The Polish beekeeper G. Tseselsky said that nowhere does diligent care play such a role as in beekeeping. Being late just a day or one missed work can ruin the results of a year’s work.
This statement fully applies to the spring period. We can safely say that spring for a beekeeper is patience and constant work. Only with the timely completion of all work will the coming year be successful for the apiary.
The content of the article
- 1 Exit from wintering
- 1.1 Removal of hives from the winter house
- 1.2 First flyby when wintering on the street
- 1.3 Cursory inspection
- 2 Spring-cleaning
- 3 Top dressing and basic inspection
- 4 Resettlement and disinfection
- 5 Fixing Weak Nests
- 5.1 Few bees
- 5.2 Small amount of brood
- 5.3 Queenless family
- 6 Spring building
- 7 Expanding families
Exit from wintering
In this article, we will touch on the general principles of spring work in the apiary and list the main stages of activities that are carried out after the wintering of bees, including in the wild.
Removal of hives from the winter house
The apiary can winter in two ways:
- The hives are insulated or not insulated (in the southern regions) and remain outside.
- The hives are moved to a specially equipped building – a winter house (winter hut).
Accordingly, the first activities carried out in the apiary will differ slightly depending on the type of wintering.
There are no freezing temperatures in winter quarters. Bees here begin to wake up already in late February or early March, because the sun warms up the building in the daytime – the temperature inside is gradually increasing.
Families that are awake can be identified by the disturbance inside the hives and the noise. This is a dangerous moment, because if the owner is overlooked, the bees are worn out, they begin diarrhea and mass death.
To avoid trouble, you need to lower the room temperature. To do this, open the windows during the day, and leave the door open at night. The temperature inside should not exceed +4 degrees!
If it is not possible to achieve the required temperature decrease due to warm weather, it is better to set the hives to the points earlier. Insects are not afraid of the cold. They are not afraid of return frosts, and even a spring snowstorm.
As a last resort, bee houses can be temporarily covered with cone-shaped roofing sheaths, which protect well from strong winds when the outside temperature drops, but not brought back into the winter house.
First flyby when wintering on the street
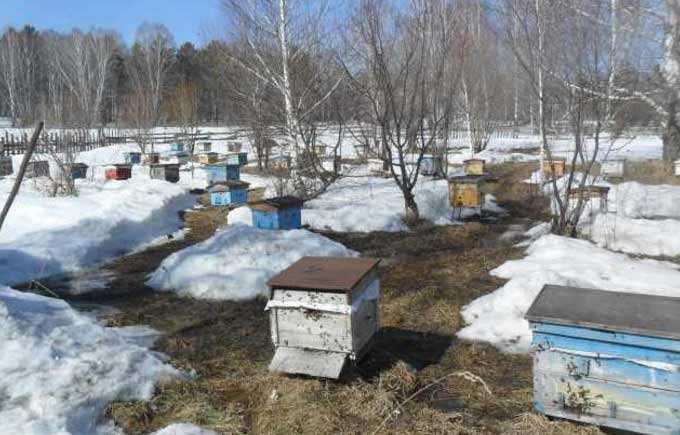
When wintering outdoors, spring for the beekeeper begins at the end of March, when the sun gains strength.
The point is cleared of snow in the middle of the month. The task of the beekeeper is to completely free the front walls of the hives from the snow and the insulation layer, if any.
Insects fly for the first time on warm sunny days. Therefore, the tap holes must be completely open and free from underfloor with a steel wire poker. In the evening, the entrances are closed – the lower one is two-thirds, and the upper half.
If puddles have formed in front of the hives due to melting snow, they are sprinkled with straw, spruce branches or covered with old boards. Insects should not drink melt water from puddles, as in this case they drown en masse.
