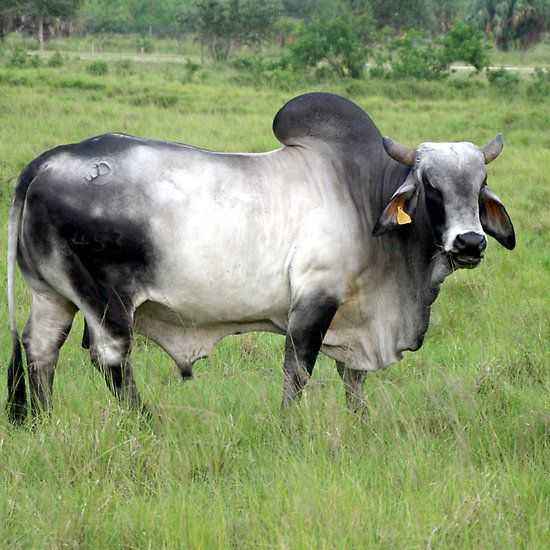
Dermatitis in a cow or tubercle is an infectious disease and affects primarily the skin of cows. Cattle dermatitis occurs due to contact with a sick animal, but there are also cases of tuberculosis infection through dirty equipment, clothing of farmers, blood-sucking insects or birds. How to treat nodular dermatitis in cows depends on how the disease began and in what condition the cattle is.
- Cattle Tuberculosis Symptoms
- The complex form of the disease
- Nonclassical manifestations of dermatitis
- How to properly diagnose nodular dermatitis
- Cattle treatment
- Disease prevention
- What happens after an illness
- The farmer must comply with the following requirements.
- Proper nutrition during illness
- Tips from the Department of Veterinary Medicine
- What should the farmer do

Nodular dermatitis of cows
Also, nodular dermatitis in a cow can appear even after the individual has been removed from the veterinary accounting. Because of this feature, outbreaks of infection can occur in a herd at different times and in different individuals. To prevent the spread of foci of infection, you need to keep the individual in quarantine, even if it has normal tests and the disease is completely cured. The fact is that tuberculosis bacteria remain active for some time and can infect other individuals in the pen.Such a disease is registered in different climatic conditions, but most often in a hot climate, so nodular dermatitis of cattle in the Krasnodar Territory is not uncommon.
Also, the disease was recorded in many southern regions: in Dagestan, South Ossetia, Azerbaijan, India and other countries. In the heat, any bacteria multiply most actively, and a simple midge bite can lead to the fact that the individual will constantly comb the affected area and bring it into the wound and other infections. The main prevention against such a disease is compliance with the conditions of keeping and caring for animals, then many infections can be avoided.
Symptoms of tubercle in cattle
Nodular dermatitis of cows can be detected not immediately, since the first symptoms, if they are noticeable, only a few days after infection. Most often, bumps on the skin in cattle appear one week after infection, but the reference materials indicate a period of 2 days to 45 days, so even during such a period of time the detection of such symptoms will indicate possible nodular dermatitis. The acute stage of the disease is typical mainly for young animals.
The main symptoms:
- temperature 40 ° C;
- lack of appetite ;;
- lacrimal fluid oozes from the eyes
- densities on the skin in the form of small pimples;
- milk yield decreases due to the general condition of cattle.
Such symptoms are typical for the initial stage of the disease.Also, in each individual, these symptoms can occur in a different form. The initial scars after some time change, the skin on the scars is separated from the outer layer. In the best case, a depression in the skin is scarred. Such particles can spread the disease throughout the herd. If the disease was diagnosed in a milk cow, then the signs of tubercle can be found in milk.
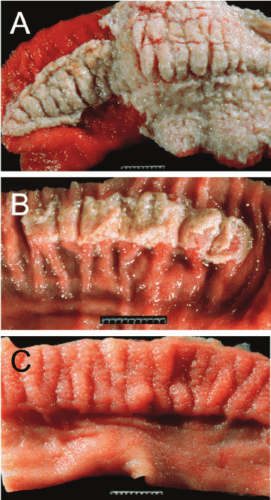
The cow’s milk becomes thick, it becomes jelly-like during heat treatment, and its color changes to pink. Infectious dermatitis in a cow can be diagnosed by analysis and examination of the skin by an experienced veterinarian. You can see how nodular dermatitis looks in a photo or video.
