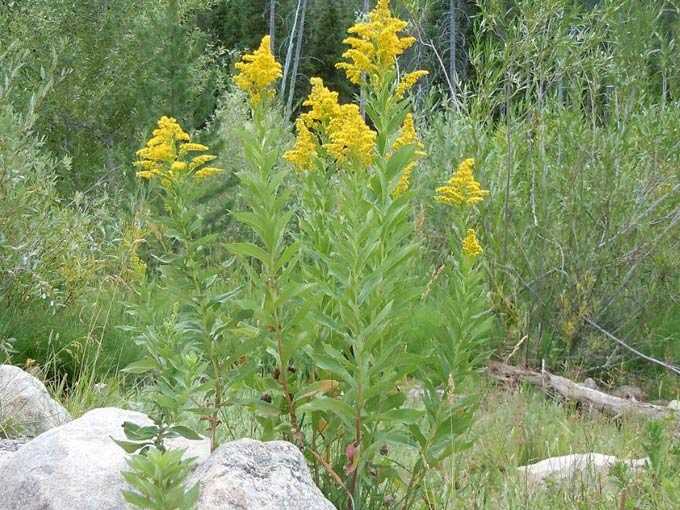
Common goldenrod (popularly “golden rod”) is distributed throughout the northern hemisphere. It is valued as a late summer honey plant, which provides the preparation of bee colonies for wintering. Average nectar productivity is 150 kilograms.
Read: Goldenrod as a honey plant
Ivan tea or cypress – an inhabitant of forest clearings, growing in one place from three to fifteen years. This is a summer honey plant with excellent indicators of nectar productivity – up to 300 kilograms of honey is collected from a hectare of thickets in a favorable year.
Read: Fireweed as a honey plant
Forest Kupyr – tall grass with pinnately dissected leaves, white umbrellas of inflorescences. It is found in the west of Siberia and throughout the non-chernozem zone. Blooms in early June, releasing nectar until autumn. Average nectar productivity is 180 kg.
Common Sweet – an inhabitant of the non-chernozem belt, blooming from the beginning of summer. Bees collect up to 160 kilograms of nectar from a hectare of dense herbage. In the western regions of Siberia, this figure is higher – up to 190 kg (here the grass acts as the main summer melliferous plant).
Read: Sleep like a honey plant
Ural ribcarp found in the Urals, Siberia and the European part. It is included in the herbaceous cover of coniferous and birch-aspen forests. The grass has tall, bare stems topped with large white umbrellas. Blooms in June. It is considered a secondary melliferous plant, but the bribe from it in favorable years reaches 180 kg.
Marsh purse – perennial with erect stems and crimson axillary flowers. It is found not only in birch forests, but also in meadows, fields (here it plays the role of a weed). July honey plant, blooming for 20-25 days. Nectar productivity from 160 to 200 kg.
Forest pollen
There are herbs that predominantly emit pollen. The nectar from them is not brought by bees, or it is harvested in insignificant quantities that have no commercial value for the apiary.
It:
Anemone – early flowering perennial, common in many regions. There are several varieties of it, readily visited by flight bees. Altai variety blooms in April, May for two weeks. It grows in coniferous forests of the European part and in Eastern Siberia, as well as in alpine meadows. The Amur variety blooms in March, April. It is an inhabitant of mixed forests. Anemone is found in deciduous forests of the European part. Blooms from the third decade of April to mid-May.
Nakay – one of the varieties of goose onions, blooming in March, April for two to three weeks. Grows in deciduous and cedar-deciduous forests. The plant has a long basal leaf and pale yellow flowers. Pollen extraction – up to 16 mg per plant.
Jeffersonia is doubtful – a perennial growing in mixed forests. Differs in large pale lilac flowers on peduncles bare from leaves. Blooms in late April, early May. Bees willingly collect small pale yellow pollen from this grass.
Kandyk the Siberian grows mainly west of the Yenisei: in Altai, in southern Siberia. Differs in red-brown color of leaves and beautiful lilac flowers with petals bent upwards. It dissolves immediately after the snow cover melts. In addition to the abundant release of pollen, it provides apiaries with a bribe of up to 45 kilograms per hectare of grass stand.
Creeping cinquefoil – an inhabitant of not only forests, but also meadows. This perennial has small yellow flowers that bloom in April and May. The edging is also yellow. The release of pollen lasts 40-45 days.
Ussuri buttercup – inhabitant of deciduous and mixed forests. Its large yellow flowers bloom in late April and early May. The release of pollen is noticeably higher than nectar – up to 9,3 mg from each flower.
Violet hill – perennial with purple or pale blue flowers, growing in mixed and deciduous forests. Blooms in April for two weeks, exuding abundant pollen (0,9 mg per flower).
Crested crested – biennial with slightly pink drooping flowers, grouped in the upper racemes. Blooms in April, May. It is more appreciated as a pollen. Up to 15-20 mg of pollen is released from one plant per season.
Poisonous herbs of the forests
Some herbaceous plants are dangerous to bees, and the collected nectar is poisonous to humans.
Aconite or “fighter” – an inhabitant of humid places, resembling lupine in appearance. It also has purple cluster inflorescences, but they are grouped less compactly. Blooms in the second half of summer. Bees that visit the flowers die during the flight and in the hives. Insects have convulsions – they crawl along the bottom and in front of the entrance. First aid consists in transferring the affected individuals to a warm place and sprinkling them with sugar syrup.
