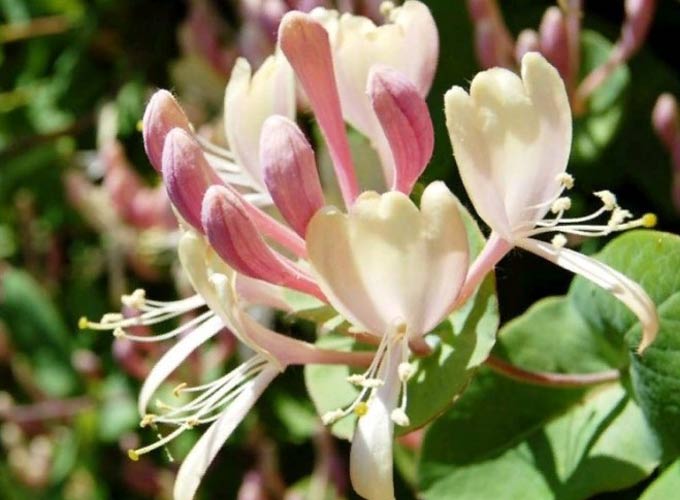
The honey plant, honeysuckle, belongs to a large family of honeysuckle, numbering about 190 species of evergreen and deciduous shrubs. They are found throughout the Northern Hemisphere, of which nineteen species grow in Russia.
These are mainly wild plants, many of which provide good yields of pollen and nectar. Certain species are cultivated for decorative purposes.
The content of the article
- 1 Significance for agriculture
- 2 Varieties and description
- 2.1 Edible
- 2.2 Tatarskaya
- 2.3 Fragrant
- 2.4 Varieties of Priamurye and Primorye
- 3 Agrotechnics
- 4 Honey productivity
- 5 Useful Properties
Significance for agriculture
Representatives of honeysuckle are able to decorate any landscape design. These are not only erect shrubs, but also climbing, creeping, liana-like plants, which can effectively decorate garden gazebos, alleys, park areas.
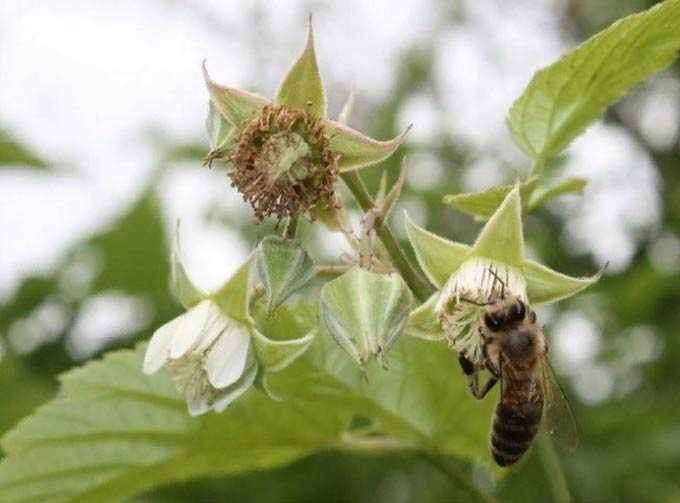
The species cultivated in Russia bloom from the end of May and bloom until about mid-June, beautifying the landscape and providing the nearest apiaries with nectar.
Edible varieties can be used to make delicious jam. Berries are also used fresh. The bark and leaves are used to prepare medicinal broths and infusions. They are also suitable for cosmetic anti-aging treatments.
The only plant of this family in Russia that is dangerous to humans is wolf berries (common honeysuckle). The fruits of the shrub are poisonous both unripe and ripe. It grows along forest edges, groves of the middle zone, undergrowth of the Caucasus. It practically does not occur in the southern regions. The flowers of the bush are yellow-white, blooming for three weeks in May-June, and the berries are deep red.
Varieties and description
The most interesting species for the beekeeper are:
- edible variety;
- Tatar;
- fragrant or honeysuckle.
All of them provide a good late spring bribe, which in many regions falls on a draft-free period.
Edible
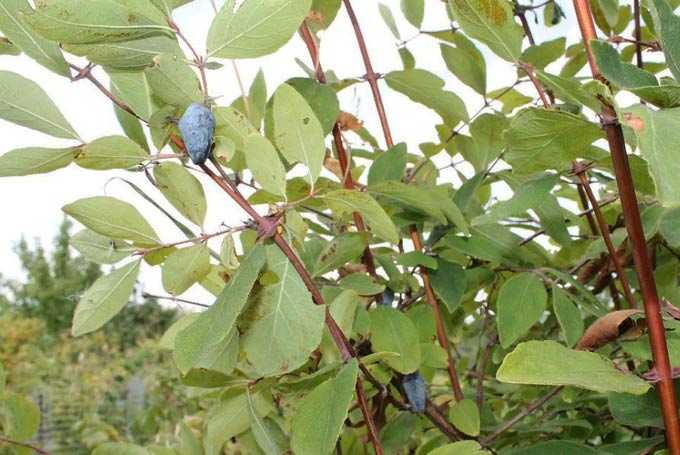
The edible variety is a bush up to two meters high, growing mainly on moist soils – on mountain slopes covered with coniferous and mixed forests, along river floodplains and valleys, in swampy areas.