Complex form of the disease
Sometimes the disease proceeds in a classic form, but it happens that cattle catch acute nodular dermatitis . The treatment of dermatitis in cows in this case should not be delayed. This form of the disease is the most complex and requires complex treatment. Symptoms in the acute phase of the disease are similar to the classic manifestation of the disease. In the acute stage of dermatitis, most often cows refuse to eat and lose weight, the tubercles on their skin can have a purulent character and grow throughout the body. The virus affects not only the skin, but also the mucous membranes, leading to purulent inflammations.
Cattle can also suffer due to the changing nature of the saliva secreted: it becomes viscous, with a putrid odor.This form can affect both calves and adults. What to do in this case? It is necessary to constantly inspect the livestock during feeding or care, and at the first suspicion of any disease, invite a veterinarian for further examination. A complex manifestation of tuberculosis can cause cattle to develop subdermatitis when the skin near the hoof becomes inflamed, which leads to suppuration.
Nonclassical manifestations of dermatitis
Nonclassical dermatitis in young calves can appear at any time. Basically, with this form of the disease, treatment is not always done on time. It is difficult for a specialist to diagnose this form of the disease, since calves may not have tubercles on the skin, and there may also be no other concomitant symptoms. Many farmers note that cattle with this form of dermatitis have loose stools and a change in temperature.
There is also an inapparent form of the disease, which is more dangerous for cattle. The only caveat is that carriers of this form of the disease spread the virus, which is released into the air and can become a source of infection for a healthy individual.
How to correctly diagnose nodular dermatitis
Disease in cows, dermatitis can mainly be diagnosed by biomaterial. The specialist takes a sample for biomaterial. Sperm, milk, purulent discharge, urine or blood may be used in its quality.Bacteriological culture is considered an effective analysis in order to find out if there are tubercle viruses. For an accurate study or in order to double-check the results, a sample of infected tissue is taken for examination. Recently, they began to carry out the latest method of diagnosing dermatitis – a bioassay.
Using such a bioassay, the presence of the disease can be determined in almost any animal, even rodents, which are one of the main carriers of the disease.
After the bioassay, the cow will show a reaction in the form of a seal at the injection site on day 6-8. In order not to confuse nodular dermatitis with other diseases, a veterinarian should be invited for examination. Do not self-medicate, even if all the symptoms scream that it is dermatitis. Many manifestations of the disease are somewhat identical, and it is possible to establish the disease accurately only by analysis.
Treatment of cattle
Dermatitis in cattle and its treatment should diagnose and carry out only by a veterinarian. Regardless of what types of disease were diagnosed, all measures must be taken to improve the condition of the animal. At the moment, no cure for tuberculosis has been invented, but the only effective method is the vaccine. Since there is no cure for nodular dermatitis, a timely vaccine provides good protection against this disease. Vaccination is carried out for all calves at the age of 2 months.The vaccine is most often given on a farm under the supervision of a veterinarian, and the drug is placed under the skin.
The vaccine gives immunity only for a while. Basically, immunity lasts no more than a year. After this, vaccination is repeated. If at least one individual is ill in the herd, it should be transferred to a separate pen for maintenance.It is also necessary to develop for her a special diet and vitamin top dressing. During the illness, the cattle body weakens and an integrated approach to treatment is required. If the cow refused to eat and lost weight, then try to restore its weight.
If the animal refuses to eat, then you can try to give your favorite food, perhaps this measure will improve appetite. It is also necessary to provide a sufficient amount of clean drinking water. During cattle disease, vitamins A, B, C, D, and E are most often lacking. It is important to consult with a specialist about which vitamin supplementation is best. In the room where animals are kept in quarantine, it is necessary to establish air ventilation and carry out continuous disinfection of all objects. A good bedding should be allocated to the cow and, if possible, fresh grass should be given. If the types of dermatitis are simple, then within 5-7 days the animal should recover.