Larkspur or “spur”, “delphinium” also grows in wet areas of the forest. Occurs in taiga and forest-steppe. The grass has sparse bright blue clusters of inflorescences with elongated yellow stamens. Blooms in the second half of summer. The collected honey is dangerous not only for bees, but also for humans. Help for insects is provided immediately after poisoning (syrup treatment, transfer to a warm place).
Minor honey plants of forests
Other herbs of honey plants (photos and names, honey productivity):
Saxifragous thigh – an inhabitant of a temperate climatic zone with feathery leaves and complex umbrellas of inflorescences. Blooms from June to August. Secondary honey plant.
Thimbus Curls grows in non-chernozem areas. Differs in a curly stem, ovate leaves with a strong odor, violet-blue axillary flowers. Blooms in May, June. Nectar productivity from 14 to 19 kg.
Mountain bug – a tall annual with a strongly branching stem, lanceolate leaves and blue-violet apical inflorescences, collected from small flowers. Blooms in June, releasing nectar until August. Secondary honey plant.
Medicinal capital letter – perennial with oblong slightly pubescent leaves and purple flowers. Blooms in mid-summer for 40-50 days. Nectar productivity up to 149 kg. It also exudes pollen abundantly – up to 330 mg per plant.
Vesennik star – an inhabitant of mixed forests, blooming in March, April. Its white 8-petal flowers with many stamens are readily visited by flight bees. Provides early spring feed, including pollen.
Forest geranium distributed throughout the European part, Siberia, the Caucasus. Avoids steppe regions. The plant has leaves divided into lobes, large pink flowers, grouped in axillary semi-umbrellas. It blooms in the second half of summer, providing a supportive honey harvest.
Highlander Serpentine – perennial with a tubular stem, lanceolate leaves, painted on the lower plane in a gray color, and pink spikelets of inflorescences. Blooms in May, releasing nectar until the end of June. Nectar productivity up to 40 kg.
Yellow goose bow or “eider” – an edible perennial, widespread everywhere. It grows not only in the European part, but also in the Far East, in Siberia. Loves shady forest areas. Blooms in late April, early May. Nectar productivity from 8 to 12 kg.
Oregano common – a source of a special type of honey with a pleasant aroma, amber color with a greenish tint. Blooms in small purple-pink inflorescences from June to September (up to 130 days). Prefers sunny edges and dry sandy soils. Nectar productivity up to 80 kg.
Zopnik – a thorny low perennial with pubescent stems, lanceolate leaves and purple whorls of inflorescences. Distributed in southeast Europe, Asia Minor and the Caucasus. Blooms in summer for 1,5 months. Nectar productivity from 80 to 120 kg.
Zelenchuk yellow – a creeping perennial with a partially pubescent stem and bright yellow floral whorls. Loves shady places. Blooms from April, releasing nectar almost all summer (until August). The average bribe is 40-46 kg. The pumped out honey will have a characteristic greenish-gray hue.
The arctic princess (other names are “glade”, “mamura”) – medicinal and food plant, characterized by trifoliate leaves, large crimson flowers. Grows in coniferous forests, found in the tundra. Blooms in early summer. The exact honey production is not known, but the grass is well visited by flight bees.
Leek or bear onion – widespread throughout mountain forests. Loves shaded areas. When flowering, it throws out long peduncles with white hemispherical umbrellas. Releases nectar in May, June. Bribes from 18 to 24 kg.
Unclear lungwort blooms in April, early May. The flowers are reddish purple, pink at the beginning of flowering. Nectar productivity from 30 to 75 kg.
Read about other herb varieties: Lungwort as a melliferous plant
Rejuvenated sharp-leaved (another name “stone rose”) – a perennial with nondescript yellow-green corymbose inflorescences. It grows in coniferous forests, preferring stony ground. Blooms in mid-summer. Can be used for decorative purposes. The exact honey production is unknown.
Snowdrop distributed in the southern and central European regions, in the Caucasus and in Asia Minor (not to be confused with the prolesky, anemone!). This plant has pale white drooping flowers that bloom when the snow melts. It is readily visited by flight bees. Appreciated for early bribes.
Noricum knotted – a poisonous herb with an unpleasant odor, common everywhere. Prefers to grow in moist areas. The flowers are greenish-brown, blooming in May. The secretion of nectar takes place until August. The exact honey production is unknown. Honey is not harmful to bees. And the plant itself is used in folk medicine.
Cleansing – a short perennial, widespread everywhere. There are three melliferous varieties: caustic (June-August; up to 95 kg), purple (June, July; up to 35 kg), ordinary (August, September; up to 8-10 kg per day). Used in landscape design and folk medicine.
Forest rank – a kind of fodder crop from the legume family. Differs in pale pink tassels. Blooms from June to September. Separation of nectar up to 30-40 kg per hectare of grass stand.
Spotted lamb – inhabitant of humid forests, preferring moderate shade. It is also found on the coasts of various water bodies. Sessile pink flowers bloom in April. The nectar is released until early September. According to some data, bribes can reach 50-60 kg per hectare.
Grassy vegetation of meadows
A lot of herbaceous plants grow in the meadows. Their combination is called meadow forbs. In some regions, there are several dozen types of herbs. The most valuable for apiaries are about 40 of them.
