Also known by the names: Elecampane officinalis,
Wild Sunflower, Elecampane, Decampane, Oman.
Elecampane has been known since ancient times. Even during the reign of
Emperor Ivan the Terrible, many healers and sorcerers considered elecampane a
plant against all diseases.
The soldiers at that time took a bunch of elecampane with them
on campaigns and it was believed that by putting it on the wound, during sleep, the plant was
able to heal the wound and give the patient a second life.
Elecampane is a plant of the Asteraceae or Asteraceae family.
The height can reach 2 m.
Has a thick rhizome with long, numerous
roots. Stems angular, erect, closer to the top of the plant
branched.
Leaves uneven, alternate, twisted, top
dark green, below – felt, gray-green, oblong
at the base narrowed into a petiole, the lower ones are petiolate, but the upper
полустеблеобъемлющие, сидячие.
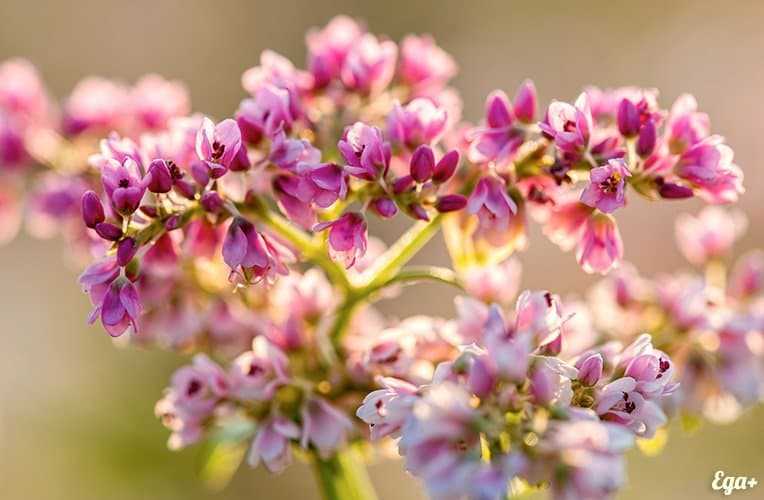
The flowers are yellow-golden, collected in baskets, which are
located on the cones of stems and branches.
The fruit is an oblong, brown, tetrahedral achene.
Elecampane is distributed throughout Europe and
Asia, as well as in Central and North America.
Elecampane prefers light areas, has good
frost resistance and dry resistance. Not susceptible to radiation levels
in the atmosphere.
Elecampane leaves are plucked from young plants in baskets
or special attachments. After collecting them, they are laid out and sorted out,
discarding dry and spoiled leaves.
Leaves
are dried in the shade outdoors, from stirring time, to obtain high-quality – dried raw materials.
The roots of elecampane are dug up in early spring or late
autumn, when the shoots have already died out or have not yet formed. In medicinal
the roots and rhizomes of plants that are older than three
years. Up to three years, the plant takes root and accumulates all useful
substances and minerals.
The dug roots are washed with water and cut into rings,
5-10 cm each. The cut roots should lie in the open air
for several days, after which they are dried in well-ventilated,
warm rooms. It is best to dry the roots of elecampane in dryers, at a
temperature from 30 to 40 degrees.
Elecampane is one of the few plants that grows well
in almost all soils.
The plant prefers sunny places in the garden and on the
personal plot.
The plant is stretched with seeds and shoots. Elecampane
tolerates drought well and has good frost resistance.
To grow a plant, you first need to
dig up the earth and fertilize it with minerals or rotted manure.
Seeds must be placed on wet cotton wool or sown
in pots. In the process of seed germination, a sprout is formed, which
can be transplanted at a height of about 5-10 cm. A hole is dug,
10 cm deep and about 20 – 25 cm in diameter. You can sow several
shoots in one hole, filling it with water almost along the edge. Wait until the moisture is
almost completely absorbed and then sprinkle with earth until the first leaf.
Elecampane sometimes needs tying, as the stems
begin to sag under the weight of many flowers. It is necessary to break through the
plant almost every week, removing the grass.
In the fall, when the plant is already beginning to prepare for winter,
and the stems begin to dry out, it is recommended to cut off the upper part
at the root, since then it will spoil the look of the entire site.
Elecampane there are about 110 species.
Only 40 species grow in Ukraine . The most famous such types:
Inula rhizocephala Schrenk – Elecampane root-headed
Inula royleana – Elecampane Royle
Inula salicina – Elecampaneus willow
Inula orientalis – Oriental elecampane
Inula oculus-christi – Elecampane of Christ’s eye
Inula ensifolia –
Elecampane swordsman Inula crithmoides – Elecampane
tall
Inula the Germanic
Inula magnifica – Inula magnificent
Inula hirta – Elecampane rough or hairy Inula
Inula caspica – Caspian Elecampane
Inula britannica – British Elecampane
Inula conyzae – Spread elecampane
Useful properties of elecampane
For medicinal purposes, the leaves and roots of elecampane are used.
Substances contained in elecampane: vitamin
E, vitamin B
and C
bitterness, organic acids, pigment, saponins, gums, helenin,
alkaloids, proazulene, resins, inulin, mucus, pseudoinulin, essential
oil, helenin, inulicin, alantol, alantone camphor , gelenin.
Elecampane preparations improve expectoration of sputum, reduce the secretory
activity of the intestine, normalize metabolism, stimulate the formation of
bile, increase urine output, and has antimicrobial and antihelminthic
properties.
Inside, elecampane drugs are used for chronic and acute bronchitis,
enterocolitis, functional diarrhea, colitis, for chronic and
acute pharyngitis, for gingivitis, tracheitis, difficult healing
wounds, periodontal disease.
As a drug, infusions are used, but most often decoctions.
Small, dry leaves of elecampane are poured with a glass of boiling water. On the water, the
bath is heated for half an hour and removed. Filter as it cools. Consume
in a warm form, 15 – 20 g for half an hour before meals.
2 tablespoons of crushed raw materials (leaves) are poured into 0.5 liters of boiling water.
Put on fire and boil until 1/3 of the water evaporates. Then
insist 1 – 2 hours and filter. The resulting broth is washed with the
oral cavity 4 – 6 times a day. Helps with stomatitis, gingivitis
and periodontal disease.
An essence is made from fresh rhizomes and roots, which is used
in homeopathy. It turns out that the drug has an antiseptic,
anti-inflammatory and capillary-strengthening effect, as well as
accelerates the renewal of the gastric mucosa.
Steamed leaves promote quick healing of cut and torn leaves
wounds.
Elecampane stimulates appetite, stimulates metabolism, eliminates
female pathology, promotes conception, acts as a sedative,
sedative, anthelmintic action.
Dangerous properties of elecampane and contraindications
Preparations containing elecampane are contraindicated in
pregnancy.
It is forbidden to take elecampane for kidney disease and cardiovascular disease
.
An overdose of the drug leads to severe stomach pain and vomiting,
in some cases, allergies are possible.
Video about elecampane
Video about the use of elecampane for the treatment of many diseases.