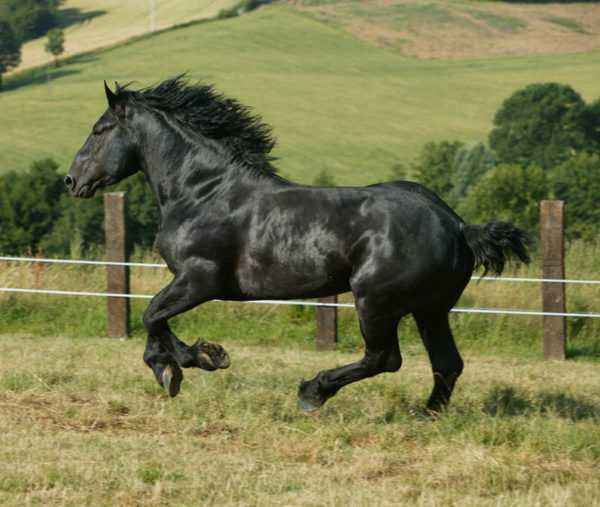
Horses are beautiful graceful animals from the equine order. Their domestication occurred approximately 5000-5500 years ago. Steppe wild horses are considered ancestors, but so far it has not been possible to reliably determine the ancestor. The importance of horses fell only at the beginning of the twentieth century, when the cart, gig and wagon ceased to be relevant.
- Origin of the horse
- Description of the horse
- Horse running
- Natural gaiters
- Artificial gaiters
- Horse breeds
- Riding breeds
- Top harnessed
- Heavy trucks
- Harnessing horses
- Maintenance and care
- Feeding <
- Breeding
- Diseases of horses
- Infectious diseases and helminth infections
- Non-communicable diseases
- Modern use of horses

Horse
Origin of the horse
The order of horse, in addition to the domestic horse, includes:
- Przewalski’s horse;
- Extinct wild horses;
- Quang;
- Kulan ;
- Mountain zebra, desert zebra and Burchella’s zebra;
- Donkey.
They are all artiodactyls, some can interbreed, but they are sterile offspring, as they have different numbers of chromosomes. A donkey and horse hybrid is called a mule or a gelding, depending on how the cross was made.
The origin of the home species is not known for certain. Most likely his wild ancestors died out after the horse was domesticated.It is believed that such horses were involved in the formation:
- Horse;
- Eastern;
- Forest;
- Tarpan.
To date, there are no real wild horses left. The tarpans became extinct over a century ago, the forest disappeared even earlier, and the Hagerman – 10,000 years ago. Only a small number of Przhevalsky horses have survived. By breeding, it was possible to breed the Hake breed, similar to Tarpan. Facts say that feral domestic horses live in America and the south of France. One of the most famous images of these animals is the rustling white Uffington horse.
Description of the horse
There are many breeds of horses, but they all have common features. Here is a brief anatomy, biological features, characteristics and description of this species:
- head with a long muzzle and dry;
- eyes are large;
- widened nostrils;
- ears are mediocre and very mobile;
- the mane is elongated, hangs to one side;
- the neck is elongated, bent, the muscles are developed;
- the chest is strong, broad;
- the back is muscular, wide, the horseman is calmly placed on it;
- the back is extended, the tail is magnificent;
- the hips are well developed;
- legs are high, with strong tendons;
- the hoof covers the tip of the middle finger;
- on the inner surface of the wrists there are horny bumps or a bump.
The horses’ digestive system is typical of herbivores.The stomach has only one compartment (artiodactyl species have 2), there is no gall bladder. The body temperature of the horse is 37.5-37.8 ° C. Breathing at rest – 8-16 times per minute, with loads – 5-7 times more often. The heart beats 40-60 times per minute, while running – 120-130 times, pumps up to 150 liters of blood. The average age of a horse’s life is 25-30 years, the champion from Britain lived to 62.
