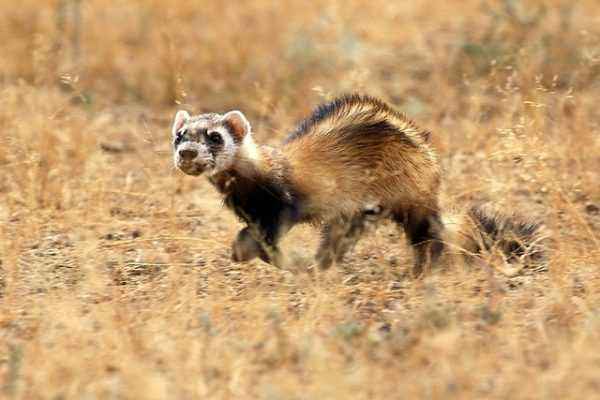
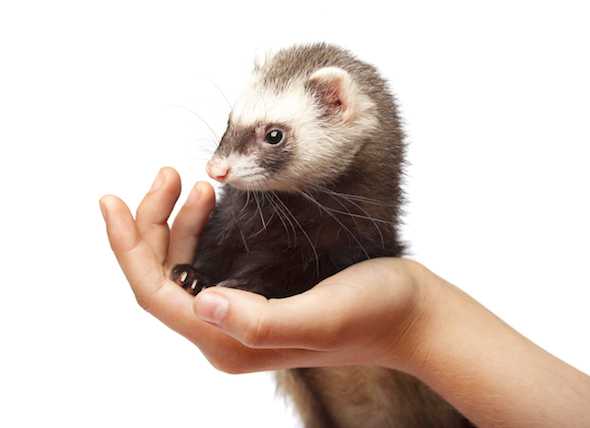
The steppe ferret is the largest representative of its species. It is widely distributed in Central and Western Europe, as well as in the Far East. For farmers, this animal is primarily a pest, because it destroys chicken coops and drags rabbits.
- view
- Square
- Ferret steppe diet
- Wildlife survival
- Steppe Ferret Reproduction

At the same time, steppe ferrets control the number of rodents in the fields, thereby preserving the crop. Such predatory children can be tamed if they can be caught alive. Despite the high population, some subspecies of these predators are found in the Red Book.
view
The steppe ferret is large compared to other representatives of the marten family. The adult has an elongated body and short legs, which makes the predator well Climbing holes The body length of the steppe polecat can reach 60 cm, and weight – up to 2 kg. Males are usually larger than females and have a more fluffy tail.
The coat of the animal is long, but does not differ in density. A light undercoat is visible through the outer hair, which is easy to notice even in the photo. The skin of these [predators is of low value to hunters, although the wall ferret is sometimes bred on farms for the sake of a fur coat.