The flowers are traditional for this family, pale yellow or yellowish white. They are located in pairs in the leaf axils. The shrub blooms in May (early or mid-month, depending on the region). Blooms from 15 to 20 days.
Valuable for apiaries as a nectar plant and a pollen plant (collection falls on the period of spring development of bee colonies). It grows mainly in the Far East and Eastern Siberia.
Tatarskaya
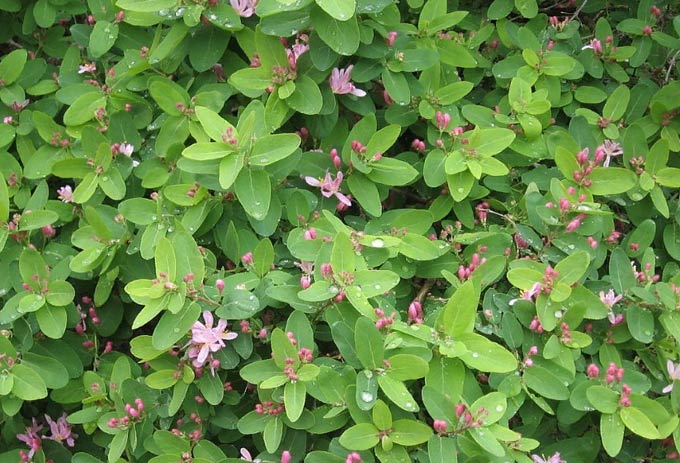
The Tatar variety is found in Altai, Siberia and practically throughout the entire European part of Russia. Although the berries of the plant are unsuitable for human food, the shrub is specially bred for decorative purposes – it looks beautiful during the period of flowering and ripening of fruits.
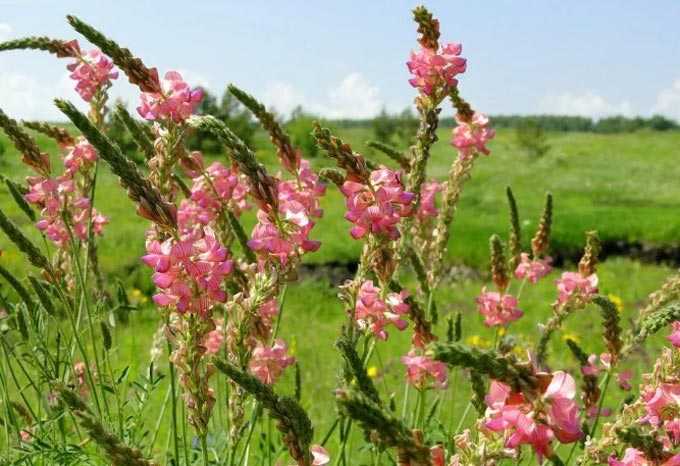
It dissolves in May and early June. The flowers are white with a pink tint. Fruits are paired, orange or reddish, often accrete at the base. The honey plant reaches a height of 1 to 3 meters (there are compact, low varieties for gardens). All shoots are hollow, covered with yellow-brown bark with small lenticels. Adult branches are gray.
Fragrant
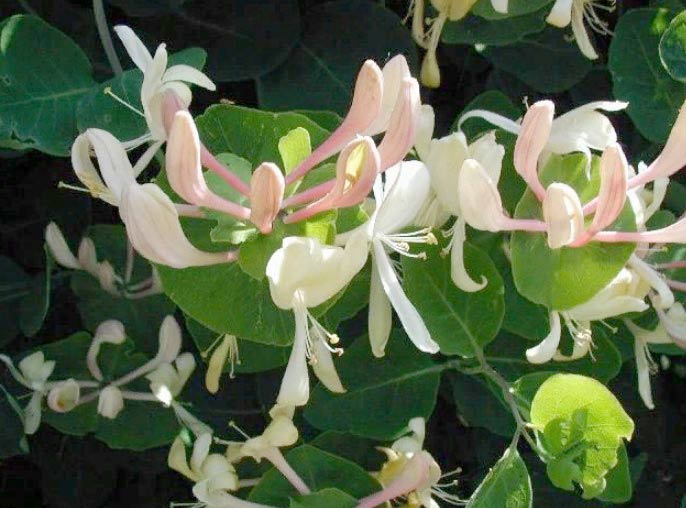
The fragrant variety (honeysuckle) is a Caucasian honey plant, also found in southern Europe.
The bush has beautiful climbing shoots. Young shoots are light green, old shoots are covered with brown bark. Prefers well-lit areas with wet soil. Occurs on forest edges, among rare bushes, along river coasts. It reaches a height of 5-6 meters.
The flowers are large enough, white with a pink tinge on the outside, and a characteristic double-lipped corolla, collected in whorls. Blossom from May to July. The orange fruit looks “glued” to the leaves due to its short stalks. Not suitable for food. The foliage is large and elliptical.