The most honey-producing species
Meadow grass honey plant marshmallow officinalis – perennial with a high stem, ovoid leaves, pale pink 5-lobed flowers. In the first year, the plant produces little nectar, but from the second season it turns into the main summer honey plant. Flowers bloom in early July and release nectar until early September. Nectar productivity from 150 to 400 kg.
Valerian officinalis – a herbaceous perennial that grows everywhere on well-moisturized soils. Not found only in the far north and south. The pale purple fragrant flowers of the plant are collected in corymbose inflorescences. They are dismissed for the whole summer. Isolation of nectar 200-300 kg per hectare of dense herbage.
Volovik medicinal – an inhabitant of the forest-steppe and Polesie. Here it grows like a field weed, often found on awkward lands, along roads. The grass has a rough stem, narrow leaves. Purple 5-petal flowers are collected in paniculate inflorescences. Bloom lasts from May to August. Nectar productivity is about 300-400 kilograms.
Kidney herb (highlander pochechuyny) is an annual with broad-lanceolate leaves and pink-white small flowers, collected in dense apical spikelets. The leaves have a characteristic brown spot. Blooms from June to August. About 225 kg of nectar is collected per hectare. Extracted honey of dark amber color. During crystallization, small sugar grains are formed.
Placun grass (willow loosestrife) is a perennial with purple spike-shaped panicles of inflorescences, preferring to grow on highly moistened soils (near canals, swamps, water bodies). Blooms from June to September. The honey collected from the herb has a rich amber hue, slightly tart in taste. Nectar productivity up to 254 kg.
Snapdragon or toadflax is ubiquitous. Differs in two-lipped lemon-yellow flowers, collected in elongated apical brushes. Blooms in June for 45-50 days. Average nectar productivity is 100-150 kg.
Milkweed It is represented in the territory of the middle zone by several varieties, including shrub forms. Herbaceous species have straight stems, alternate, sometimes serrated leaves. When the stem is broken, a milky white juice is released. The flowering time depends on the species. Nectar productivity in favorable years is up to 270 kg per hectare.
Comfrey – a moisture-loving perennial growing in meadows and pastures of the Caucasus and the European part. For apiaries, two of its types are valuable: medicinal and rough. The medicinal variety has purple-violet curl-shaped inflorescences and leaves with a faint cucumber odor. Bloom from May to September. Nectar productivity up to 180 kg. In a rough variety, the inflorescences are light purple, resembling drooping panicles. Blooms in summer. The exact honey production is unknown.
Creeping thyme (other names “Bogorodskaya grass”, “thyme”) is a herbaceous shrub that thrives in a temperate climate. It is found everywhere. Its mauve apical clusters bloom in May. Isolation of nectar takes place until the last decade of August. Nectar productivity from 130 to 170 kg. The pumped out honey has an unusually fragrant aroma. The closest relative of thyme is fragrant thyme. This shrub grows in the steppes. Blooms in May, June, providing bribes up to 180 kg. The flowers are small, whitish-pink, grouped at the tops of numerous stems.
Wild sage (oak) – a herbaceous perennial with low tetrahedral stems, strong-smelling lanceolate leaves. The structure of blue-violet flowers is two-lipped. Apical spikelets are formed from them. The honey plant is widespread in Siberia, in the Caucasus, in the European part. Prefers steppe slopes of hills, mountains, forest edges. Blooms in June for 45-60 days. Nectar productivity from 110 to 280 kg.
Shandra white (common) is found throughout the European part, as well as in Central and Western Asia. The perennial has high stems, covered in the lower part with whitish hairs. The leaves are ovoid, wrinkled. The flowers are white, grouped in axillary whorls. Bloom lasts from June to August. Nectar productivity from 50 to 200 kg.
Secondary honey plants
Siberian Buzulnik, as the name suggests, grows in Siberia, as well as in the Far East. The grass has a high ribbed stem, heart-shaped leaves on elongated petioles, large yellow inflorescences. It blooms at the end of summer, providing bee colonies with preparation for wintering. The exact honey production has not been established.
Veronica long-leaved – another inhabitant of lowland meadows. She has beautiful elongated spikelets-inflorescences of blue color, sharp lanceolate leaves. Blooms for the whole summer, attracting a large number of flying bees. Average nectar productivity is 100 kg.
Adonis or spring adonis – a low May melliferous plant with large yellow flowers, blooming from the beginning of May. Valued as a plant that provides supportive bribes. Nectar productivity is about 30 kg.
Elecampane British refers to secondary melliferous plants. The grass has single low stems, oblong leaves, pubescent from below, yellow baskets of inflorescences with an orange core. Bloom lasts from June to September. Nectar productivity 10-12 kg.
Strawberry timber grows, including among meadow grasses. Its stems with white inflorescences rise above a rosette of triple leaves. Flowering lasts from the last decade of May to mid-June. Average nectar productivity is 13-40 kg.
Alfalfa is hop-shaped occurs throughout the European part in the steppe zone. In the mountains it can grow at an altitude of 2 meters above sea level. Differs in dense apical inflorescences of a light yellow shade. It blooms almost all summer, releasing from 300 to 25 kg of nectar from each hectare of herbage.
Cuff – perennial with palmate-lobed leaves, pubescent along the bottom. The flowers are inconspicuous greenish-yellow, grouped in corymbose panicles. Differs in long flowering from spring to the first autumn cold weather. Nectar productivity 100-120 kg.
Field mint – wild plant of the non-chernozem strip, preferring to grow in damp places. Its mauve small flowers are collected in axillary inflorescences of the upper leaves. Bloom from mid-summer to autumn. Provides supportive late-summer bribes.