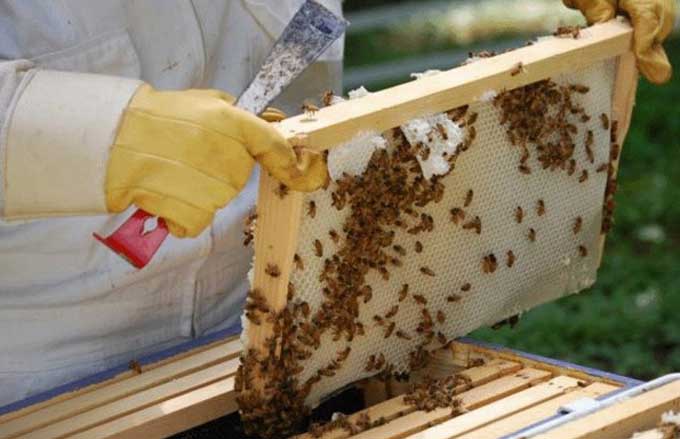
Cursory inspection
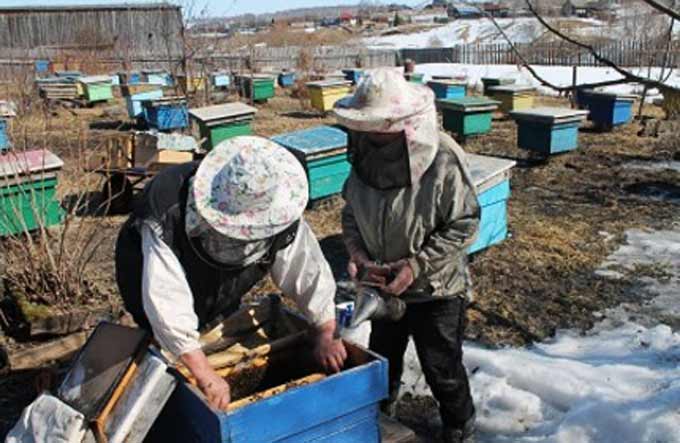
As soon as the daytime temperature reaches +12 degrees, it is necessary to perform a cursory examination of each family. Choose a clear, windless day for work. It is best to do the inspection on a warm afternoon.
The purpose of this inspection is to combat high humidity. Warming mattresses are replaced with new, dry ones. It is advisable to preheat the natural mattress filler indoors, for example, by laying straw on top of a cooling rustic stove.
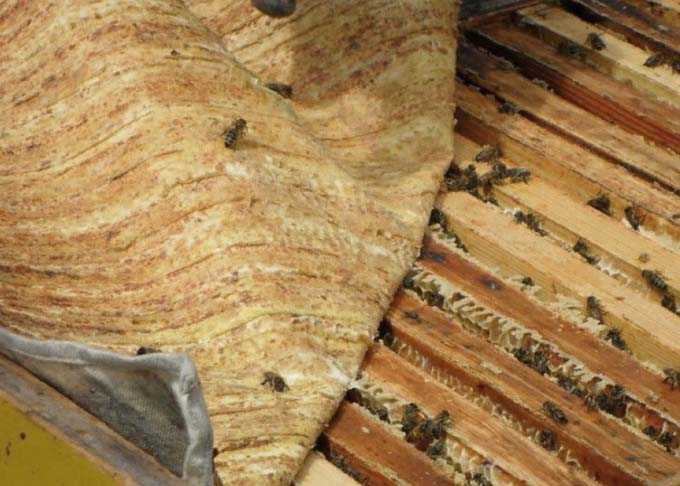
The canvas placed on top of the frames change at the same time. Especially if they have traces of mold or wax moth activity.
Weakened families are fed with honey combs. The frames are pre-warmed up in the house! If there is no comb honey, you can install a feeder with warm sugar syrup next to the last frame in the nest. To attract the attention of insects to feeding, a canvas is sprayed with syrup using a natural bristle brush.