Varieties of Priamurye and Primorye
In the Primorsky Territory and the Amur Region, in addition to the edible species for apiaries, other varieties of honeysuckle are also valuable:
Humpback – a tall bushy plant, reaching a height of five meters. It blooms with bright golden flowers in the last decade of June. The honey plant easily rises to a height of 500-600 m above sea level. Prefers coniferous and deciduous forests.
Ruprecht – also a tall variety of shrubs, widespread east of the Bureya River. It is a June honey plant with bright yellow flowers that prefers to grow on rocky slopes, river coasts, and forest edges.
Maksimovich – a variety common in the Khabarovsk Territory and Primorye (south and central part). Blooms in June.
Grows in deciduous and cedar forests, preferring well-lit forest edges. Differs in beautiful purple-violet flowers. It is considered a valuable honey plant in Primorye.
Agrotechnics
Any of the listed representatives of the honeysuckle family can reproduce in three ways:
- using cuttings;
- seeds (for obtaining seedlings);
- and by means of stem layering.
The last method is most convenient for propagating climbing and creeping species, such as honeysuckle.
Planting can be done at any warm season – in spring, autumn, summer. In summer and spring, seedlings are planted, obtained from seeds and previously kept in flower pots. In autumn – cuttings or root layers.
The soil should be well moistened. And the prepared area is a sufficiently illuminated place. Slight shading of the lower branches is allowed (planting mixed with bushes of other plant species). The best soil is fertile loam.
Row spacing from 2 to 3 meters. The distance in the rows is selected depending on the variety – the higher the bushes, the more it is (usually in the range from 1,5 to 2,5 meters).
Young plantings are regularly watered, and the holes are gently loosened. For the winter, the bushes are recommended to be tied up to avoid snow damage. The first flowers will appear 2 years after planting in open ground.
Honey productivity
The honey productivity of honeysuckle depends on the variety grown on the site or near the apiary.
Here are the indicative figures for harvesting per hectare of plantings:
honeysuckle (fragrant) – gives from 20 to 50 kilograms;
Tatar – up to 60 kilograms;
edible – from 15 to 28-30 kilograms (according to other sources, up to 50 kg);
Maksimovich – up to 36-40 kilograms.
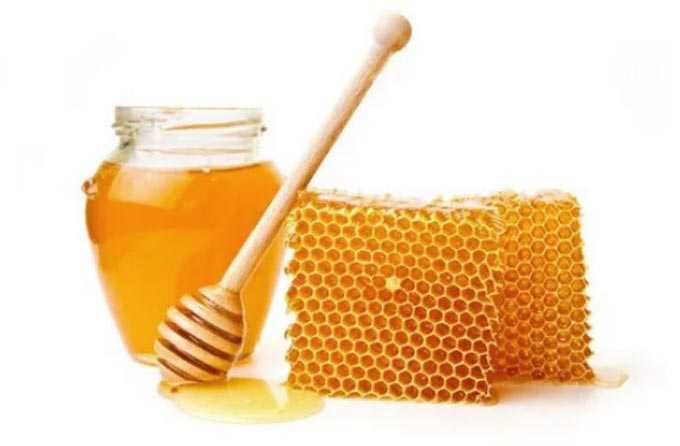
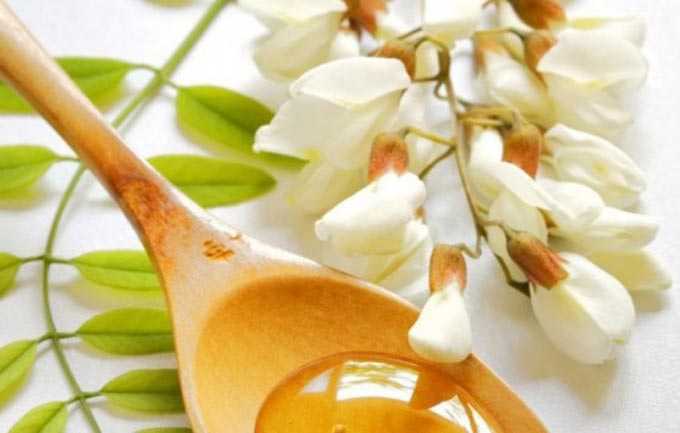
The collected pollen is dirty yellow. And the honey pumped out of the honeycomb is light yellow, with a pleasant herbaceous aroma.
Useful Properties
Honey obtained from honeysuckle is recommended in folk medicine:
- to strengthen blood vessels;
- for toning and cleansing the body of toxins;
- as a vitamin supplement to the daily diet;
- as an integral part of home cosmetic masks (used for skin rejuvenation);
- as a sedative for nervous excitability.
However, all parts of the plant will benefit. Fresh berries lower blood pressure, increase the level of hemoglobin in the blood. The flowers are used as a natural diuretic. The hair is rinsed with a decoction of the bark to strengthen it, bleeding gums are treated. Cuts and purulent wounds heal with crushed foliage.