When breeding cattle farmers may have some difficulties. The most common question among all breeders is what kind of disease can be in cows and bulls? Indeed, a lot of different problems can be observed in animals, most often arising from improper care and breeding.Diseases and treatment of cows should not be ignored, since any ailment in animals requires the intervention of a veterinarian. It is necessary to understand, if possible, how to determine the disease at the initial stage of development, how to treat and prevent it.
- Causes of Disease in Cattle
- Foot and mouth disease in bulls and cows
- Smallpox in cows
- Brucellosis in cattle
- Rabies cattle
- Non-communicable diseases of cows and bulls
- Inflammation of the lungs
- Hypodermatosis in cattle
- Traumatic reticulitis and pericarditis
- mastitis in cows
- Atonia Gastric
- Conclusion <

Diseases of cows and bulls
Diseases of cows most often occur due to the occurrence of infectious microbes viruses or parasites. In this case, you need to have separate pens in the room where you can quarantine diseased individuals. If you keep sick and healthy cows and bulls together, then with a viral infection, the entire population can cover one disease. Among the most insidious ailments, radiation sickness, various inflammations of the udder, mastitis, rabies, rashes such as smallpox, heme are distinguished.
Non-communicable diseases are not so insidious, but they can knock down the whole herd. Such diseases include postpartum problems arising from poor maintenance or inadequate monitoring of animals, as well as problems with milk production, stone disease is desirable.
Causes of diseases in cattle
- Inadequate living and housing conditions. In colder climates and in unheated rooms, cows may get udder, especially during lactation.
- Wet and dirty flooring can provoke peculiar lichen and inflammation.
- Poor room ventilation creates a favorable environment for the development of any disease, especially viral.
- Poor, poor diet leads to major problems with digestion and vitamin deficiency.
- Under inappropriate conditions of keeping cows and bulls can pick up almost any disease. Most often these are colds with fever.
Foot and mouth disease in bulls and cows
Infectious infections and fungal diseases of cows and bulls can be dangerous for animals, as they spread throughout the herd, but also for humans. Infectious diseases in cows often occur, and the most dangerous is foot and mouth disease. Such a disease begins with the fact that only 1 or 2 cows become infected, then the disease can spread to the whole herd.Foot and mouth disease from a bull or a cow can be picked up by a person, moreover, he willingly infects children, therefore, when working with a sick individual, maximum caution should be exercised. The main signs of the appearance of foot and mouth disease are a decrease in milk yield, a decrease in the appetite of the cow, an increase in the body temperature of the animal.
Further, teeth creaking, salivation, and, in some cases, cracking of the nipples may appear. It is worth paying attention to where to start treatment: first of all, you need to invite a veterinarian, since foot and mouth disease is a complex disease and it is not worth treating it yourself. In the early stages of development, foot and mouth disease is successfully treated with antibiotics. The main thing is to notice the symptoms in time and proceed to treatment.
When inflammatory processes appear on the skin, many veterinarians prescribe treatment with disinfectants, for example, iodine, potassium permanganate, and acetic acid solution are popular for such purposes. If symptoms of the disease are observed in only one individual, it should be placed temporarily in a separate pen. If you keep sick and healthy individuals together, there is a risk of spreading the disease to the whole herd.
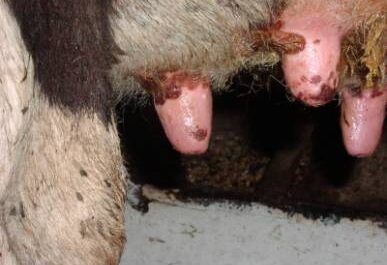
Smallpox in cows
Basically, this disease occurs in young cattle aged 6- 8 months. Such an ailment is not uncommon. It is easiest to notice smallpox in young heifers after calving, as warts appear on the udder of the nipples. Such formations on the genitals lead to the fact that milk yield is significantly reduced, the fat content of milk becomes less.There should be no scabs, warts and inflammations on the genitals. Bulls have warts on their stomachs. Smallpox leads to the fact that the quality of milk begins to change. Animals themselves can refuse to eat and be passive.
The incubation period in smallpox lasts from about 4 to 8 days, after cows and bulls there may be an increase in body temperature, roseols form on the skin over time, which grow into papules . Infectious growths in young animals, the so-called pustules, are different. It is possible to carry out treatment for smallpox at home. To do this, farmers first clean pustules with cotton soaked in collodion. Then you can lubricate the warts with boron or zinc ointment.