Stimulation of bees in early spring:
Spring-cleaning
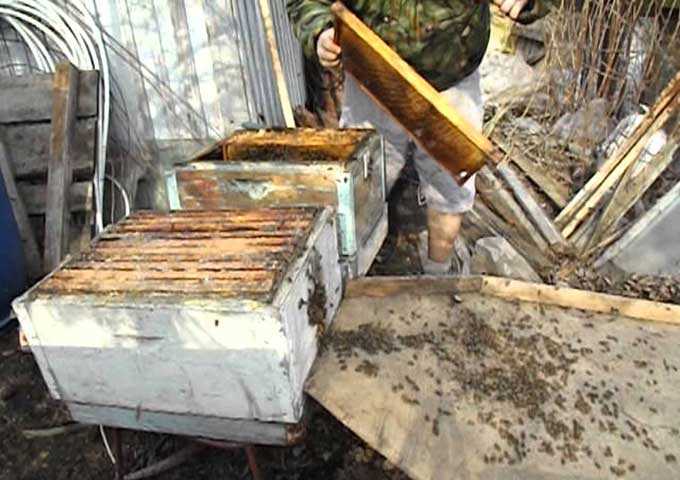
Spring work in the apiary after wintering includes cleaning the bottom of the hives from the accumulated decay and pieces of wax. April is chosen for general cleaning and is often combined with an in-depth examination of families.
The confiscated submarine must not be thrown on the ground! Dead bees are gently swept out with a brush and spatula and then poured into a bucket or wooden box.
Moldy ceiling boards, frames, damp mattresses (pillows), laps must be disinfected or replaced. They are collected and taken away from the hives to avoid spreading the infection.
Before cleaning, prepare fresh heated mattresses, clean laps, a portable box, a bin for rubbish, chisels, a brush and a scoop. For weakened nests, you will need combs with honey or feeders with warm syrup warmed up at room temperature.
Frames are made up in a portable box. Then they collect the dead water in a bucket, clean the areas with diarrhea and mold with a chisel and damp rags.
Rags are an irreplaceable thing, because it is with its help that you can remove dust from the bottom, avoiding it getting into the lungs of the beekeeper. Please note that dust in hives may contain mold spores and fungal pathogens that cause allergies or serious illness! In particular, aspergillosis affects the human bronchopulmonary system.
Top dressing and basic inspection
For a thorough inspection of each overwintered hive, you need to choose a suitable warm sunny day in April.
It is not worth delaying the inspection, since cloudy weather with precipitation often sets in after the sunny first decade of April.
Note: Do not inspect nests in cool, windy and rainy weather! You can freeze the brood. In addition, insects are aggressive, massively fly out of the nest to protect it, sting and, as a result, die. Families are getting weaker.
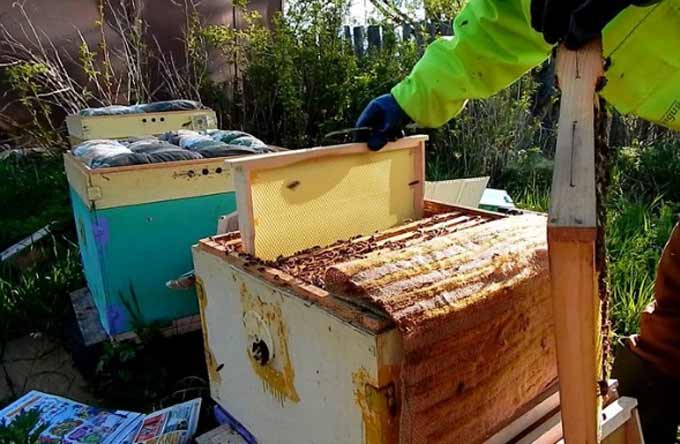
There should be as many frames in the nest as it is planted with insects, plus 1-2 frames with food. Heated frames are substituted at the rate of 8-10 kg per family. If the feeding frames are not available, one frame is left without brood, and a feeder with syrup is attached to it.
After an in-depth examination, the nest is insulated – newspapers are spread on canvas, and a warm mattress is laid on top. The holes are reduced by two-thirds.
All tools used for work are washed in a soda solution. Metal parts can be ignited in a fire.
Resettlement and disinfection
If a mouse has entered the nest during wintering, the bees are transplanted into another house. And the dirty hive is moved away from the apiary and placed on a stable stand.