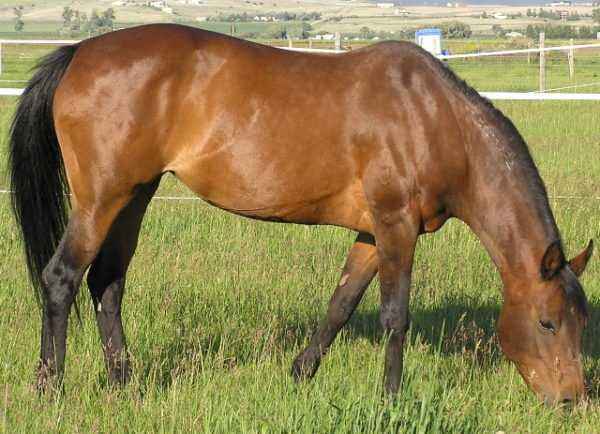
Presumably wild horses were striped, had a dark color along the ridge. Here are the most famous colors and colors of horses:
- black (black suit horses);
- bay;
- red;
- brown -ginger;
- gray or gray;
- dark gray;
- gray in apples;
- chubaray;
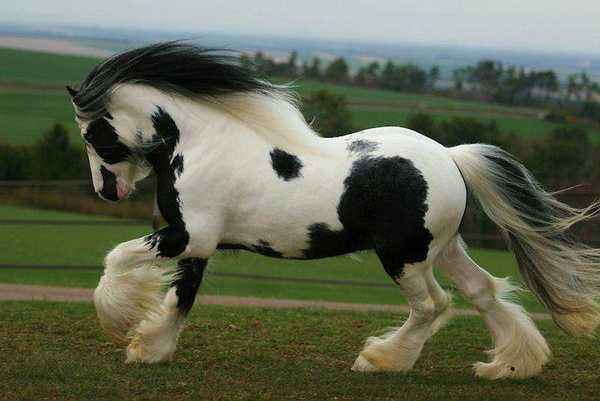
- piebald spotted (these are white horses with spots);
- white or albino;
- magpie black and white;
- playful;
- gold.
Many colors are extremely rare, as they arise due to gene mutations. They are especially highly regarded.
Horse Riding
An important characteristic of a domestic horse is its running, or gait. Distinguish between natural and artificial types. In the first case, a gait is a kind of running characteristic of any horses in nature. Artificial paces are specially developed by man. Often this type of running is used in dressage competitions.
Natural gait
Natural horse gait include:
- Step – calm walk, only one foot comes off the ground.
- Lynx is a fast gait, 2 legs simultaneously tear off the ground, right rear and left front and vice versa.
- Gallop – a very fast run, in which the horse completely breaks off the surface and freezes in the air, horses at a gallop can run fast, at an average speed or slowly.
- Ambler is a special type of lynx, characteristic of only some individuals, 2 legs come off the ground on one side, such horses sometimes run fast turn over.
Artificial paces
Own different types of artificial paces circus and sports horses. To work out such a step, you need to practice horses for a very long time and on a professional level, using special devices: cavaletti, long cord. Known types of horse steps created by man:
- Passage – a slow lynx, the horse beautifully extends his legs forward and lifts them high up, like a hopper.
- Piaffe – passage made on one place
- Spanish step – the horse walks like a ballerina, bringing forward a straight front leg.
- Three-legged gallop – one front foot is extended forward and does not touch the ground.
- Gallop to the back – walking with a jump backward.
Most often, rare artificial gaits are used at parades and exhibitions. Passage and piaffe are the main steps that are evaluated when dressing. There are no people who would not be fascinated by these graceful walks.To demonstrate, you need a good rider, an ace in his profession. Not every horse can train a beautiful gait; a high degree of animal intelligence is needed.
Horse breeds
After the horses were tamed, more than 100 breeds were bred. Some of them still exist. The classification has not been finalized, they are conditionally divided into the following groups:
- horse;
- horse-drawn;
- light and heavy-duty;
- high pack animals.
Classify horses according to the type of breeding on the factory, herd and mixed.
Breeds that have been bred in a specific territory since time immemorial are called aboriginal . Varieties resulting from targeted selection are called cultural. There are also transitional forms. In addition to horses of usual height, there is still a small pony breed.
Riding breeds
Riding varieties first appeared in the countries of the East, they were bred by Arabs. They came to Europe during the Crusades. Before that, Europeans bred mainly pack horses and heavy trucks. Here are the main representatives of riding horses:
- Arabian horse;
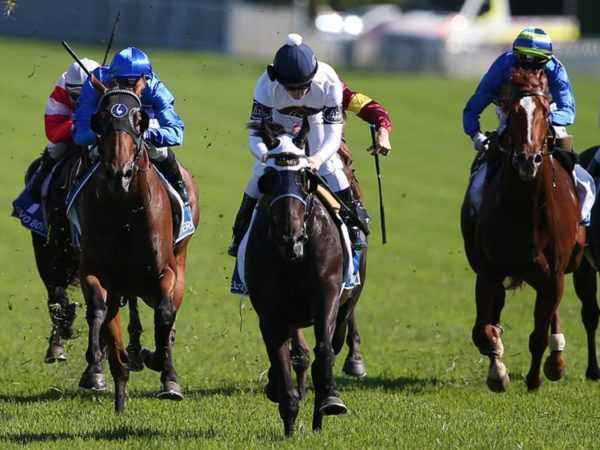
- thoroughbred horse (the most famous modern stallion California Chrome);
- Terskaya;
- Hanover;
- Akhal-Teke or Akhal-Teke;
- Trakenskaya;
- Budenovskaya;
- Kabardinskaya.