Nonea (Russian nun) – a minor early summer honey plant. Found in the Black Sea region, southern Siberia, Ukraine, the Caucasus. The grass has oblong lanceolate leaves, purple panicles of inflorescences. The exact honey production is unknown.
Meadow goatbeard – a resident of the European part and regions of Siberia with a temperate climate. This biennial with high bare stems blooms from the second year of life. Golden yellow flower baskets bloom in June and August. Average nectar productivity is 80-100 kg.
Klopogon Daursky belongs to the flora of Primorye, Amur and Transbaikalia. Grows in dry valleys, blooming in August. White small flowers of black cohosh are collected in pleasantly smelling racemose inflorescences. The secretion of nectar continues in September. Nectar productivity from 50 to 80 kg.
Kermek or “statica” – occurs in the middle zone up to Altai and Siberia. The grass has low straight stems topped with loose lilac clusters. When dry, a so-called tumbleweed can form from the plant. Blooms from late June until the first frost. Nectar productivity up to 50 kg.
Autumn kulbaba – a perennial with high stems, the flowers of which strongly resemble medicinal dandelion. In the European part and in the Caucasus, this grass forms a continuous carpet on meadows. It is valued as a late summer honey plant, secreting nectar from mid-summer to autumn. Nectar productivity is about 100 kg.
Small rattle – an annual parasitizing on the root system of neighboring plants. It has lanceolate leaves with a serrated edge, a branched stem, yellow double-lipped flowers, grouped in brushes. Flowering lasts all summer. The rattle is common in southern Siberia, European regions and the Caucasus. It is a secondary melliferous plant. Nectar productivity up to 22 kg.
Saussurea broadleaf – a perennial growing in the east and west of Siberia. Occurs, including in alpine meadows, in sparse forests. The plant has a simple grooved stem, ovoid leaves, purple-violet corymbose inflorescences. Flowering lasts from July to late August. Nectar productivity from 100 to 140 kg.
Cherokoren medicinal – a biennial who has chosen the slopes of hills, ravines and the coast of water bodies. Differs in erect stems covered with fine fluffy hairs. Dark pink flowers are collected in paniculate inflorescences. The grass has an unpleasant odor. This feature is used by beekeepers to fight mice in apiaries. Flowering lasts from June to early August. Nectar productivity up to 70 kg.
Common chernogolovka – an inhabitant of meadows, river and lake coasts, swamp outskirts. The grass has hairy stems in the upper part, ovoid leaves, dark purple spike-shaped inflorescences. This is a summer honey plant blooming in June and July. Bribes up to 60 kg.
Immortelle or sandy tsmin (dryweed) is a short perennial herb found in the middle zone of the Russian Federation, Belarus, and Ukraine. The immortelle has erect stems, dotted with small narrow leaves. Flower baskets are lemon-yellow, rounded, very small. Corymbose panicles are formed from them. Flowering lasts from June to October, until the first severe frosts. The plant is readily visited by flight bees. The exact nectar production is unknown.
Pollen
Geranium meadow prefers humid places, found on forest edges. The lilac flowers of the plant bloom in June, releasing nectar until August. The grass provides the apiaries with pollen (collected up to 79 mg per plant) and nectar – up to 52 kilograms per hectare.
Highlander Serpentine – perennial with fist-like stems, lanceolate leaves and small pink flowers, grouped in the apical cylindrical inflorescences-spikelets. Flowering lasts a month – from the end of May to the last days of June. Nectar productivity does not exceed 40 kg. Also, a black-brown polish is brought from the plant.
St. John’s wort perforated – a medicinal herb, common throughout the European part, Western Siberia, the Caucasus. The stems are covered with numerous bright yellow flowers. It blooms in summer, providing the apiary with pollen. Little nectar is emitted. In addition, the grass is not visited by flight bees during the flowering of other melliferous plants.
Field marshall – perennial with bare even stems, basal lyre-shaped dissected leaves and bluish-purple heads of inflorescences. It blooms in July, providing the apiary with a pollen flow. Low nectar productivity.
Two-leaved plank – extremely important early spring melliferous plant, widespread in the central zone. The Siberian variety, respectively, is found in the forests and meadows of this region. The grass has drooping flowers of a bluish-purple hue, resembling bells in structure. Flowering lasts from April to early May. Nectar productivity is insignificant, but the collected nectar stimulates the spring development of bee colonies. Collecting pollen up to 11 kg per hectare.
Field harness – herbaceous perennial with woody stems covered with thorns at the base. Leaves are sticky from glandular pubescence. Pink small flowers are collected in the axils of the leaves at the tops of the stems. Flowering occurs in June and July. In the conditions of the south of Russia, Ukraine and Western Siberia, it provides bribes of up to 25 kg of nectar per hectare. This plant mainly serves as a source of pollen (pollen).
Cyanosis – perennial with bluish-purple apical clusters of inflorescences. It blooms from the second year of life from the end of May for 40-45 days. Can be grown for decorative purposes. Provides apiaries with a good supply of pollen and nectar. Nectar productivity from 80 to 100 kg. Pollen per hectare of crops is brought up to 313 kilograms.