these animals depends on the habitat and time of year. Sometimes, due to the shedding process and natural conditions, the steppe hori can radically differ in their color. However, all representatives of this species have common features. The following characteristics are characteristic of the predator’s hair:
- The hairline is darker at the ends and lighter closer to the body.
- The undercoat is light. Common shades are beige, white, sand and coffee with milk.
- The muzzle has a pronounced dark mask.
- Paws, the tip of the tail and stomach are the darkest parts. The color can be almost black.
The presence of a bright dark mask on a white face is considered a distinctive sign when describing a steppe ferret, however, absolutely white individuals are also found among this type of animals.
Usually, the cause of the appearance of the White Steppe Chorea is the lack of melanin in the body. Due to the popularity of this phenomenon, albinos are considered a separate subspecies of this predator.
Range
Western, Eastern and Central Europe are considered to be the original habitat of the steppe polecat (steppe horek). Also, these animals can be found throughout Asia.The subspecies is widespread in countries such as:
- Austria;
- Czech Republic;
- Ukraine;
- Russia;
- Mongolia;
- China.
The predator prefers to settle in open areas, in contrast to forest species.
This animal can be found in the steppe, on the edge of the forest and on pasture. In inhabited areas, the ferret is found much less frequently and does not fit the human dwelling unnecessarily.
It is noteworthy that the appearance of such a predatory animal largely depends on its habitat. For example, ferrets in Western and Eastern Europe have a darker color and larger body, while Asian predators can be smaller and lighter.
Such a large range of the steppe trochae is due to several factors:
- Predators can adapt to any meat in wild nature. Ferrets in the north eat rabbits and birds, while southern subspecies calmly feed on lizards and large insects.
- Predators are highly intelligent, so they often stock up on food. This helps ferrets survive the cold period.
- The dense undercoat allows the animals to maintain body temperature and protects them equally well from heat and cold.
- The maneuverability and flexibility of the body helps ferrets avoid large enemies, and sharp teeth provide predators with a victory in a fight against animals such as gophers, foxes and badgers.
The greatest danger At present, deforestation and the development of steppes are for the population of these animals. Even intensive hunting does not harm this breed as much as the development of new territories.
Despite the high population and wide distribution, some subspecies of these animals were on the verge of extinction. Since 1996, the Amur steppe ferret has been listed in the Red Book of Russia, and zoologists are currently engaged in the breeding of these predators.
Steppe Ferret’s diet
Representatives of this species of marten are nocturnal animals. The steppe ferret goes hunting at dusk, and in the afternoon it is slept in a hole. The body structure of these animals has a feature: a very short intestinal tract. Because of this, ferrets have an increased metabolism. Active hunting animals compensate for a long sleep. In the wild, the animal can sleep up to 18 hours, and in the remaining time to hunt, go around the territory and make supplies.
To get food in the dark, ferrets help night vision and dexterity. Animals easily catch rodents, chasing prey and tearing their burrows.
The ferret is an obligate predator and can not eat anything except meat.Typically, the diet of the animal consists of such animals:
- hamsters, mice and rats in the steppes;
- amphibians and lizards;
- birds and eggs;
- invertebrates.
Sometimes the ferret can hunt snakes, but the predator does not have resistance to poisons. At home, steppe ferret can be given veal, boiled chicken and fresh fish. It is forbidden to feed these animals with food for cats or dogs, as well as soy. The ferret’s stomach doesn’t digest meat substitutes, so the predator can die.
Survival in the wild
In the wild, the Steppe Chorea do not have many natural enemies. They include wolves, foxes and wild dogs. Also, birds of prey such as eagles, owls and hawks can hunt animals. However, these predators do not pose a serious threat to the animal population. Ferrets have good physical characteristics that allow them to slip out of the claws of the enemy. Also, small predators have special glands that emit a pungent odor. This feature of the body protects animals from enemies such as foxes, as it greatly knocks down the trail. In addition, the animals have a good birth rate, so a natural reduction in the number of ferrets is not a problem.

A much greater danger to the steppe ferret is widespread landfills and buildings.The animal cannot adapt to similar living conditions and often perishes from garbage. Curious ferrets rummage around in heaps or crawl into technical pipes, after which they choke on them. That is why some subspecies of the representatives of the marten family were on the verge of extinction.
Reproduction of the steppe ferret
Before starting the mating process, the female seeks shelter. Steppe hori use burrows of their victims or abandoned houses of larger rodents as dwellings. Predators do not like to dig holes on their own, preferring to eat gophers living in them, and then equip the room to their liking. Usually, the passage widens for this, but the camera remains intact. The ferret’s entrance to the hole reaches 12 cm in diameter, while gophers are characterized by a size of 6 cm. The body of these animals is designed so that with a prolonged estrus the animal can die, therefore, at home, the non-tribal pet should be sterilized. Mating ferrets looks pretty aggressive: the male bites and drags the female very strongly at the withers, animals can injure each other. With a successful mating, estrus ceases and the female carries the young for 40 days. Offspring of trochees are born in May or July.
Nora before birth is insulated with dry grass and leaves. Puppies are born blind, naked and cannot take care of themselves.Female ferrets are very caring and practically do not leave the nest in the first months of their life. The puppy’s eyes open by the end of the fourth week, after which the mother gradually transfers the ferrets to meat food. The first hunt in young animals usually occurs at the end of the third month.
The offspring is with the female until the fall, after which it usually leaves the parent hole.Late cubs can stay with their mother all winter.