Most cattle breeders who do not have enough knowledge can often take the usual condition of the animal as painful. And vice versa: due to a lack of knowledge, one cannot respond in time to the development of a particular ailment that can cause significant harm to the entire population.It is precisely because of the untimely request for specialized help that often the formation of neglect of most dangerous diseases that can not only harm health but also cause death.
- Definition signs of the disease
- Features of the progression of the disease
- Possibility of infection
- Description of the clinical picture of the disease
- Methods for diagnosing the disease
- Infection control
- Finally

Foot and mouth disease in a cow
Based on this, for each owner it is extremely important to have a basic information about the most common types of diseases and infections that can harm livestock. So, for example, it is very important to have information about the danger that foot-and-mouth disease in a cow is fraught with, as well as to have at least a general idea of how to deal with this problem.
Identification of signs of the disease
In essence, foot and mouth disease belongs to the category of cow diseases of a viral-infectious nature, manifested through pathological processes that can occur both in the body of the domestic and in the body of wild representatives of cattle.To date, this disease has a number of identified and structured signs that appear regardless of the species of animals that the virus infects. In the list of these signs, one can distinguish:
- the presence of febrile seizure;
- when the mucous membranes in the mouth, nipples, crevices between the hooves are affected;
- damage skeletal muscle in young cattle.
The danger is that in the world there have been more than one cases of infection of the human lizard virus, and in this case the risk category was mainly formed by children.
Foot and mouth disease of cows is annually recorded in the vast majority of countries of the world, so be completely confident in safety and ignore new precautionary rules should not be. That is why the damage received by industry as a result of the spread of the disease is summed up, and to familiarize specialists and the public, figures are annually shown that indicate problems with a drop in fatness, milk yield from a particular cow, a significant drop in the quality indicators of the products being manufactured. It is safe to say that the disease of foot and mouth disease in cows, due to its massive spread, introduces significant inconvenience to natural economic activity not only in certain territories, but also in entire states, where agriculture and animal husbandry are often a priority branch of the economy.
Features of disease progression
The virus organism, which belongs to the category of causative agents of foot and mouth disease in cows, contains RNA. To date, 7 certificates and more than 70 varieties of viruses provoking this disease have been identified and studied. The presence of typologies and varieties exhibiting bacterial particles can also have a number of immunological features.
- Immunity of each variant of the virus that provokes cattle diseases in relation to other species and varieties.
- Foot and mouth disease It is particularly resistant.
- The surface of the skin of cows covered with hair is able to retain live viruses for 50 days, while in the case of feed or soil layer we can talk about a shelf life of almost six months.
Described These signs clearly indicate a special “survivability” of the virus, which significantly complicates the treatment process. To ensure their own safety, people in contact with sick animals can process clothes with hot steam, which leads to lightning-fast elimination of the complementary activity of viruses. In addition, they demonstrate the high efficiency of the treatment agent in the form of a solution that includes caustic soda and formalin.
The manifestation of the first signs of foot and mouth disease in cows should be an occasion not only for taking treatment measures, but also for protect the health of the herder.
Possibility of infection
There are many ways through which the virus is transmitted, and all of them are obvious. First of all, it should be remembered that the causative agent of the virus often lives on the surface of the outer clothing of a person who has been in contact with sick animals. Given the fact that foot and mouth disease can survive even in conditions of prolonged transportation, the possibility of its production during this period is extremely high. Another very common route of transmission of this virus is through contaminated feed provided by an unscrupulous supplier or seller. It is under these conditions that the disease receives the most favorable conditions for development.
When the virus leaves the area of initial reproduction, the viral cells penetrate the bloodstream and, together with it, are transported throughout the body, affecting the organs of the immune system, blocking the necessary response from organism. In addition, a feature of the virus is its concentration in the zone of the heart muscle, as well as the skeleton muscles, followed by changes in their work. Based on this intervention, the process of deformation of the tissue fiber of the heart muscles occurs with a negative impact on their functionality, as well as performance.