Grassy vegetation of hayfields and pastures
Common thistle (thistle) – thorny biennial with lilac-purple inflorescences, distributed throughout the non-chernozem belt. There are several types of plants: garden, marsh, bristly, variegated. All of them are good honey plants. They bloom from mid-summer to late autumn. The average nectar productivity of common thistle is 90-130, field (pink thistle) – 120 kg. The latter is a vicious weed.
Peas – herbaceous perennial, widespread everywhere (including in Siberia and the Far East). Has many plant forms. The mouse pea has blue-violet flowers, collected in apical racemes on bare stems. The pair-pinned leaves end with tendrils. Bloom lasts from June to August. Bribes from 185 to 370 kg. The fence peas have red-purple inflorescences, they bloom in May. The secretion of nectar lasts until July. Low honey productivity up to 10-15 kg. This honey plant provides only supportive early summer flow.
Cornflower – a representative of the Aster family, with an area in the Non-Black Earth Region. Several of its species are valued as melliferous plants. Meadow variety with lilac-pink baskets blooms from June to early September. Nectar productivity up to 80-120 kg. Scabios (rough) appearance with lilac-purple single inflorescence baskets gives nectar from June to October. Nectar productivity up to 400 kg. The blue cornflower, in contrast to the listed species, lives for 1-2 years. It has loose purple flower baskets that bloom from May to August. Nectar productivity up to 50 kg. Pumped honey with a viscous consistency, with a pleasant aroma.
River gravilat – a resident of the middle zone, the Caucasus, Siberia. Differs in pubescent brown stems, drooping brownish-red flowers. This is an early summer honey plant, providing bribes from 70 to 150 kg.
Clover – one of the main and most valuable pasture plants. Differs in trifoliate leaves. The height of the grass and the color of the inflorescences may vary depending on the variety. A mountain type of clover grows in dry meadows in eastern and central Europe. Blooms from early summer. Inflorescences are white-yellow. Well visited by bees. The exact honey production is unknown. Red clover (meadow) blooms from July 40-45 days. Nectar productivity from 65 to 200 kg. Pink clover blooms from June and secretes nectar until early September. Average nectar productivity is 100-125 kg. White clover (creeping) provides bribes from 75 to 100 kg.
Read: Clover as a honey plant
The common mongrel – a resident of the European part, the Caucasus, Siberia. Often grown as an ornamental plant. The grass has single stems, pinnate leaves, globular large heads of blue inflorescences. Blooms for the whole summer, providing bribes of up to 650 kilograms and more.
Read more: Mordovine as a honey plant
Motherworts common (heart) – a tall perennial with pubescent stems, petiolate leaves and small pink flowers of the axillary type. Blooms from July to August. In the European part, it provides bribes up to 200-300 kg.
Read: Motherwort as a honey plant
Wild radish – an annual weed growing, including in gardens and fields. She has branched stems and light yellow flowers. The secretion of nectar lasts from June to September. Nectar productivity is about 150 kg even in the north.
Sabelnik swamp – a beautiful herbaceous shrub that has taken a fancy to wet meadows. The stem of the plant is covered with glands and protruding hairs. The leaves are trifoliate. The flowers are dark red or brown, 5-petaled. Blooms in the middle of summer, providing bribes from 30 to 170 kg.
Field and garden sow thistle – a perennial herb with thorny leaves and bright light yellow umbellate inflorescences. Both species known in the temperate climatic zone are malicious weeds of fields and vegetable gardens. Bloom all summer, providing bribes of up to 380 kg.
Read: Sow thistle as a honey plant
Common rape – a weed with golden yellow fragrant buds. The fruits look like cylindrical pods. Blooms for up to 90 days from May to August. Nectar productivity from 35 to 180 kg.
Read: Rape as a honey plant
Straight cleanser – an inhabitant of the black earth regions. This is a short grass with tetrahedral stems, oblong-lanceolate leaves, purple two-lanceolate flowers, collected in whorls. Blooms all summer, providing bribes of 110-120 kg.
Lamb Is a ubiquitous weed. There are two types: white clap, better known among the people as “deaf nettle”, and purple clap. In both species, wrinkled leaves look like nettles. The flowers are small, located in the axils. They differ in color depending on the species (white or purple). They are dismissed from May. The secretion of nectar lasts until September. White Yasnotka provides bribes of 100-150 kg (a record 542 kg were recorded in the Krasnodar Territory). Nectar productivity of purple is about 56 kg.
Secondary honey plants and pollen plants
Mytilist’s knotweed or meadowsweet is found in the meadows of the middle zone, Siberia, the Caucasus, Central Asia. The grass has erect stems, feathery leaves and thick yellow-white panicles of inflorescences. It is used in landscape design, but the honey productivity is insignificant – 5-10 kg per hectare. At the same time, the meadowsweet provides a good inflow of pollen.
Mug (popularly “burdock”) is a widespread weed. Blooms from the second year of life. The inflorescences are lilac-pink spherical, wrapped in spiny, subulate leaves. Honey plant of the second half of summer, providing bribes up to 100 kg.
The horned lyadvenets – perennial with numerous drooping stems, small leaves and a loose apical head of inflorescences. Blooms all summer. Bribes from 30 to 60 kg.
Mother and stepmother ordinary – an early spring melliferous plant. In the North-West and in the Non-Black Earth Region, it is one of the first to bloom, immediately after the snow melts. Long bloom – 30-40 days. Bribes 13-22 kg.
Read: Mother and stepmother as a honey plant
Taraxacum officinale – one of the most common meadow melliferous plants, blooming from late spring to autumn. Helps out apiaries in free-for-take periods. Nectar productivity up to 50 kg.
