How to treat a cow’s hoof ? What are the symptoms of such diseases and what are their causes? Such questions often arise among farmers, especially with little experience in breeding cattle. A veterinarian or zootechnician can give a detailed answer, but everyone who holds a cow should know the basic rules of care, signs of pathologies and treatment principles.
- Pathologies and the causes of their occurrence
- Corolla phlegmon
- Subdermatitis
- Aseptic subdermatitis
- Purulent subdermatitis
- Erosion of hooves
- Strawberry disease
- Injuries and injuries
- Lameness and pathology joints
Pathologies and the causes of their occurrence
Cow almost the entire spends life on its feet. Constantly presses the hooves.If improper care, they are damaged, an infection gets into the skin and the stratum corneum, inflammation occurs.The hoof consists of two halves with a blade in the middle. It is covered with horn tissue that grows all its life. In summer, the horn stitches off. In winter, this process slows down. because the hoof requires trimming.
Why can leg diseases occur in calves and cows? Previously, people believed that such a nuisance is a corruption or conspiracy. Now, of course, no one will attribute the trouble to evil spirits or evil people. There are several reasons for the pathology:
- Weakening of the immune system.
- Improper maintenance, dirt in the stable, hard bedding.
- Ignoring regular inspection and poor care.
- Incorrect feeding.
- Cattle walking on rocks and hard roads for long distances ..
They are especially sensitive to various infections and damaging factors of calves, therefore, young animals are examined at least as often as 2-3 times a week. Carefully adhere to hygiene in the stable, regulate the load during grazing, try not to drive the calves on hard roads. In winter, animals should not freeze. An ordinary stick is useful for cleaning hooves, and you need to trim them with a special knife. The treatment, which is carried out regularly, will help to avoid diseases, and treatment will not be needed.
Here are the main pathologies of the hooves:
- corolla phlegmon;
- aseptic pododermatitis;
- purulent pododermatitis;
- erosion;
- strawberry disease;
- wounds and injuries;
- lameness.
>
The correct treatment of diseases of hooves in cows and the prevention of pathologies allows maintaining milk production at the proper level. If you do not follow the limbs of animals, you can lose not only productivity, but also a whole herd, because when an adult or a calf completely stops their legs, animals often have to be slaughtered.
Phlegmon of the corolla
Phlegmon of the corolla is an inflammatory purulent process in the fiber, which is located under the skin. It occurs after damage and the entry of microbes into the wound, especially against a background of weakened immunity. Main symptoms:
- Cattle are limping.
- There is severe pain.
- There are signs of a tumor in front.
- The temperature rises.
- Appetite decreases.
- The depressed state of the animal appears.
- There is a low milk yield.
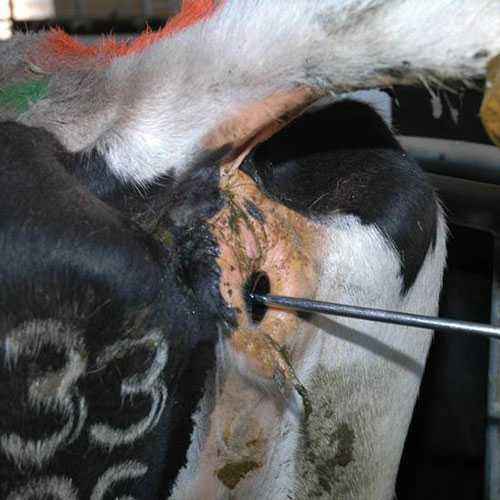
A sick cow needs complete rest and a daily change of bedding. Antibiotics are administered intramuscularly, urotropin and calcium chloride are dripped intravenously. Alcohol compresses are placed on the foot, Vishnevsky ointment, ichthyol ointment is applied, the antibiotic is treated or chipped off the sore spot. To relieve soreness, the affected area is pricked with novocaine. If an abscess forms in place of the phlegmon, it is necessary to open it.
Pododermatitis
Diseases of the hooves of cows called pododermatitis are inflammations of the skin base. They can be purulent or aseptic.
Aseptic pododermatitis
Aseptic pododermatitis can occur in serous or serous-fibrous form, be acute and chronic. The main causes of pathology are bruises, squeezing, walking on roads with stones, keeping on a hard bedding or hard floor. Symptoms of the disease:
- The cow stands with legs wide apart or crossed.
- The stratum corneum is yellow or purple, covered with spots.
- The temperature rises in a sore spot.
- On palpation, pain occurs.
- In the acute form, it is clear that the tissues are swollen, in chronic, the horny tissue is overdried, brittle, can be stratified.