Description of the clinical picture of the disease
foot and mouth disease as a disease has a special clinical picture. So, the incubation period of the virus rarely exceeds 1 week, after which the first symptoms begin to appear. Moreover, cases were previously recorded when the incubation period exceeded a three-week rate. At the same time, as already mentioned above, the symptoms and signs that the disease has are always the same, and mainly consist in the following:
- An increase in body temperature to indicators exceeding the 40 ° C mark.
- The presence of a depressed mood in the cow.
- Reduced daily milk production, which cattle demonstrates.
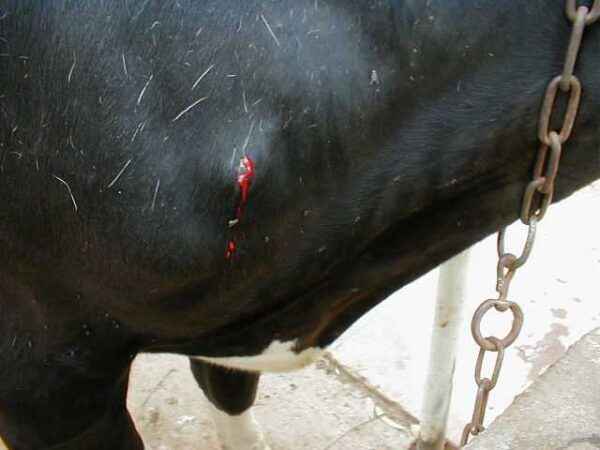
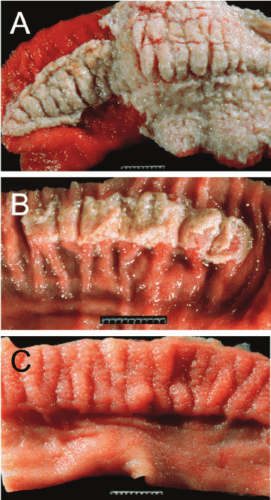
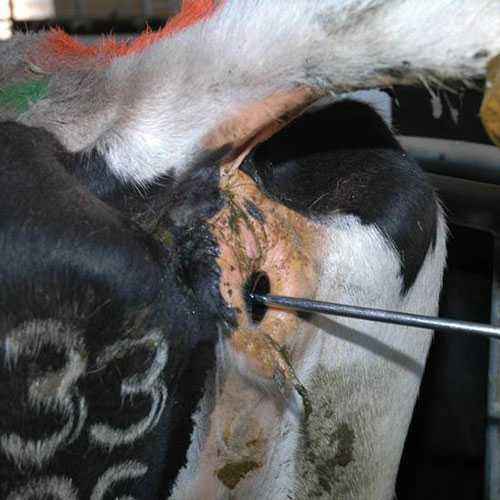
- Appearance in the oral cavity, as well as on the surfaces of the tongue, in the nasal passage of the vesicles inside which there is a liquid – aphtha, while on the first pairs this liquid is transparent, and after a while it becomes cloudy . These neoplasms burst often in three days.
- The appearance of neoplasms (aphthae) in inter-experimental spaces, crevices and corollas: after rupture, such aphthae form ulcers, together with the escaping fluid, spreading the virus, which can infect in the shortest possible time not only nearby animals, but also the person who cares for the livestock.