Read: Dandelion as a honey plant
Tmin – an essential oil herb with a smooth branchy stem and a white-pink complex umbel of inflorescences. It is often bred in vegetable gardens. Blooms in May. The secretion of nectar lasts until August. Average nectar productivity is 50-60 kg.
Common chicory – a tall perennial with a branching stem, lanceolate toothed leaves, beautiful blue-blue flowers. It is found everywhere in nature. It is cultivated in vegetable gardens as a salad crop. It blooms in the second half of summer, providing bribes from 50 to 100 kg.
Curly thistle – ubiquitous biennial with thorny leaves and purple apical inflorescences. Blooms all summer. It is readily visited by flight bees. The exact nectar production is unknown.
China meadow – a summer honey plant with yellow moth-type flowers, paired leaves, equipped with antennae. It blooms in the middle of summer, providing bribes of 15-20 kg.
Herbaceous vegetation of swamps and reservoirs
Vegetation that has taken root well near water bodies and bogs is not distinguished by high honey productivity. Basically, secondary melliferous plants grow here. There is only one record holder in honey collection – the egg capsule is yellow.
Yellow eggplant – an inhabitant of reservoirs of a temperate climatic zone, belonging to the family of water lilies. Its leaves are floating, oval, with long petioles. The flowers are yellow, small, planted on erect, bare peduncles. The grass blooms from early summer to the second decade of September. It is readily visited by flight bees. Nectar productivity up to 300 kg.
Pollen
White water lily Is another aquatic plant that attracts bees. The flowers of the grass are of a characteristic shape, have a snow-white hue, yellow stamens are located in the center. The leaves are very large. Flowering lasts from mid-May to the third decade of August. The water lily supplies the bees mainly with pollen. The collection of nectar is insignificant.
Cloudberry – swamp melliferous plant with edible orange berries that look like raspberries. The flowers of the honey plant are single, white. The leaves are rounded, wrinkled. Blooms in the first half of summer. Nectar productivity is insignificant. But at the same time, the plant emits a lot of pollen.
Secondary honey plants
Butterbur false (fake, felt) grows in the middle zone and in the Caucasus, forming continuous thickets along the sandy and pebble shores of reservoirs. Peduncles appear in April, early May. They are covered with small leaves wrapping the peduncle like scales. The honey plant blooms from the beginning of May, releasing nectar and pollen within a month. Nectar productivity is insignificant. The value of butterbur is that nectar appears in inflorescences even on cool days.
Three-leaved watch – perennial perennial with bare stems and pink-white bell-shaped flowers. Most often found in the non-chernozem zone. Blooms from mid-May to early August. Refers to secondary melliferous plants. Nectar productivity 15-18 kg.
Common loafers found in the European part. The grass has an erect stalk, lanceolate leaves, 5-petal yellow flowers, collected in panicles. Blooms in June, releasing a small amount of nectar and pollen until August.
Vodokras ordinary (frog) grows on the surface of water bodies, in their coastal part. The grass has elliptical leaves and white flowers on bare legs. Blooms in July. Secondary honey plant. Nectar productivity is about 5 kg per hectare of thickets.
Highlander amphibian (popularly “pike grass”) – grows both on the outskirts of reservoirs and on their coasts. Distributed in the middle zone, Siberia, the Far East, Belarus and Ukraine. The stems of the grass are densely covered with linear or elliptical leaves. The inflorescences in the form of spikelets are pink in color, outwardly reminiscent of the snake highlander. Bloom in May and June. Nectar productivity up to 50 kg.
Pulmonary gentian – an inhabitant of the European part, Siberia, the Caucasus. Grass shoots are densely leafy. The flowers are bright blue, bell-shaped. Grouped along the tops of the stems in the leaf axils. Late summer honey plant blooming in August. The release of nectar is insignificant, but it is stable – in drought and after night cold weather.
Amphibian pearl crusher – bog perennial of the middle zone. Differs in fleshy straight stem, oblong leaves without petioles, yellow clusters of inflorescences. Blooms in early summer. Can be eaten as an additive to salads. Refers to secondary melliferous plants.
Marsh marigold – a short perennial with recumbent stems, whole shiny leaves, bright yellow small flowers. Blooms in April, May. The green parts of the plant are poisonous to humans! Nectar productivity is insignificant – a secondary melliferous plant.
Iris yellow – tall marsh grass with long leaves and bright yellow flowers, strongly resembling irises in structure. Blooms in early summer. An average of 15-20 mg of nectar is released from the flowers. Iris provides supportive bribes.
Redberry or vaccinium excellent – a herbaceous shrub found in wet areas of the taiga, in the Primorsky Territory, on Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands. The leaves of the plant are obovate, the berries are red, exuding a specific smell. The grass is often called “bedbug” among the people. Bell-shaped pink flowers bloom in June and July. Nectar productivity 10-20 kg.
Long-leaved buttercup grows in the middle zone, Ciscaucasia and Siberia. Differs in a high hollow stem, large narrow-lanceolate leaves, bright yellow 5-petal flowers. Blooms in early summer. It is a mediocre honey plant.
Broadleaf – a tall perennial herb with a hollow stem, feathery leaves and white umbrellas of inflorescences. It is found in the European part, Siberia along the lowlands, peat pits. It blooms in late summer, being a secondary honey plant.
