In the family of ducks there is such a bird as a teal-cracker. Outwardly, it is a small bird with a specific voice, the sound of which is like a crackle. For this, the bird got its name.
- Distinctive external features
- Geography of residence
- Behaviors
- Food and breeding conditions

Teal cracker
Distinctive external features
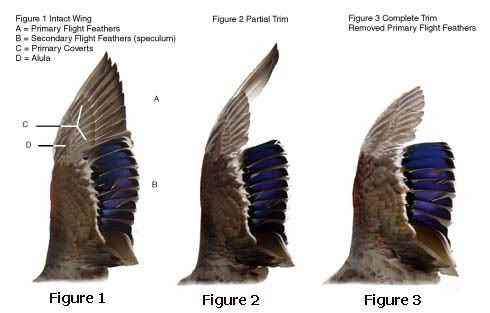
The treshkunok is a rather small duck, which can be noted in the photo, the teal tuskunok by description is close to the widespread waterfowl shank. no more than 40-41 cm, its wingspan reaches 69 cm. Garganey ranges from 0.29 to 0.48 kg
garganey very similar to his kinsman, who even like the name -. Teal To avoid confusion, you should pay attention to the distinctive features of the breed..
The males have bright distinctive external features:
- in the mating season they are distinguished by a white stripe of sufficient width extending above the eyeball, which is clearly visible against a common brown background and is easily recognizable in the field environment ,
- the teal has a head covered with dark brown feathers on top, the sides of the body are the same color,
- the plumage of the chest and neck is colored in chocolate and intertwined with longitudinal white mottled, the rest of the body is gray with an olive tint,
- the tail feathers are brown,
- the sides are painted gray with a gray, diluted black flowing pattern,
- the white abdomen and the area of the undertail, intersected across with variegated feathers.
In flight, a teal crackler is distinguished by a gleaming green mirror on its wings.
A similar color has a subspecies of the whistle. However, the crackler is larger in comparison with it.
The female teal of the cracker in the photo is distinguished by a dimmer coloration of bluish-blue tones with spots on the wings. Unlike males, the duck does not change its plumage and remains monotonous throughout the entire period: brown in the upper part and motley-white from below.
The crackling duck differs from other representatives of teal in a plain white chin and neck. The young generation of the species of crackers, regardless of gender, is distinguished by red plumage on the chest and sides and bright variegation on the abdomen.
Geography of residence
You can see crackling teal in Eurasian temperate latitudes, starting from the British Isles, ending with Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands. Nesting of crackers was recorded in the west and south of France. The northern border of bird habitat runs through Scandinavia and Finland to the White Sea and the Pechora River Valley. Representatives of teal can be found on the shores of the Sea of Okhotsk. They build their homes in Switzerland and Croatia, in the Balkans and in Bulgaria, were noted in the central Turkish region, in Azerbaijan, the center of Kazakhstan, as well as in China and Mongolia.
A temperate climate is suitable for these birds taiga and semi-deserts, steppes and mixed forests. They nest on small lakes with growing reed and sedge vegetation. In winter, they prefer to live on flood rice fields, close to dams with sewage. Often stop on vacation on the seashores and bays.
In winter, the cracker completely flies away from its places of origin, moving south, preferring west or east of Africa. Large clusters of ducks were recorded on the swamps of the White Nile in Kenya, on the southern side of Uganda and a little in Tanzania. Only selected crackers reach Zambia, some winters in Pakistan and India. Eastern ducks migrate to the south of China.
Behavior
Its name was given to the teal crackler, thanks to a special cry of males.The sounds of ducks resemble dry crackling cracker type “crere-crerere”. In everyday life, such a crackling sound can be obtained by combing the teeth of a hairdresser. Male teal crackers make their unique sounds not only when they are on the ground or in the water, they also crack when they are in the air.
For females, such a voice is unusual, they are more silent, only sometimes you can hear them sonorous and high-pitched quacking.
A teal-cracker is a migratory bird that travels for the winter to the African tropics and to the Asian southeast. At the same time, it forms swarms of rather large sizes, located in river deltas and on swamps. These ducks return later than other duck representatives, and fly away much earlier. Prefer birds for nesting to open ponds near meadows.
Crackers adapt well to captive conditions and are able to breed in zoos and bird kennels.
Food and breeding conditions
In the mating season and during breeding in spring and summer, ducks prefer to eat mollusks, being more animal-eating. Their diet includes various insects and larvae living on water (for example, water bugs, mosquitoes), small invertebrates, crustaceans. They can be enjoyed by fish fry and tadpoles. Among plant foods in the autumn-winter period, crackers include on the menu herbal shoots and seeds, sedge, wild rice, sorrel.
The teal-clapper is monogamen, selects one partner for breeding.
The clods reach maturity by the age of one year, and move to the breeding site in March already in formed pairs. Mating courtship, the drake begins by swimming in circles around the female with her beak lowered into the water column and feathers ruffled on her head, giving her unique voice. and tall grass. Inside, it is lined with dead wood and down. Oviposition of cracking teal usually includes up to 9 eggs of elongated oval shape (sometimes it can be from 6 to 14), which the female incubates for 3 weeks. Hatched chicks take to the wing and begin to fly after 40 days.