When breeding cattle, many farmers have difficulty identifying and treating diseases. The most common problem is sores on the udder of a cow. This part of the body of the cows is extremely vulnerable, in this regard, first of all, special attention should be paid to dairy cows. If any disease of the udder in cows is detected, a veterinarian should be invited to further examine the animal.
- Diseases of the udder in cows
- Mastitis in cows
- Types of mastitis
- Edema of the udder in cows
- Bruises and bites of insects
- Furunculosis in a cow
- Papillomas and warts on the udder of cows
- Smallpox in cattle

Diseases and sores of the udder in cows
Compaction in the udder or any other disease requires treatment. If you do not treat the udder in cows and the seal in the udder of a cow, milk stagnation or inflammation can occur. As a prophylaxis against sores of the udder, a burenka massage can be done. To prevent a cold from attacking animals, it is necessary to monitor the temperature in the barn and establish good ventilation in the room. In a musty room, animals can get sick with various viruses and infections.
Udder diseases in cows
First of all, udder diseases can attack females during pregnancy and after calving. At this age and condition, cows are considered the most vulnerable. If stiffness is noticeable in burenka, milk from the nipples is difficult, effective treatment is required.If the milk channel has narrowed a little or has become overgrown with adipose tissue, then during milking the milk passes through it with difficulty. Milking yields are noticeably reduced. With this disease, something solid can be felt in the nipple, while he himself is tight. In cattle, seals in the nipple and in the milk canal are noticeable.
This disease is characterized by the fact that, with insufficient milk delivery, it remains in the milk channel, which can lead to mastitis in the future.
If stupidity is found in the initial stages, saline baths can be used to treat it. It is also recommended to massage the udder with iodine ointment. If these measures did not save the female from stupidity, then after each milking a tube is inserted into the milk channel and left in this position for a couple of minutes, then the tube is removed and the remaining milk is dispensed. Treat the udder immediately, as soon as seals or inflammation become noticeable. It is also necessary to observe hygiene indoors and during milking. Most often, females get sick in farms where farmers violate hygiene and certain sanitary standards.
Mastitis in burenki
A disease such as mastitis is considered the most common among cows. Mostly, mastitis affects individuals during lactation. With such an ailment, milk becomes not so tasty, its fat content can change. A calf born to a female with mastitis has a risk of negative consequences.Mastitis can be of various types. You need to treat it right away, because if you start it, it goes into a chronic or acute form.
Types of mastitis
- Subclinical mastitis is dangerous because its symptoms are practically impossible to recognize. More often than not, a cow simply leads a habitual way of life, and outwardly it is difficult to notice changes even in colostrum. To identify this form of mastitis, tests are required.
- Clinical mastitis can be mild, moderate or severe. With a mild form, mastitis can be noticed only by the fact that milk contains spools or clots. With an average shape, the udder of the female swells, sometimes only on one side, it becomes reddish, milk yield noticeably decreases. In severe cases, cattle may experience a temperature, a complete lack of appetite, no milk yield, milk may have lumps.
It is necessary to treat mastitis based on what kind of cow was found and at what stage . For examination, you need to invite a veterinarian who can examine the animal and make an accurate diagnosis. Sometimes the veterinarian prescribes a whole range of treatments: antibiotics combined with massage and proper nutrition will quickly return the old milk yield and improve the well-being of the female. Most often, mastitis is detected at an early stage and is compensated by a completely correct massage.
Massage the udder with clean hands, as if imitating clay sculpting. Thus, stagnation of milk resolves from massage movements, seals go away, inflammation subsides.It is better to make it a rule to carry out milking, only washing the udder with warm water. Hands should be washed with antibacterial soap so that dirt and bacteria do not get into milk. Also, mastitis most often occurs in cold and damp areas where there is no heating. What mastitis looks like on an udder in a cow, you can look at a photo or video.
Edema of an udder in cows
If a cow has a swollen udder, what kind of tumor is it and what do in this case? Such a tumor is called edematous and congestive udder swelling. The disease occurs due to a general circulatory disturbance in a cow. First of all, females fall into the risk zone during pregnancy or after calving. Swelling occurs as a result of the fact that an active flow of blood comes to the udder. Swelling can be seen on the next milking, as it is visible on the skin near the nipples, then the swelling spreads to the vulva. Symptoms may be different, depending on the condition of the female.
Typically, the body temperature of cattle is normal, but the skin at the site of the edema is thickened. Basically, if the burenka has swelling, the milk may be slightly watery, but its amount does not change. It is possible to cure such a disease, the main thing is to notice cow problems in time. At the initial stage of the disease, the edema goes away on its own within 1 week.
If the swelling did not go away and the udder is swollen, the diet of this individual should be reviewed and products containing sodium chloride and solid feed should be excluded from it.It is best to leave high-quality hay, not raw and not rotten. To move the individual more, you need to let it out for a walk in the fresh air. With moderate physical activity, edema should disappear. You can slightly reduce water consumption, if before it was given in excess of the required norm. In this case, the veterinarians prescribe injections.