Pemphigus vulgaris named so because of the small air bubbles that cover the small leaves floating in the water. During flowering, it throws peduncles above the water, crowned with small clusters of large yellow flowers. Blooms all summer. Secondary honey plant. Up to 1 mg of nectar is released from one flower.
Arrowhead arrowhead perennial perennial, which took a fancy to the outskirts of reservoirs. Differs in white flowers with a bright red spot in the center. Leaves are both underwater and floating or towering above the surface of the water. Blooms all summer. Up to 0,5 mg of nectar is obtained from one flower.
Susak umbelliferous – a tall aquatic grass, throwing out a bare stem with pink umbrellas of inflorescences during flowering. It blooms in summer, being a secondary melliferous plant. Up to 2 mg of nectar is collected from one flower.
Aloe cutter – a floating plant that forms continuous thickets in ponds and lakes. Outwardly it resembles aloe. Leaves are elongated, with spines along the edge. The flowers are small, white. Blossom in the middle of summer. The grass is used to feed livestock and to fertilize vegetable gardens. Bribes from one flower 0,5 mg of nectar.
Plantain chastukha – occurs in temperate climates everywhere along the banks of reservoirs, damp meadows. Differs in oval leaves, high flowering shoot, large inflorescences of pale pink flowers. Mediocre honey plant blooming in summer.
Orchisia spotted (cuckoo tears) is a water-bog perennial with erect stems, ovoid leaves with purple spots, and red-purple spikelets of inflorescences. This is a typical inhabitant of the forest-steppe zone, having mastered damp meadows, the outskirts of swamps, the banks of reservoirs, wet edges and glades. Blooms from the third decade of May to July. Nectar productivity 15-20 kg.
Herbaceous vegetation of deserts and semi-deserts
In desert and semi-desert regions, all melliferous plants can also be divided into groups: main, secondary, mainly pollen plants. This includes some cultivated drought-resistant species that are not demanding on growing conditions, for example, sowing alfalfa (its feral form).
There are not so many record holders in honey bribe. It:
Camel-thorn – a typical inhabitant of desert regions, outwardly looking like a herbaceous thorny shrub. Its shoots are covered with leaves, purple moth-type flowers are concentrated in the axils. Flowering lasts all summer. Nectar productivity up to 150 kg. Pumped out honey of a whitish hue, during crystallization turns into a fine-grained mass.
Hyssop – a semi-shrub herbaceous perennial with erect shoots, small sharp leaves, labiate flowers, collected in apical spikelets. The color of the spikelets depends on the variety. There are lilac-purple, pink, blue, blue, white varieties. In one place, the dwarf shrub grows for 5-10 years. Not picky about soil moisture. Can be grown for decorative purposes. Nectar production depends on the region and variety. In the Moscow region, up to 121 kg of honey is obtained from pink-colored species.
Read: The benefits of hyssop as a honey plant
Lucerne sowing found in the south of Russia, including in a feral form. Feels great in arid regions. In culture, it is cultivated in the middle lane and in the south. It is used in agriculture for fodder purposes. Blooms with violet-blue tassels. Summer honey plant with nectar productivity from 20 to 80 kg (according to some data, up to 300 kg).
Read: Alfalfa as a honey plant
Psoralea stone fruit (another name “ak-kurai”) is a drought-resistant perennial herb with tall shoots, simple leaves, loose white-purple clusters of inflorescences. Covered with soft white hairs and brownish glands. Found in Central Asia. Blooms in early summer for 20-30 days. Control hives yield 2 to 9 kg per day. For the entire flowering period, strong colonies collect 100-150 kg of honey on this plant.
Cotton – industrial crop cultivated in many countries of Central Asia. The flowers of cotton are large enough, beige, white or yellow, depending on the variety. It blooms for two months from mid-July to the third decade of September. Nectar productivity 100-200 kg. Honey is collected mainly from bracts.
Secondary honey plants and pollen plants
Watermelon – an annual, a field crop that thrives in a semi-desert climate. It is cultivated in the Primorsky Territory, Central Asia, in the south of Russia and Ukraine. Unisexual light yellow flowers of watermelons bloom in July, August for 50-60 days. Nectar productivity per hectare is about 15-20 kg. Watermelon honey is subject to rapid crystallization – it is not suitable for wintering bee colonies.
Džut – industrial crop cultivated in Uzbekistan and a number of other Asian countries. The annual has small yellow flowers that bloom in July. The nectar is collected by bees until the end of September. The exact honey production is unknown.
Melon Is another melon crop grown in the south and in central Russia. Melons have large heart-shaped leaves, small pale yellow flowers. Blooms in the middle of summer, showing nectar productivity from 20 to 30 kg.
Jujube – an annual with a woody stem, common in Europe, Central Asia and the Mediterranean. The flowers of the grass are pink-purple, grouped in whorls at the tops of the stems. Blooms in the middle of summer. One hive brings up to 15 kg of nectar per day.
Indau (arugula, walleye, eruka sowing) grows in central Europe, Asia Minor and Western Asia, the European part of Russia, in Eastern Siberia, Moldova, Ukraine. The plant has a branched stem, covered with hard hairs, yellowish inflorescences in the form of rare long brushes. Blooms in June and July. Nectar productivity up to 70 kg.
Kenaf – industrial crop grown in Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan and Uzbekistan. The grass has thick stems, ovoid leaves, large yellow flowers with a dark orange core. Bees collect nectar from extra-flowered nectaries (the cult self-pollinates practically without the participation of insects). Nomadic apiaries receive up to 49 kg of honey from each hectare of crops.