The ancestor of most modern breeds is the Arabian horse. Alkhetinskaya and Kabardinskaya varieties that are actively involved in breeding are also considered indigenous.
Horse-harnessed
These breeds began to appear actively in the 18th and 19th centuries. When breeding, the horse and cargo varieties were crossed. The most famous breeds of this direction:
- Orlov Trotter;
- Lippician, Lipitsian, or Lipitsian;
- Fjord;
- Russian trotter ;
- Freiberger;
- American curly Bashkir, or Curly Bashkir;
- Oldenburg;
- Pinto;
- Greater Poland;
- Cartesian;
- Hungarian;
- Ranger Colorado;
- Aztec;
- Flemish;
- Okhotnitskaya.
The main characteristic of draft horses is their speed and endurance, although they are inferior to riding horses in terms of running speed. Their physique is strong, graceful. The size of the draft horse is medium, the horses are not high at the withers.
Heavy trucks
The breeds of horses for heavy vehicles are one of the oldest in the world. These are large and strong horses, capable of dragging huge loads. The heavy truck looks like a powerful, often bore-footed horse, landing of the hull is low. It doesn’t move very fast, in no hurry.
Among these varieties there are real champions in weight and height.Here are the representatives:
- Dastrier;
- Schleswing;
- Black Forest;
- Bityug;
- Brabanson;
- Lithuanian heavy truck;
- Shair, or Shair;
- Kleidesdal;
- Tori;
- New Aleksandrovskaya;
- Tinker;
- Boulogne.
Having lost their practical significance, many breeds of heavy horses began to disappear. Active work is underway in France, Germany, Scandinavian countries, and Russia to conserve these varieties.
Harnessing horses
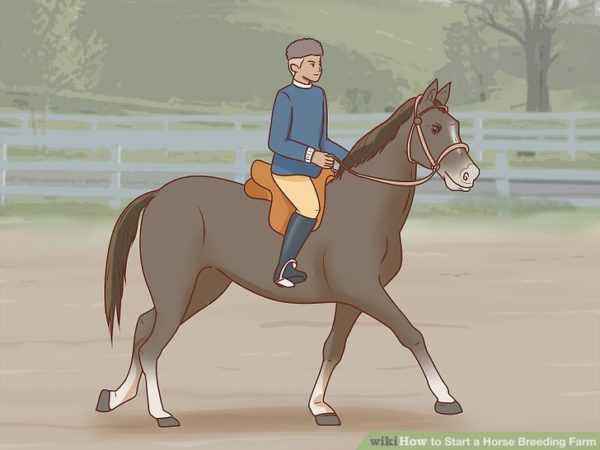
An important part of using a horse is harnessing Whether outfitting. The riding is a saddle in which the rider can sit. Under it lay voltrap to the saddle is not rubbed the horse’s back. The body covers the blanket or belt. Its function is protection against the cold. For example, in Siberia or Arkhangelsk there are real severe frosts, you can not do without blankets in this case. Fastens the saddle cinch. It is a wide belt that spans the props and fastens on both sides of the saddle.
The bridle and halter are fixed to the horse’s face. The bridle has a bit, snaffle, mouthpiece, which are attached to the animal’s mouth. A halter is a bridle without fishing.Another kind of bridle – hakamor or hert, leather braid without iron, is long and short. To control, they also use a dowel, schenkel or martingale, a sliding motive of chambon. The rope is tied at one end to a cinch, at the other – to the bridle, does not allow the horse to raise its head to a horizontal position and stand on its hind legs. A hobbled mare is tied with a rope called a chumbur or a champ. In order to prevent the horse from being scared, blinkers should be lowered into the eyes. The legs protect the nails, and the ligaments protect the soft bandages.
Harnesses for pack horses are arc and arcless, one-window and two-window. In such teams, a clamp, brace, lining, martins, underbelly, reins, chest belts are used. There is also a mixed version, where the root horse is harnessed to the arch, and the draw horse without it. Ammunition is made of leather and metal, arcs are made of wood.
How to harness a horse to a wagon, shafts or sledges? It is necessary to carefully study the scheme, see how this is done in practice. Without experience and skill, this is difficult to do, because the horse often snorts and butts.