As a prophylaxis, it is recommended to put the smallpox vaccine. The peculiarity of the vaccine is that it protects against infection. This method is carried out in the form of injections and is prescribed by the veterinarian. To prevent the development of smallpox in the pen, it is worth paying attention to maintaining cleanliness in the room and animal hygiene. Home care should be appropriate and timely. You can look at the photo or video of the growths in cattle during smallpox.
Bovine brucellosis cattle
Among the diseases in cows is infectious brucellosis, which is developing rapidly and is considered very dangerous. A week after infection, cattle may experience a situation where the entire lymphatic system, as well as the gastrointestinal tract, is swollen. Signs of brucellosis can still be seen on the udder. In the third week after infection, if the disease is started and not treated, damage to the liver, spleen, all lymph nodes, and even the eyes occurs. It is recommended to carefully monitor pregnant females, since brucellosis lesions mainly occur in this category of animals. Young animals rarely get sick with this disease.If a pregnant female has caught brucellosis, then it can cause a miscarriage.
Brucellosis is so insidious that even exposure to low temperatures in the animal room will not help get rid of it. The disease can occur in heated pens, and in cold ones. Such an ailment can occur in a latent form from one week to several months. The first noticeable symptoms of brucellosis are gynecological.
There are gynecological processes in the uterus, develop pathology of the fetal membrane. A veterinarian with experience is needed to diagnose the disease. Brucellosis is diagnosed using bacteriological studies. So that pregnant females do not undergo such an ailment, a veterinarian should be invited for preventive examinations and for sampling tests at least 1 time within 3 months. As a prophylaxis, it is recommended to maintain optimal conditions for living and keeping cattle.
Rabies of the bovine cattle
There are symptoms that it’s impossible not to notice, you need to know their description. There is nothing simpler than recognizing rabies in cattle. There are manifestations in animals immediately after infection, sometimes it may take some time. Rabies is manifested in cattle in the literal sense of the inappropriate behavior of animals. If the cows are sick, they can throw themselves at people, do not eat normal food, chew rags or bedding, and behave inappropriately.
A certain part of the brain is affected that interferes with its normal functioning. The animal may begin to salivate, become aggravated, or, conversely, a sense of fear disappears. Sources of infection with such an insidious disease are still unknown. There is no cure as such. To examine the whole herd for rabies, you need to invite a veterinarian.
Non-communicable diseases of cows and bulls
Many farmers believe that non-communicable diseases are not so insidious and can be treated, slowly. This is actually not the case. Although diseases are not transmitted as an infection, infection can cause significant damage to the farmer. The disease affects the number of milk yields. Each farmer should know the description of such diseases at least briefly, so that with possible symptoms he should know how to treat his burenka and in what form to give these or those medicines. how many diseases have similar symptoms and it is quite difficult for an inexperienced person to recognize an ailment. The veterinarian will also take the necessary tests and, based on their results, will confirm or deny the presence of the disease.
Inflammation of the lungs
A sign of lung inflammation is primarily a cough for 4-12 weeks. Inflammation of the lung occurs in animals that live in inappropriate conditions.If the conditions of detention do not meet the requirements, the disease will spread – after some time it will be confirmed in another cow, and then in another.
If cattle have a cough, this symptom should not be missed. Of course, coughing does not mean that animals have pneumonia, but if you skip treatment of individuals at this stage, then the disease will soon go into the chronic phase.
In animals, there may be an increase in body temperature up to 40 ° C and diarrhea. Only a veterinarian should treat pneumonia. Antibiotics are usually prescribed, but if you take the risk to give them yourself, this will be a big mistake. The fact is that even an effective medicine, chosen incorrectly for a particular cow, can only worsen the situation. The veterinarian prescribes antibiotics taking into account the characteristics of the disease and condition, the weight of the animal and the presence of related factors. Lung inflammation spreads most often in rooms where there is a damp and cold floor, wet and dirty litter, and there is a lack of normal air ventilation. Individuals who are deprived of daily walks and have a deficiency of vitamin A are sick.
Hypodermatosis in cattle
Carriers and ticks can be carriers of this disease. Infection occurs in the summer, when the period of activity is observed in insects. They accumulate mainly in the place where the animal has thin skin, for example, in the area around the eyes or on the limbs. Eye places are the most favorite among parasites.Insects can bring not only hypodermatosis into the eye area, but also many other diseases.
Constantly biting ticks or gadflies around the eyes causes dirt and infections to enter the wounds. The animal is combing the bite.
Prevention of the disease is to regularly inspect the cattle for bites and hanging ticks. If insects are found, they must be removed from cattle skin. Wounds and combed places should be treated with special tools. Many farmers carry out special autumn antiparasitic treatments.