Hutma Thuringian – very tall perennial (up to 2 m) with branched stems, heart-shaped 5-lobed leaves, pink large flowers. Grows in Altai, Central Asia and Kazakhstan. Blooms in the second half of June. Bees collect nectar and pollen until September. Nectar productivity up to 200 kg. Pollen bribe 500 kg per hectare.
Herbaceous vegetation of fields (agricultural land)
In this group of melliferous grasses, the undisputed leaders in honey collection can be distinguished, to which it is customary to move nomadic apiaries. The rest of the species are pollinated by the wind, or produce insignificant amounts of pollen and nectar. Their significance for apiaries is insignificant.
Mustard mustard grown in the southern and middle regions of the European part. Its yellow friable inflorescences in the form of a shield or brush bloom in May and June. Bribes of nectar from 35 to 150 kg.
Read: Mustard as a honey plant
Sowing buckwheat – the most valuable cereal and melliferous culture of the forest-steppe zone. In the climatic conditions of Kazakhstan and Altai, buckwheat provides up to 50% of the commercial honey bribe. Flowering occurs in the summer for 30-45 days. Apiaries specially roam the buckwheat fields in order to obtain a highly valued variety of honey on the market. Nectar productivity from 70 to 200 kg.
Read: Buckwheat as a honey plant
Coriander seed grown as an essential oil plant in the central black earth regions of the Russian Federation. In the south, it occurs in a feral form. The grass has tall (up to 1,7 m) straight or geniculate stems, light green leaves of various shapes and white-pink (less often purple) simple umbellate inflorescences. Blooms in June for 20-25 days. Nectar productivity from 100 to 500 kg.
Persian clover (“shabdar”) – a perennial grown for livestock feed. Blooms in summer for 1,5 months. This variety can be distinguished by the small blue-pink heads of the inflorescences. Nectar productivity from 150 to 355 kg.
Read more: Clover as a honey plant
Pasternak inoculum grown on household plots in Bashkiria and the Volga region, as a spice and flavoring seasoning. The culture has sharp-ribbed shoots, feathery leaves, yellow flowers. Honey plant in the second half of summer, blooming at the end of July. Nectar productivity is about 120-150 kg.
Sainfoin sowing (sandy) early summer honey plant, found both in the wild and in the fields. Grows well in the middle lane, in the south of Siberia. Perennial nectar productivity reaches 280 kg.
Read: Sainfoin as a honey plant
Secondary honey plants and pollen plants
Anise ordinary – an annual crop grown in the fields of the southern and middle lane to obtain oil with a characteristic odor. The plant is used in the pharmaceutical industry. White or creamy anise blossoms bloom in June and July. Nectar productivity per hectare is 40-50 kg.
Corn – a tall grain crop with a powerful stem, large elongated leaves and yellow-green panicles of inflorescences. It is grown in the southern regions of Ukraine and Russia. It blooms for 45-50 days in summer. Pollen bribes 20-22 kg per hectare.
Sunflower cultivated in the southern regions of Ukraine, as well as in the Caucasus, Siberia, the chernozem regions of Russia and the Volga region. The honey plant has a powerful hollow stem, large heart-shaped leaves and beautiful orange-yellow baskets of inflorescences. Blooms in the last decade of July for 25-30 days. Nectar productivity is 40-50 kg.
Read: Sunflower as a honey plant
Rape cultivated for oil and biofuels. The culture is demanding on the climate – mild winters are required for good germination. It is sown in two terms in spring and before winter. Winter crops bloom in early spring, spring crops in late May and early June. Nectar productivity from 30 to 90 kg.
Read: Rape as a honey plant
Flax ordinary cultivated in the northern and middle zone of the Russian Federation, in Ukraine. The perennial has erect, branched stems, narrow leaves and large blue-blue flowers. It dissolves in the summer for 5-10 days, providing a supporting honey yield of 10-15 kg.
Sowing peas gives only supportive bribes. Its white flowers are visited by flying bees only in hot summers (in favorable years, wind pollination occurs). Pea fields are of value for apiaries, mainly in mixed cultivation of crops with phacelia or white mustard. In this case, the bribe reaches 40-50 kg of honey.
Read: Peas as a honey plant
Vika – a crop grown in a mixture with oats or rye. Nectar productivity depends on the variety and type of crops. Rye and winter vetch variety (furry) provides an early summer bribe of 140-200 kg. Oats and vetch seed variety provide nectar productivity up to 20 kg.
Read: Vika as a honey plant
Horse beans grown in the middle lane, in the Far East, in Siberia. Depending on the variety, they are used as a garden plant (large-grain forms) or a fodder field (species with small grains). The stems of the grass are weakly branching, erect, the leaves are paired, the flowers are white moth type. Blossom in the middle of summer for 25-28 days. From this culture, bees collect mainly pollen. The nectar is obtained through the bumblebee bites at the bottom of the flowers. Nectar bribe in some years reaches 50-60 kg.
The herbal variety is extremely rich. In our review, only some of the herbs that give pollen and honey to apiaries are considered. Beekeepers are successfully expanding their natural food base at the expense of honey plants specially sown near apiaries: sweet clover, goldenrod, motherwort, phacelia and other plants.
You can read about the correct organization of the safety area here:
What honey plants are sown for bees