Prevention of the disease
Prevention of nodular dermatitis consists only in the timely formulation of the vaccine. Also, due to the fact that the disease can actively spread, all measures should be taken to protect a healthy population. If you worked with an infected animal or you have a suspicion that some individuals may be ill with something, then to find out these diseases, cattle must be isolated in a separate pen. Every time when working with a sick calf, bull or cow, care must be taken.All work equipment and clothing should be immediately disinfected.
You cannot go into the infected individual in the same shoe and then go to the corral to healthy animals. Every day, all rooms where animals are kept should be treated with disinfectants. Cows are not allowed to drink and eat from the same bowl. In order for the whole livestock to have stable immunity, it is required to give only high-quality and balanced food. Periodically, the herd should be fed with various vitamin and mineral supplements. Only in this case, the animals will have strong immunity that can withstand viruses and infections.
What happens after a previous illness
Even if cattle is cured, cattle can observed at the site of the appearance of tubercles regeneration of the skin. The more complicated the form of the disease, the more rashes on the body. In those places where there were tubercles, the wool may fall out and not grow for some time. Also, any disease can cause complications, negatively affect the body.
In order to somehow support the work of all organs, you need to gradually restore strength and take the herd for a walk. As complications, there are frequent cases when bulls cease to be able to fertilize females. Cows can be diagnosed with inflammation of the udder, mastitis. As a prophylaxis, massage of the udder can be recommended.If the diagnosis is officially confirmed, then the veterinary commission makes a decision on quarantine for a period of 1 year.
The farmer must comply with the following requirements
- If there are animals in the herd that have been ill dermatitis, even if all tests are normal now, the farmer has no right to sell livestock and move animals to any place outside the quarantined zone.
- The farmer has no right to sell the animal or use it in the meat or dairy industry. The milk and meat of these cows is considered infected.
- The owner of the sick cows must necessarily carry out a number of preventive measures to destroy flies, mosquitoes and other insects that may be the source of the disease.
Proper nutrition during illness
If the animal became ill in the summer, then the basis of the diet should include juicy and fresh food, silage is considered their main component. Corn, sunflower, tops and meadow grass should be given. The daily norm is about 15-18 kg. If the cow refuses to eat or eats less, then you need to take action or so she will lose weight, milk yield will decrease. You can give root crops: sugar beets, fodder beets and carrots. It is very important to feed root vegetables, as this favorably affects the quality of milk.
Raw potatoes improve the yield of milk, so it is recommended to give some potatoes when they are reduced. For one adult, no more than 10-12 kg of potatoes should go.A whole storehouse of vitamins is found in cabbage, Jerusalem artichoke and fish oil. Salt is given by cattle for any type of feeding at the rate of 10 g per 100 kg of animal. Concentrated feed is also given as feeding based on the productivity of the cow and its condition after the disease.
Tips from the Department of Veterinary Medicine
Currently, there have been active cases of the spread of the disease in the territory Krasnodar Territory, therefore, the Russian Department of Veterinary Medicine made a whole list of recommendations. It is very important to carry out measures to eliminate insects and rodents. In many farms, rats and mice walk in whole colonies. It is necessary to direct measures to destroy the carriers of infections. It is also necessary to eliminate holes in the room where cattle are kept. To protect against insects, install special mosquito nets on the windows, use electric repellents and do not leave the doors open in the evening.
Ventilation must be installed according to all standards, as well as equipped with a fine mesh so that mosquitoes do not fly from there. and midges. In unfavorable areas, where such a disease is mainly fixed, it is necessary to control animals and try to bring the situation to a new level, because if infected animals get to another compound, they can infect other individuals, and the virus spreads.
What a farmer should do
First of all, every farmer who does not want to suffer losses due to a widespread infection needs to identify his livestock. The farmer must monitor the annual vaccination. For her, you can invite a veterinarian to the farm. When living in rural areas it is very important to find specialized veterinary centers, which should be located at least in large towns and villages.
In such centers they can explain and carry out preventive measures against various diseases of cattle. A farmer can also carry out a control slice using a bioassay. In Russia, nodular dermatitis is not uncommon, it is an extremely common disease, therefore, when deciding to breed and raise animals, you need to invest money and time in them. Only then, with the right approach, it will be possible to protect the livestock from diseases and get healthy offspring.