Sick cattle are kept on a clean bed. First apply cold, and then warm compresses. The wound is treated with iodoform, rivanol or furatsilinom. With severe pain, when the leg is swollen, they are chipped with novocaine. You can make a salt bath, and then treat the hoof with an antiseptic. To prevent the disease from recurring, the conditions of cattle are changed, the heifers are grazed exclusively on grassy pastures with soft soil.
Purulent subdermatitis
Purulent subdermatitis can occur as an independent disease or aseptic complication . Often, the pathology is associated with infection in the wound. Often purulent pododermatitis sick calves. The main symptoms:
- Fever, both local and general.
- Lameness.
- Soreness on palpation.
- Cracks and wounds.
- Swelling and redness of the corolla.
- Fistulas and excretion of pus.
If purulent pododermatitis is detected, the calf is washed well with warm water and soap. treat the affected area with an antiseptic. Often there is a need to remove the stratum corneum within healthy tissues. After that, the site of the operation is carefully treated with an antiseptic, an antibiotic, and a clean dressing is applied. An antibiotic is also administered intramuscularly.
Erosion of the hooves
Erosion occurs with the uneven development of 2 parts of the hoof. An uneven load is created, which is why one half of the stratum corneum erases more.The disease is complicated by inflammation and suppuration, often occurs at a young age. If the calf falls to its feet, is limping, unstable, dragging the front or back limb, it is necessary to examine the hooves. It happens that with erosion, one leg becomes higher and the other lower.
Diagnosing erosion is quite easy. You can immediately notice that one part of the hoof is longer than the other. With an advanced disease, the stratum corneum becomes inflamed and suppurates. In order to cure the pathology, a special heel is applied to the healthy part, which reduces the load and promotes further more uniform growth of the hoof. It is imperative to regularly clean the cow’s legs, graze it in meadows with soft soil, and change bedding several times a week.
Strawberry disease
There are still no reasons for this disease found out. Most veterinarians associate it with improper care and maintenance. The base of the hoof and the skin around the corolla are affected. The name “strawberry” is due to the fact that red tubercles and a tumor appear on the skin and corolla, in appearance resembling strawberries. The main symptoms of this disease of bovine hooves are:
- lameness;
- swelling of the affected area;
- characteristic changes in the skin.
There is no specific treatment for the disease. A vaccine was invented, but it was ineffective.The problem is often solved by itself, if you change the conditions of detention, regularly change the litter, feed the cattle with a quality and balanced feed. It is important to keep the hooves clean, you can periodically treat the sore spot with an antiseptic.
Injuries and injuries
Injuries and bruises are common problems that arise with the hooves of cows. An animal can damage its legs in a pasture, against sharp branches, twigs, in fights among themselves (this is primarily characteristic of a bull or a growing calf). If the hoof is wounded, it swells, bleeds, and lameness appears. In this case, you need to immediately treat the wound with an antiseptic, bandage so that suppuration does not occur. Until the cow recovers, it must be kept in a stall on a clean litter.
Bruising may occur if the cattle fell, hit a hard surface. With bruises, visible tissue damage is not noticeable. Hematoma, edema may occur under the skin, movements will be limited. With bruises, a cold compress is needed, complete rest. If muscles, tendons or ligaments are damaged, the cow has dislocated leg, a tight bandage should be applied. To relieve pain, a bruised place is punctured with novocaine. In fractures (open or closed), the leg is immobilized.
Lameness and joint pathology
Lameness in cattle can occur due to prolonged confinement without sufficient movement.With this disease of cow hooves, the horn grows, this prevents the animal from moving normally. If you do not help, the tissues become inflamed, they can suppurate.
It is unlikely that you will be able to properly cut the hoof yourself, it is better to consult a specialist. The cow is placed in a special installation, the limb is fixed. An excess layer of the horn is cut off with a mechanical or electric knife, having previously cleaned it. At the end, the cut site is treated with an antiseptic.
Cow’s hoof disease can be combined with joint pathology. Arthritis develops with poor livestock, in damp conditions, after injuries. Old animals often suffer from the disease. Joints can become inflamed after injuries. Arthritis is serous and purulent. The main symptoms of the pathology:
- The joint swells, its shape changes, the legs swell.
- The joint is hot, with a purulent form there is a fever.
- The heifer cannot to stand or lie (when the legs are completely denied, the animal is kept in limbo).
- Behavior becomes apathetic, appetite decreases, milk yield decreases.
The treatment of joint lesions is rather difficult and long. The animals are given regular massage, they warm the diseased limb with an ultraviolet lamp. Compresses with anti-inflammatory drugs, ointments, local blockade with painkillers help. Best if treated by a skilled veterinarian. With purulent arthritis, they often resort to surgery, they perform joint puncture.