Processing Order:
- At the beginning of disinfection, the walls and bottom are wiped with a damp cloth soaked in soda solution.
- Then scrape the inner surfaces with a chisel and collect the debris.
- The hive is wiped again with a damp cloth.
- After that, the still damp bee house is burned from the inside with a blowtorch, as an option, it is treated with a flame from a tourist gas can.
To do this, the hive is laid on its side, the wall that is on top is burned. The hive rotates until all the walls are disinfected. The corners and the area of the tap holes are especially carefully burned! Then the hive is placed upside down and the “floor” is burned. All surfaces are calcined until the wood is slightly darkened.
Frames with dryers are cleaned to “shine” from excess wax and propolis. Ceiling boards and crossbars are processed in the same way, which are used to prevent the laps from sticking to the frames. After completing the cleaning, everything is wiped off with a damp cloth and dried outside in partial shade.
The scrims are cleaned of propolis, and the mattresses are freed from the old filler. The fabric is washed in warm water and odorless laundry soap. It is hung in the sun and dries well within 2-3 days.
Bunches of lemon balm, mint or oregano are placed in a cleaned hive. The scent of lemon balm is especially attractive for the bee colony.
If the weather is cool, cleaning empty hives can be postponed until early May. To prevent the bees from getting inside, you need to tightly close the lid and the entrances.
Fixing Weak Nests
At the April examination, it is necessary to assess the quality of the uterus.
If it dies, there will be no open brood in the nest. And when the frames with brood are supported, insects begin to lay fistulous queen cells on them. Another sign is a weak supply of pollen to the nest.
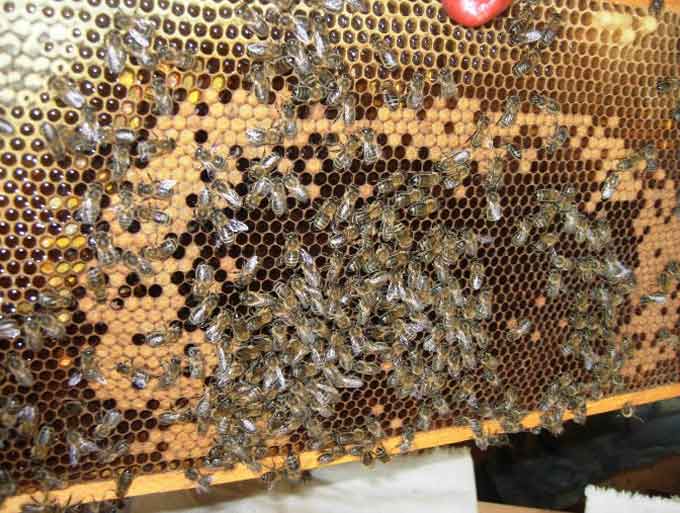
If the queen is alive, the quality of the brood is assessed. There should be a lot of it, sowing lies in a continuous carpet without gaps.
The uterus itself is also examined. It should be free of varroa mites. If they are found, the nest must be treated urgently! It is important to determine the condition of the wings. If they are frayed, this indicates an early replacement of the queen with bees.
Few bees
Families with a small brood are subject to correction, which is carried out during a second examination (the temperature should not be lower than +15 degrees).
The fix includes the following activities:
With a weak queen and a small number of bees, young bees from strong colonies are planted in the hive… To do this, on a sunny afternoon, when the working insects have left the strong hive, bees are shaken off from 2-4 frames into a portable box.
At the same time, make sure that the queen is not accidentally between the bees! They put it back in place and take another frame.
The box is installed 10 meters from the old hive. Any flight bees accidentally caught in the carrier return home. After that, the notch near the box closes to 0,5-1 cm, and it is set for 40 minutes in partial shade.
Before planting in a weakened hive, young bees are sprayed with sugar syrup with the addition of a decoction of lemon balm or mint. All insects in a weak nest are treated in the same way. This is done so that the “owners” do not kill the young, mistaking him for a thief.