Maintenance and care
You should learn everything about horses before starting these animals or just go horse riding. Keep animals in stables that have:
- Stall. The room where the horse stays temporarily, eats, inspects and brushes. There are no partitions in the stall, it is a closed paddock with a strap for tying horses and a manger for food.
- The stall. A house or a place where the horse lives constantly. Its area is 3.6 × 3.6 cm, so that even a lying mare fits there. A separate stall is made for each domestic horse, blocking it with incomplete lattice partitions. Instead of a lattice, there may be weaving. Doors are designed in such a way that the horse couldn’t open them independently, with a height of not more than 1.1 m. You can exit the stall to the general gallery or directly to the street.
- Territory or levada for walking. The area is 100-200 m².
The stables are no less than 2.6 m high. The floor is best made concrete with a rubber coating. Litter is made of straw. In the stalls, gutters are installed to drain liquid waste, then manure needs to be less frequently removed. They clean the stalls daily, completely change the litter once a week.
Direct care of the horse with your own hands includes:
- body cleaning;
- combing the mane and tail, its you can braid;
- cleaning hooves;
- bathing;
- forging;
- special attention is paid to the teeth of the horse.
For cleaning use a natural brush with a stiff bristle, it is desirable that the horse is confused. Start from the head on the left side, go to the sides, back and croup. Repeat the procedure on the right side, scratch the mane and tail, you can also braid them (horse hairstyle can be very interesting). At the end, hoofs and legs are cleared.To clean the hooves use special brushes, sticks and hooks, cream for lubrication. Only a professional can forge a horse, do not do it yourself. A shod horse is less likely to damage hooves.
Feeding
The health of horses depends on proper feeding. Many owners also want to know how much it costs to feed an animal. The horse’s daily or daily ration, which weighs about half a ton, consists of the following products:
- hay (the best option is clover with legumes or meadow) – 10-13 kg;
- oats, granola, cereal mixes – 5 kg;
- bran from oats or wheat – 1-1.5 kg;
- carrots – 2-3 kg.
Together with the carrot, the animal can eat other vegetables. Be sure to include regular salt, vitamin supplements in the diet. The horse’s annual diet consists of:
- 4-5 tons of selected hay;
- 2 tons of grain mixture or oats;
- 0.5 tons of carrots and others vegetables;
- 13 kg of salt.
In summer, a horse can graze on a pasture, while the amount of hay is reduced, but not completely removed. You can not immediately put the horse on green feed, this should be done gradually. Before you let the horses fast, you should feed the hay well. It is necessary to ensure that the food is fresh, without signs of decay and mold, poisonous plants are not found in the hay. Thoroughbred horses are quite fastidious in their diet, with their own tastes.
Animals are fed several times a day.A horse drinks 60-80 liters per day, suitable for drinking a bucket or a small barrel. Do not give too much horse drink immediately after exercise, this can negatively affect digestion. The horse is given water before eating so that the food is better absorbed. From open sources, domestic horses can only drink when there is complete confidence in the quality of the water. Since it is difficult to find such reservoirs, it is better to train a horse to drink only at home.
Breeding
In order to breed domestic horses, you need to have a lot of experience. Thoroughbred specimens should be knitted exclusively in accordance with the breeding parameters with the permission of the relevant organizations. Before mating, selection or scoring is carried out, as well as chipping and registration for couples and broods. Males unfit for breeding are neutered, their branding is necessarily carried out. The stallions that were castrated are called horses.
Mares are ready for breeding at 3-4 years old, the stallion is considered sexually mature at 3 years old. The main conditions for successful mating is the hunting of the female. The best time for horse mating is from March to June.
There are several ways of mating:
- hand knitting;
- cooking;
- mowing;
- artificial insemination.
When manually mating, a mare in hunting is brought to a special area. Two trained assistants hold her by the bridle with her own hands.A stallion who will sit on a female is let down behind. He throws out the seed after about 3 minutes, after which the mating must be stopped. The stallions are led away to their place, and the mare is walked for half an hour. The control mating is carried out after three days.
When cooking mating, the stallion with the mare is closed for several days in the fence. Intercourse occurs naturally, but the percentage of fertilization is lower. The kosyachny technique is somewhat similar to the cooking. A herd or herd of 20-25 females and one pedigree stallion is formed. It is found in a pen or in a separate pasture throughout the breeding season. The stallion itself selects mares in the hunt and mates with them. The method is productive, but it is difficult to plan signs of offspring.
Artificial insemination of domestic horses is carried out at stations using special tools. It is used in cases where it is necessary to impregnate a female with sperm of an elite stallion, and he is at a great distance. The advantage of the method is that mares are less likely to be injured, they are not transmitted sexual diseases. The percentage of positive results is high.