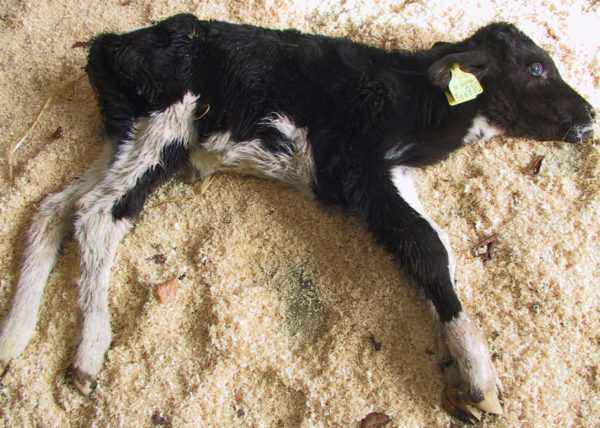
The body of a young cow reacts to development in a slightly different way. Newborn calves rarely suffer from the formation of aphthae, and the clinical picture is generally similar to gastroenteritis.It is for calves that such a disease poses the greatest threat, because, based on statistics, we can talk about their extremely low survival rate. With full confidence, it can be argued that the degree of danger of foot and mouth disease for humans and animals is equal. hemorrhagic inflammation, purulent mastitis, as well as the presence of bruising in the peritoneum and intestines. Such a disease affects most organs and systems, leaving the animals a minimal chance of recovery, because in situations of neglect, treatment does not bring any results.
Methods for diagnosing the disease
to determine the presence of a problem, it is necessary to carefully monitor external signs. In this case, confirmation of the diagnosis, as well as further treatment can be carried out only on the basis of a laboratory study taken from animal biological material. A laboratory study aims to identify and establish the type of virus that provoked the disease.
The next point after the diagnosis should be the choice of the substance, which will be used for vaccination, based on the data obtained.It is important that before the vaccine is introduced, the animal should exclude other diseases that are similar in nature to the lizard, since such vaccination will not only fail, but can also cause significant damage to health, which will make the treatment even more problematic.
So, a person who does not have sufficient experience can easily confuse foot and mouth disease with the following ailments of a microbial nature:
- ulcerative erosive inflammation of the epithelial tissue in the digestive tract;
- viral vesicular stomatitis;
- smallpox e rashes and so on.
In order to exclude such errors, the specialist must clearly follow the instructions.
Fight against infection
An effective treatment for foot and mouth disease in cows is vaccination. Today, due to the wide variety of types of viruses that provoke this ailment, pharmaceutical companies do not produce medical therapeutic drugs that are directly aimed at destroying the virus. It is considered correct to treat the symptoms, while the fight against the pathogen is at the mercy of the immune system. At the same time, vaccinations demonstrate high efficiency, due to the timeliness of which the immune system reacts faster to the manifestation of viral activity.
Most cattle breeders give vaccinations only when all signs of the disease are on the face. Although this approach is popular, it has a number of significant drawbacks.First of all, there is the problem of choosing a vaccine, because for effectiveness it should contain exactly the type of virus that is in the body of the animal. In addition, individual immunization cannot prevent the transmission of the virus to the rest of the livestock. A method that is able to give the desired protective effect is based on the simultaneous immunization of all types of cattle that lives in the farmyard.
During mass manifestations of the primary sign of foot and mouth disease in cattle, its treatment is not expected, since in this case the destruction is appropriate all animals in order to stop the spread of the virus among others. Those representatives of the livestock who do not show signs of the disease are recommended to be slaughtered, because in this situation the meat is quite suitable for use in food, otherwise special authorities can forcibly transfer all individuals to special enterprises where animals are exterminated.
The treatment process of foot and mouth disease must be characterized by efficiency and compliance with all norms and rules. The bottom line is that the period in which the sick animal can receive treatment and heal is very short, and in some cases does not exceed a day. The recognition of the disease allows you to stop the viral infection in time, which carries the danger of all living creatures living in the farmstead, as well as the people who provide it with daily care.
In conclusion
Animal instinct does not imply an active demonstration by the cattle of the symptoms of the disease, so mindfulness is the main thing in this case. Diagnosing the problem, among other things, involves a series of procedures aimed at disinfection.
So, manure must be destroyed, as well as milk received from a sick cow, since these products of the vital activity of an infected animal are highly likely to contain viruses that are ready at any time to hit a new body with a disease that most often ends in death. Based on the foregoing, we can confidently say that the effective control of foot and mouth disease largely depends on the timeliness of actions.