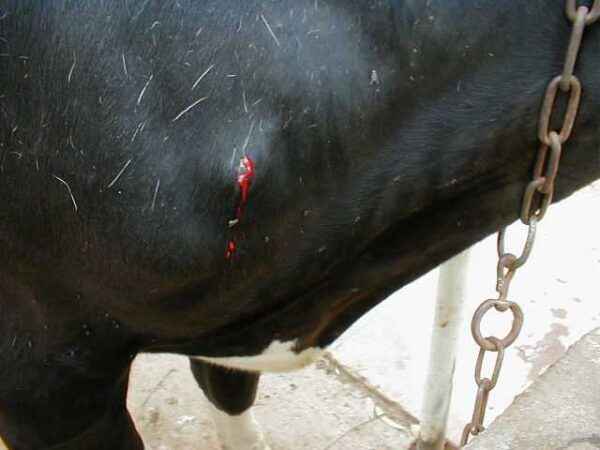
Bruises and insect bites
Injuries and bites in animals, which often graze in the fresh air, are not uncommon. Indoors, if the barn is full of unnecessary things, a burenka can get a bruise or fill up cones. With minor injuries for some time, the bruise of the udder easily resolves on its own. If a bruise or blow is caused by a heavy object and there are hematomas on the udder, there may be clots in the milk. The body temperature of the animal may be above normal. To bruise the udder, a cooling compress must be applied to relieve swelling. You do not need to do a compress for the entire udder, only for a bruise. The fraction of the udder that has undergone a hematoma should be lubricated with liquid clay.
You can also enter a 10% solution of calcium chloride or gluconate. If there is a bite of a cow beyond the udder, you should figure out if it is an insect or a snake. The fact is that in the summer, cows graze in the fresh air and eat fresh grass, as you know, snakes can be found in it. Also in the summer, it is full of gadflies and other blood-sucking insects.
Burenki can accidentally step on a stone, which will be next to the snake, during a walk.If the female was bitten by a wasp or snake, you need to immediately take action. A swelling may form after a bite. If the cow combed the bite, it must be treated with disinfectants. For consultation, you should contact a veterinarian or invite a specialist for a full-time examination of the animal.
Furunculosis in a cow
Furunculosis is characterized by purulent inflammation of the nipple, glands, skin hair sacs. It mainly arises from non-compliance with hygiene. Furunculosis of the nipple occurs in most cases in cows during lactation. Symptoms of furunculosis can be seen during milking. There are inflammations on the skin of the nipples that contain a hair root in the center. Place on skin inflammation takes on a yellow or reddish tint. Furunculosis is recommended to be treated exactly in the area where it was formed. The hair must be cut at the beginning and at the end of its growth.
If wounds have formed on the skin of the nipples, they must be treated with anti-inflammatory and disinfectant solutions. You can treat the skin with iodine solution or ichthyol ointment. Abscesses are opened and processed using penicillin until complete recovery. When furunculosis has passed, there should be no wounds or inflammation on the skin. As a prophylaxis, hygiene should be observed. Animals must be washed thoroughly, and the udder treated with warm water. After emptying the cow, the floor must be washed with disinfectants.
Papillomas and warts on the udder of the cows
Many farmers do not pay enough attention to such formations as a wart or hanging papilloma on the nipple or on the skin of the udder. Outwardly, the symptoms may not appear at all, only during milking new formations can be noticed on the nipples. Warts can hang or be dense, and they come in different sizes. Similar formations occur due to an infection in the body, so the disease must be treated as soon as it becomes noticeable.
The share of the udder can be affected by papillomas due to cracks in the skin and nipples. Cracks in the skin may appear after calving. If after the birth of the calf, tears and small cracks become noticeable on the nipples of the heifer, they need to be lubricated with moisturizing agents. Even if the growths disappear on their own, the infection from the body will not go anywhere – it needs to be treated. To date, there are a number of vaccines that successfully fight viruses and pathogens of such diseases.
Smallpox in cattle
Cowpox is a viral disease that appears as rashes on the skin, ulcers and pustules. Rashes or tubercles can appear anywhere on the udder, stomach, leg, trunk. Smallpox is accompanied by a short-term and slight increase in the temperature of the body of the cow. Lymph nodes can become inflamed if the general condition is unsatisfactory. Skin rashes can pass on their own after a while.The disease cannot be left untreated, as milk yields are significantly reduced due to the general condition of the burenka.
If the immune system of the cow is suppressed by drugs or other diseases, the infection may proceed to the next phase. Only a veterinarian can determine the presence of smallpox. The carriers of the disease in agriculture can be mice or even pets, so when working with an animal that has been diagnosed with smallpox, it is better to keep it in a separate pen for the duration of the disease. As a prophylaxis against smallpox, you can use a special vaccine. Before choosing a product, you should invite a veterinarian for a more detailed consultation, he will give an idea of the relevance of such an event.
In the room where cattle are kept and raised, there should be no dirt or bags of food, to which the mice will come herds. It is necessary to close up all the holes in the barn, to carry out a general cleaning of all pens and work equipment every week with the use of disinfectants. If special machines for milking cows are installed on the farm, they must be washed and treated with antiviral solutions. Gloves should be worn when working with animals.