Shedding in laying hens is a natural process that begins in late autumn. Birds change their plumage to a denser one, which prevents them from freezing in winter. Chicks molt several times in the first year. During puberty, spring molting is characteristic of them. In addition, there are situations when birds begin to lose feathers due to illnesses, improper living conditions. In poultry farms, in order to maintain high productivity, the process is called artificially.
- deficiency of vitamins and minerals;
- malnutrition, which leads to a lack of nutrients in the body of the chicken;
- stressful situations ;
- skin diseases, infection with parasites, helminths .
Pathological molting in chickens can begin at any time of the year, for example, in the summer. The intensity of feather loss is different.Sometimes the owner may not even notice problems in the appearance of the bird. Only a decrease in the number of eggs begins to cause alarm. But there are cases when chickens lose almost all plumage, then they need immediate veterinary help.
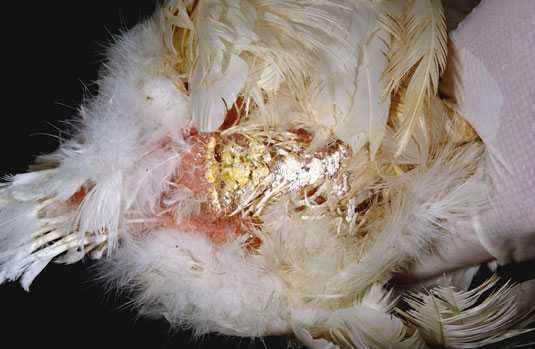
Most often pathological molting is caused by poohoedy or gnawing . How these parasites look can be seen in the photo on the Internet. In addition to feathers falling out, laying hens noticeably have reddening of the skin, white coating at the base of the rods, they constantly itch. Loss of plumage during vitamin deficiency and metabolic disorders is accompanied by a decrease in egg production, sexual activity in roosters. Birds become lethargic, eat poorly, sometimes they have intestinal problems.
How does natural molting go
Natural molting of chickens begins in the fall, in October or November. First, the feathers begin to fall out in the neck, then the back sheds, after it – the tummy and wings. The last update is the plumage on the tail. If you look at the photo, you can see how pathetic the faded birds look. Fortunately, the process does not last very long, after which the laying hens become even better than they were before the change of plumage.
During the molting period, the hens have increased skin sensitivity, so they can react painfully to any touch. Even roosters show less activity after the start of feather changes. Chickens try to hide away from people and other birds, lose their appetite, and rush poorly.Any breed behaves in a similar way, even the most contact and affectionate.
Age or juvenile molting occurs at different periods of the chicken’s life. The cover is lost several times during the first months, until a real adult feather grows:
- the first begins 7-8 days after birth and lasts about 4 weeks;
- the second starts at the age of 7 weeks, lasts up to 14 weeks;
- the third begins in the spring, when the chicks turn 16 months old, after which the birds become full-fledged laying hens, capable of fertilization and hatching eggs
Natural molting processes are associated with the activity of thyroid hormones. They largely depend on the length of daylight hours. When chickens molt in winter, daylight hours are very short. If it is artificially lengthened, the period of plumage renewal is significantly reduced.
It happens that in chickens at any age, natural molting begins in the summer, in July or August. Feather change lasts 2-2.5 months, almost no eggs at this time. If there are no signs of illness, such layers should be removed from the herd. Their productivity will plummet in the coming months. Neither females nor males that constantly have summer molting are allowed to breed.
Artificial molting
Understanding the processes that lead to molting in chickens allowed poultry farms call it artificially. At the same time, molting time is significantly reduced.All birds lose feathers at the same time, and herd productivity is not particularly affected. After a temporary cessation of masonry, the hens are carried even more intensively, the general egg production of the livestock is significantly increased. Artificial molting can not be carried out at home: too fast and forced change of feathers can not only damage the health of the bird, but also destroy the whole population.
