Guayaquil (Psidium guajava) a species of woody plants of the genus Psidium (or Guava) of the myrtle family, which includes the well-known myrtle, the same feijoa and eucalyptus. These trees are native to South and Central America. One of the first mentions of this plant was made by Pedro Cieza de Leon in the book “Chronicle of Peru” or “Peruvian Chronicle”.
In addition, there are pineapples, guayavas, guavas (inga), guanavanas (annona), avocados, and several types of currants with delicious peel, chrysophyllums (caymitos), plums.
– Cieza de Leon, Pedro. Chronicle of Peru. Part one. Chapter XXVII
Guayava, a fruit. Farmer Burea-Uinsurance.com Sakurai Midori
Contents:
Botanical description of guava
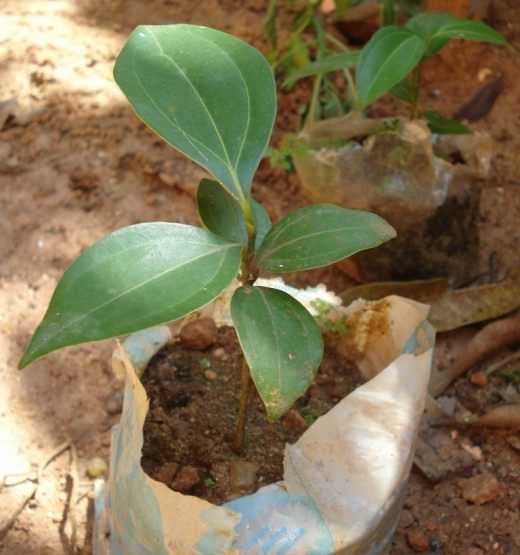
Guayava – small evergreen, sometimes semi-deciduous trees with widely spreading branches, up to 3-4 meters high, but can reach twenty meters in height. They have a smooth pale pink or light gray bark, sometimes covered with cracks. The leaves are slightly pubescent below, glabrous above, dark green in color.
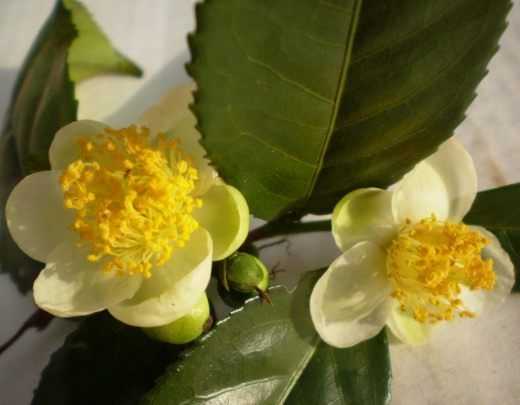
Flowers solitary or in clusters in leaf axils with 4-5 petals. Fragrant, greenish-white or white, up to 2,5 cm in diameter, with numerous yellow or greenish-yellow stamens. Flowering 1-2 times a year. There are both cross-pollinated and self-pollinated varieties. The honey bee is one of the main carriers of pollen.
Fruits are round, oval or pear-shaped, with a slight musky aroma, sometimes too strong. The color of the thin skin of the fruit can be yellowish white, bright yellow, reddish, greenish white or green. The mass of fruits of cultivated varietal crops is on average from 70 to 160 grams, length is 4-6,5 cm, diameter is 5-7 cm. The pulp of the fruit is from white to bright red, filled with hard seeds up to 3 mm long.
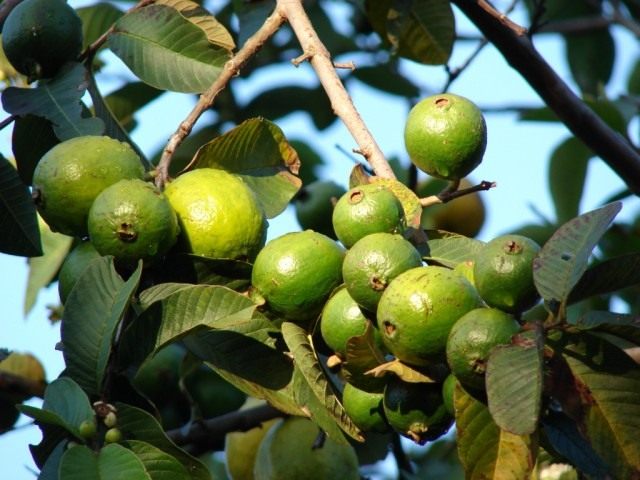

An adult Guayava tree produces up to one hundred kilograms of fruit in the main crop, and much less in subsequent crops. Fruit ripening occurs 90-150 days after flowering.
Growing guava
The common guayava is unpretentious to soils, but it grows and bears fruit better on light fertile soils, it loves moisture. It can be grown in small buckets and containers indoors. In winter, guayava enters a dormant period when the temperature drops to + 5 … + 8 ° C, so it can be placed in a cool room.
With the onset of warm sunny days in March, the guava needs to be transferred to the veranda or balcony and watered well so that it starts growing. In April and May, when frosts pass, it can be taken out into the yard and placed in a cozy, sunny place.

In June, the guayava blooms with stamen white flowers and begins to set fruit the size of a cherry. In August and September, the fruits increase and begin to ripen: at first they turn pink, and when fully ripe, they become dark red. The fruits contain proteins, fats, carbohydrates, pectin, carotene, many vitamins and other useful substances. For medicinal purposes, they are used primarily for the treatment of chronic gastritis.
When planting a plant in a container, it is imperative to make a hole for water drainage, and pebbles should be covered with a layer of 3-5 cm at the bottom.Then the container is filled with a light fertile soil mixture: 3 parts of deciduous humus or deoxidized peat, 1 part of fertile soil and 1 part of sand.
Reproduction of guava
Guayava propagates by seeds, which must be harvested after ripening and sown immediately, as well as green lignified cuttings and layering. From seeds, it begins to bear fruit in the fifth year, and from cuttings and cuttings – in the third. Guayava is not damaged by pests and diseases, it grows and bears fruit generously up to 30-40 years. It must be transplanted every 2-3 years in a large container with the addition of fertile soil mixture.

There are other types of guava (pear-bearing, Guinean, aromatic, apple-bearing), which can also be grown in containers, although some of them bloom and rarely bear fruit under such conditions (they are more thermophilic and yield only in warm greenhouses and greenhouses, because for successful growth and fruiting, they need a temperature of + 25 … + 28 ° C and good lighting). From seeds, these species usually begin to bear fruit in the seventh year, from cuttings – in the fourth or fifth, they also love moisture and light fertile soil.
Compotes, preserves, marmalades, jams are prepared from the fruits of all types of guava, and they are also consumed raw.