Traumatic reticulitis and pericarditis
Another disease that causes problems in the gastrointestinal tract is reticulitis. If an individual swallows a foreign object, and this happens in corrals where conditions of detention are not met, then it may have the following symptoms: muscle weakness, especially if it is a calf only after calving, which drags everything it finds into its mouth, and its body temperature is lowered , pelvic limbs summed up under the stomach. There is no lactating function, the animal is passive. In this case, surgical intervention is necessary. Prevention should be to clean pastures of objects that could harm livestock, especially metals and unnecessary things.
Pericarditis is considered a slightly different disease and results from traumatic injury. With this disease, you need to support the work of the cardiovascular system.The head of the cow is kept steady, the animal doesn’t particularly move it unnecessarily, the gait is very smooth, cautious, without sudden movements. When urinating and defecating, the animal may make moans. Genital damage may occur. In the absence of appetite and proper nutrition, the metabolic function is impaired. The disease must be treated in the early stages, first of all, the work of the heart should be supported. For this, a solution of caffeine with glucose is used. If such treatment yields a positive result, iodide or diuretic substances can be used for further treatment.
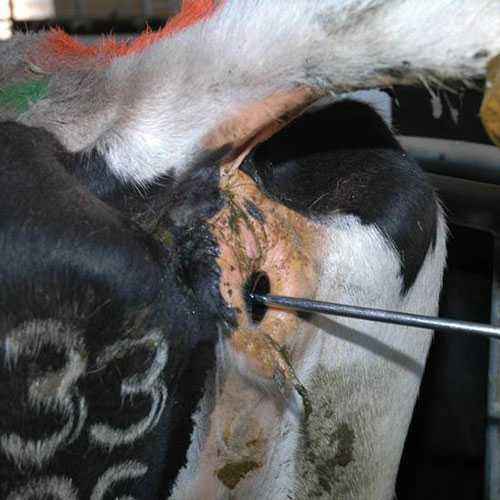
Mastitis in burenki
Mastitis is considered a disease that affects only females, most often after calving or while carrying a calf. There are times when mastitis can affect females due to inappropriate conditions of detention, for example, if the room is cold, damp, and poor nutrition. If it became noticeable that the milk of Burenka became somehow tasteless, has an unpleasant odor, or it contains clots or even pus, these are sure signs of mastitis. Prevention is to provide comfortable conditions for both the baby and the Burenka after calving.
First of all, after calving, the calf is allowed to let the colostrum go to him. This is necessary for the female and the calf. Milking a cow should be done only with clean hands, before each milking it is necessary to wash your hands with antibacterial soap and wipe the udder with warm water. After calving, swelling may form on the udder.
If you notice suspicious symptoms of mastitis, you need to show the burenka to a veterinarian. Mostly antibiotics are used to treat mastitis. During lactation, you can carry out a special massage of the udder so that the milk does not stagnate and the udder does not swell.
Atony of the pancreas
This disease occurs mainly in adults, like cows , and in bulls. Atony of the pancreas is a lack of muscle tone of the pancreas. Such a disease appears due to stagnation of food or its indigestion. Symptoms of the disease are: lethargy, sometimes apathy, lack of appetite, in some cases a temperature of about 40 ° C, a noticeable decrease in milk yield. If you do not give such symptoms significance, the disease goes into the next phase and can provoke intestinal obstruction.
There can be many reasons for the appearance of such an ailment, the most basic ones are feeding cattle with bad and poor-quality feeds, feeding only with solid feeds, straw or bad hay. Use of rotten potatoes and mold hay by animals.
Changing the type of feeding, especially in the autumn, provokes a certain resonance in the animal. If cattle were grazing all summer and fed only on fresh grass, and immediately began to be fed concentrates with the arrival of autumn, this could adversely affect the gastrointestinal tract of pets.
Infection with atony of the stomach can occur due to poor-quality water for a drink.You can only drink clean water at room temperature.
The treatment of such a disease should be comprehensive, only in this case you can count on success.
First of all, it is necessary to normalize the work of the pancreas, improve the microflora in the organs, eliminate the process of decay and intoxication. Properly selected therapy improves cattle in the first few days. With the timely start of treatment, the full restoration of the work of the pancreas occurs in 5-7 days.
Conclusion
If you follow all the basic rules for caring for cattle, carry out preventive measures on time and vaccination against common diseases, the livestock will always be active and healthy. Any disease of bulls and cows is curable, the main thing is not to miss the appearance of symptoms, otherwise veterinary medicine will be powerless. In general, the main rule: you need to do everything on time.