There are many methods to speed up the process of changing feathers. The most commonly used types of artificial molting are:
- chemical;
- hormonal;
- zootechnical.
Chemical procedure
To cause accelerated molting chemically, concentrated feeds with a certain ratio of trace elements and biologically active substances are used. They affect the synthesis of hormones in the pituitary, hypothalamus, thyroid gland and genital endocrine glands. As a result, the sexual function of chickens and roosters is inhibited, the hormonal background is as close as possible to that characteristic of natural conditions during molting. The process lasts 2-3 weeks, after which the egg production quickly resumes.
Hormone technique
The hormone method is based on the use of thyroxine, progesterone and other similar drugs. Shedding comes and ends very quickly. After a week, laying hens can give twice the number of eggs.If hormones are used improperly, dosages are changed, a persistent decrease in productivity can be caused, since the bird’s own endocrine system ceases to work. does not require the use of expensive drugs. Chickens are given a water diet for 4 days: they give only drink, but do not feed. At the same time, the duration of daylight hours is sharply reduced, and birds are kept in the dark for almost a whole day. Amid stress and starvation, birds begin to quickly lose feathers. Such forced molting does not last long. Egg production resumes within 1.5-2 weeks after the termination of the diet.
Care for poultry during molting
Many beginning poultry breeders ask: “My hens molt what should I do?” If the feather loss is natural, no special bird care It is advisable to keep the hens most of the time in the chicken house at this time, especially when it’s cold outside. They’re walking, it’s worth building a shelter that protects from rain. It’s important to regularly remove feathers in the house so that different types of bacteria and parasites do not breed .
When molting occurs, physical contact with the bird It is also impossible to change the composition of the herd, buy new chickens or send old ones for slaughter. When molting, the bird loses weight, because the meat yield will be less than usual. In addition, changing the composition of the herd is an additional stress for the bird, because of which the molting is often delayed. New birds can bring infection with them, and immunity in molting chickens is weakened.
When there is a suspicion of pathological shedding, you should consult a veterinarian. The disease can affect both the whole herd and individual individuals.If it is found that the problem arose due to improper maintenance or feeding, it is corrected. Skin diseases (especially those caused by fungi) are sometimes very difficult to treat. Use fungicides, antibiotics , antiseptics. They fight parasites with the help of insecticides.
Feeding birds during molting
It is necessary to feed laying hens correctly during molting. All necessary nutrients, vitamins and minerals must be present in the feed. It is very important that a sufficient amount of the amino acids methionine and cysteine enter the body of chickens: they affect the synthesis of hormones, are the building material for future feathers.
The basic rules for feeding hens in this period are as follows:
- the amount of protein in the diet is increased to 22%;
- in the menu increase the number of vegetables;
- introduce additional feeding in the evening;
- increase the amount of minerals due to chalk, shells, eggshells, salt;
- give chickens vitamin supplements .
to layers provide the required amount of protein, they are given meat and bone meal , broths, cottage cheese, boiled egg. If it is possible to let chickens out into the yard, they themselves can find food with proteins: snails, worms, larvae, beetles, etc.
Vitamins are found in fresh vegetables and fruits. Chickens are given pumpkin, which ripen in the fall, zucchini, peeling apples and pears, mountain ash.Beer yeast, sunflower meal, wheat germ and wheat bran will be beneficial. Grain and wet mixers can be made with your own hands or you can buy ready-made compound feeds enriched with protein, vitamins and minerals.
In order not to feel losses from a decrease in egg production, there must be birds of different ages in the herd, then their molting will not start at the same time. Part of the chickens will be carried, the other will change feathers. Shedding time can be reduced due to artificial lighting, proper feeding. Vitamins A, group B (primarily B1 and B3), D, E. are introduced into the diet.
How long does the laying time for the laying hens last? The duration of the normal process at home is 4-6 weeks. By winter, most birds already grow new feathers. If the molt is longer, consult a veterinarian or an experienced livestock specialist.