The content of the cows includes a large number of features. The breeder should properly equip the barn, organize a balanced diet and regularly carry out veterinary preventive measures. If the main purpose of breeding cows is to get milk, you should also know what is the dry period. The dry period in cows is the prenatal period of time, which is characterized by the active development of the fetus.
- Physiological factors of the dry period
- Why you should choose special diets for dry cows
- How cows are introduced to the dead wood group
- Features of feeding cows in the dry season
- Feeding cows during the rest period
- Nutrition during the transitional period
- Feeding rate
- Nutrition of feeds
- Diet for the day
- Conclusion
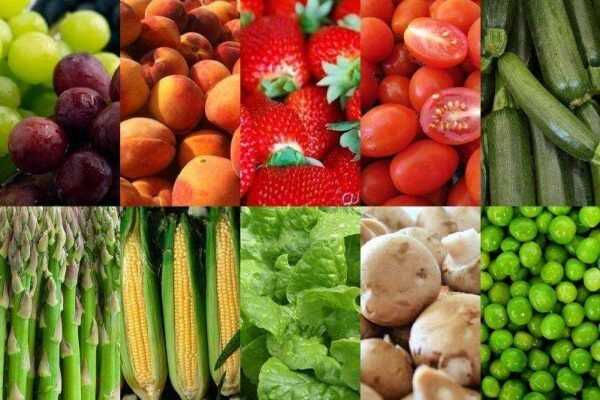
In order for the calf to grow strong and healthy, it is important to provide his mother with food rich in vitamins and minerals. During the dry season, vitamins in the feed are much less than in fresh hay. In addition to hay, special additives must be added to the diet of the cow in the first dry period. Every day,
Physiological factors of the dry period
The dry period falls on the last 2 months of the pregnancy of the cows. This is due to physiological changes that occur during gestation. As in humans, pregnancy in livestock has the same duration of 9 months. After fertilization, the embryo develops slowly.Externally, during the first 6-7 months, signs of pregnancy are subtle. At this time, the fetus gains only a fifth of its mass – 6-8 kg, but in the last 8-9 weeks there has been a sharp increase in growth. The cow itself suffers from such activity.
In cows during the dry period, metabolism is accelerated. Cattle expends its own forces on the ripening of the fetus, losing a large number of useful trace elements. The farmer’s task is to make up for them. This can be done by organizing the proper feeding of pregnant cows. Without human help, the cow begins to lose weight, and calving can cause problems. In addition to complex births, poor calf immunity is also possible. For livestock purposes, this must be monitored, therefore, it is necessary to calculate the ration in starting cows not only in quality, but also in quantity, because excessive feeding is a direct path to obesity, and this can also affect the course of labor.
Why you should choose special diets for dry cows
Specially selected diets for cows of this period can improve the health of the fetus and its mother. A balanced diet also allows you to:
- maintain normal weight of the animal and influence its postpartum productivity;
- reduce the risk of mastitis and postpartum paresis;
- strengthen cardio -vascular and nervous system of a cow.
Cows in dead wood most often have a shortage of useful trace elements.The most important in the process of bearing and ripening the fetus is selenium, as well as vitamins A, E and D. All of their animals can get through food. The main thing is to know what products they contain and how to use them rationally.
How cows are introduced to the deadwood group
The content of a pregnant cow differs little from the content of ordinary ones, it is not yet fertilized animals. Such care lasts up to 7 months of gestation. It is during this period that it is necessary to prepare a reliable basis for the health of the hatched calf. The transfer of cows (to dead wood) is most often carried out medically. Such a scheme requires knowledge and the implementation of certain measures that will ensure the greatest efficiency of the whole process. The farmer should:
- Select low-fat diets or remove them. Feeding dry cows should affect the reduction of milk production.
- Remove tubers and root crops from the diet of dairy cattle.
- Reduce the silage content to 20%.
- Exclude from the diet for dry cows food waste from which lactation is activated.
If dry cows are organized such a “diet menu”, this will affect the volume of their milk. If all the preparatory measures do not give a result, it is necessary to reduce concentrated feeds.
Features of feeding cows in the dry season
There are 2 periods for these cows: rest and transition.Their features depend on individual physiological factors. The animal organism can enter a period of rest 7-8 weeks before childbirth, and a transitional period – 2-3. Each cattle breeder needs to know about the features of this important time in the life of a cow, since the health of the livestock depends on how its content and feeding are well-organized. to avoid obesity. This is the main task of the breeder.
In the transition period, the amount of nutritious feed should be increased. This need is associated with replenishment of the energy reserve spent on the active growth of the fetus. Nutrient diets also help to avoid complications during childbirth.
Feeding cows during the rest period
The dry period of rest is accompanied by an active weight gain of dairy cows. In order to avoid obesity, you should give her more products such as:
- haylage;
- hay;
- premixes;
- silo.
The diet of dry cows from these products has a low calorie content and a high content of vitamins and minerals. It is important to use only high-quality feed purchased at specialized points of sale.
Food during the transition period
The dry transition period also has its own characteristics.Experts advise in the last 2-3 weeks before birth to increase the nutritional value of feed. From the feed ration, 2 times of 3-4 kg of hay should be replaced by concentrated feed. For these purposes, specialized feed is best suited. It can be prepared independently, but only if you know all the proportions in composition.
Feeding dairy cows (during dry periods) requires more careful control over the mass of food that the animal consumes. In anticipation of labor, the animal’s appetite noticeably worsens, so it’s important to provide it with nutritional supplements that will help to avoid labor and postpartum problems.
Feeding rate
The cows will have a dry period feed standards. This norm is expressed in units. The food consumed per day is calculated based on:
- Cow weight and its correct growth (per 100 g of weight – 1 unit). In cows during the dry season, an increase in live weight of 800–900 g is observed daily (deviations to the smaller and larger side indicate errors in the organization of the diet).
- Average annual milk productivity. For 1000 kg of milk yield – 1 unit.
- Fatness of livestock. If it should be increased, the feed norm increases by 2-3 units.
Nutrition of feeds
Proper maintenance and feeding of such animals plays an important role in ensuring labor safetyThe main thing is to keep the cow within the same range of body weight. The most effective way to do this is to regulate metabolic energy and digestible protein. This technology does not require special skills. The main thing is the ability to use reference materials. Some of them show the nutritional table of the feed.
Other useful trace elements such as copper, zinc, manganese, cobalt, iron, etc. are also important for dry animals. Their norm varies in different limits. For copper, one feed unit accounts for 5-14 mg, for phosphorus – 4-6 mg, and for iodine – up to 1.5 mg.
Daily ration
The duration of the dry period for each cow is different, as well as the portion sizes (the amount of feed depends on the weight of the animal, its productivity and fatness). Also, the feed itself can be different, since dry cows have two periods (rest and transition), therefore, the feeding of the animal should be calculated correctly. An example is a cow, which should produce 5 tons of milk per year. Her diet:
- haylage – 12 kg;
- silage – 11 kg;
- bean-cereal grain – 4000 g;
- hay – 2000 g;
- premix – 100 g;
- molasses feed – 500 g
Conclusion
If the dry period is shortened, then this carries unit development of the fetus, as well as milk production volume, so it is important to carefully monitor the diet of the animal and control its weight. Many farmers are advised not to give beginning to livestock Cows foods containing calcium. For dry animals this trace element is harmless, but if the cow consumes it in large volumes, it can be imprinted on the metabolic processes of its calf, so calcium is not recommended for dry cows.