A couple of days after transplanting into the hive, you can install 2-3 frames with brood – now there will be someone to look after him.
Small amount of brood
In families that overwintered as layers, the queens sow well. To strengthen such a nest, it is required to substitute a frame with a sealed brood taken from a strong family..
The frame is portable without bees! All are brushed off with natural hair and remain in their hive.
The brood frame is placed in the center of the nest to reinforce the cut (weak colony). After which the nest is insulated. The procedure can be repeated four days after the brood emerges.
Queenless family
A family with a dead uterus can be kept in two ways:
Attach the remaining bees to a good nest… The union will be more successful if a family with a fetal uterus is planted in a queenless hive, and not vice versa! When combining, bees from both nests are sprayed with a syrup containing a decoction of lemon balm. All fistulous mother liquors are removed beforehand. Families can be reunited within 4-5 hours after removal. The united family is examined no earlier than after 9-10 days, when the new brood is completely sealed!
If a layer with a queen is substituted into a queenless colony, it is locked in a queen cage for a day until the bees themselves nibble the foundation and free the “queen”.
The second method involves a direct uterine transplant.… It is launched at night through the notch or directly onto the honeycomb. Previously, the hive and uterus are sprayed with mint syrup. The hive is fumigated with smoke, the entrance is closed for one minute, a second fumigation is performed and the uterus is launched into the entrance.
Spring building
Until the beginning of May, beekeepers have a short break in their work. At this time, you can prepare frames, tidy up inventory, disinfect empty hives.
The main task in late spring is to create conditions for maximizing the egg production of queens.
Until mid-May, all overwintered insects are naturally replaced. Only young bees remain in the nests, and during this period there are more brood than worker bees. If the nest came out of wintering with a force of 10 streets (2 kg of insects), then by mid-May it will only retain the same volume.
Bees in May need to be fed by substituting low-copper frames from stocks or giving out a liter of sugar syrup every two days for each hive… For its preparation, a kilogram of sugar is taken for every liter of water.
Also it is necessary to install a drinking bowl with water at the rate of one drinker for 3-5 hives. This will save the worker bees the time it takes to transport them to their nests. Drinking bowls are placed in a sunny place, protected from strong winds. Water must not stagnate!
The holes open to full width. Winter heaters are removed, ventilation windows under the covers are cleaned. The mattresses are only left on top of the boards. In the north-western regions, the insulation from the frames is not removed until the beginning of June!
Frames for brood are put in time… Low-copper or empty honeycombs with even, unwrinkled cells are taken. For the successful rearing of offspring, feeding frames with bee bread, harvested in the fall, are also installed in the hives. Usually the need for such feeding arises during a prolonged spring with cold weather and snowstorms.
Expanding families
Expansion begins from the moment insects fill the last frames – the bees find themselves in the street between the frame and the dividing board.
Drying is installed between the outer frame and the dividing board. In strong families, foundation can be installed so that insects start building honeycombs.
Important: If by the end of May the colonies are not provided with new frames for even laying of eggs, young insects may fall into a swarming state! Established frames with foundation will help to relieve such a mood – the bees will actively build new honeycombs.
At the end of May, shop buildings with dry land are installed. In weak nests, they are in no hurry with this stage, making it possible to grow a family.
The task of the beekeeper on May days is to constantly monitor the number of free frames that are used for laying eggs by the queen and storing the brought nectar by working bees.
In good weather, frames with excess honey, crooked and dark combs can be replaced with foundation. Wax is released from insects with sufficient flow in the garden and in the fields. In the absence at this time of frames with foundation, bees begin to build honeycombs on dividing boards and walls of the hive, which complicates the care of the beekeeper (extra work is required to clean and remove wax).
The apiary in the spring requires maximum attention from the beekeeper, consistency in the work performed and hard work. But the time and effort spent is necessarily compensated by a good harvest of honey.
More about March jobs: What to do in the apiary in March
More about work in April: What to do in the apiary in April
More about the May works: May in the apiary – a brief overview of the works