Pregnancy of a horse lasts 330-350 days, it gives birth to one foal, very rarely – two.
Diseases of horses
and horse diseases come in many different types. It is important to know their names and the main unusual symptoms in order to contact the veterinarian on time.Self-medication is not necessary, it can cause complications and even death of a domestic horse.
Diseases can be infectious and non-infectious.
Infectious diseases and helminth infections
Infectious pathologies can be caused by bacteria, viruses and helminths. Transmitted through water and food, insect bite, air. Here are the most common equine diseases:
- glanders, for the diagnosis of which malleinization is used;
- infectious pleuropneumonia;
- washes;
- infectious anemia or INAN;
- brucellosis or infectious abortion;
- viral or protozoal encephalomyelitis;
- adenovirus infection;
- swamp fever;
- leptospirosis;
- rabies.
In bacterial infections, in order to prevent the horse from falling down, antibiotics are given in large doses. There are few specific antiviral effective agents, therefore horses are treated, removing intoxication and symptoms. Immunomodulators can accelerate recovery.
The best infection prevention is vaccination. Not to vaccinate a horse is a murder, and a mad mare is also dangerous for humans. To control insects, they use repellent.
Of the parasitic pathologies in horses there are:
- parascaridosis;
- strongyloidosis;
- oxyurosis;
- diphylobotriosis ;
- pinworms;
- alfortiosis;
- anoplocephalidoses;
- rhinestrosis;
- onchocerciasis;
- paraphilariosis;
- pyroplasmosis;
- nuttalliosis;
- gastrostylosis.
Piperazine, fenbendazole are used to treat helminthiasis , phenylbutazone, albendazole, ivermek, flax seeds and other antiparasitic drugs. Drugs are given as a preventive measure. For the benefit of the animal, a specialist should choose a medicine.
Non-communicable diseases
Noncommunicable diseases of horses are often associated with improper maintenance and nutrition, horses can make them unnecessary. Many arise due to heredity, age. The reasons for the large number of such pathologies have not yet been elucidated.The most common somatic non-communicable diseases:
- tympanitis or tympanum;
- cataracts and other eye diseases;
- flu;
- bronchitis;
- anemia;
- vascular aneurysm;
- edema;
- intestinal colic;
- non-infectious diarrhea or diarrhea;
- hepatitis;
- cryptorchidism;
- bronchitis;
- rhinitis;
- rhinopneumonia;
- allergy;
- anestrus;
- myoglobinuria;
- Wobbler’s syndrome;
- mastitis;
- dermatitis and biting midges;
- diseases of the joints in which they give chondroprotectors, powder Stride, adekvan, chionat, bonharen and rotivovospalitelnye; ankylosis, arthritis, rheumatism, osteoporosis, brockdown, bursitis;
- purulent inflammation of the hooves;
- split hoof;
- clubfoot;
- pathology teeth;
- abscess;
- bear’s roll;
- malignant tumors.
Signs of somatic pathologies can be erased. Diseases develop gradually, symptoms do not always fit into the classical clinical picture. Even a baby with a birth defect cannot always be detected. Without the participation of an experienced veterinarian, it is impossible to diagnose them. Only a doctor can prescribe an injection, syrup, tablets, inhaler, etc. If the horse cannot be cured, it is cut or sent to the slaughter.
Modern use of horses
Gone are the days when people could not imagine life without horses .The horse allowed the peasant to feed his family, the cabman – to get good earnings. Equipment of military companies, ordinary transportation, could not do without horses, they received meat and milk. A drop in the number of livestock began to be observed a century ago.
Most often, horses take part in sports. This race, and racing with carts, and dressage, and show jumping, and vaulting, and trail. You can teach horses to perform in a circus, but more often they are used for horseback riding. Often horses are taken to parks and rides everyone there. This is a good way to make money, but you cannot name it a profitable business. Skidjoring is becoming popular. Toy horses like Braer, bouncers, pedal carts are very fond of children.
Recently, horses have been used in the treatment of children with cerebral palsy, people after serious injuries. A horse becomes a true friend of children, brings them a lot of joy, and sometimes cries when parting.
In many regions of Russia and other countries, horses still plow land, transport goods and are indispensable in agriculture.
How much is a horse? Any thoroughbred horse is very expensive, it costs a fortune. Price ranges from a few thousand dollars to millions. An ordinary horse without a pedigree can be bought for 100-200 thousand rubles. The maintenance will cost 1-2 thousand rubles. per day, depending on the season, breed and other factors.A drafty or pit horse is usually cheaper to maintain than a horse, it will earn on itself. Training horses at racetracks are also not too expensive.