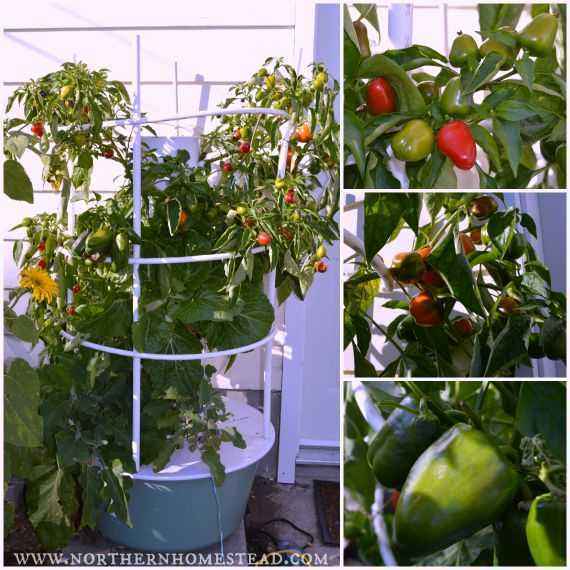
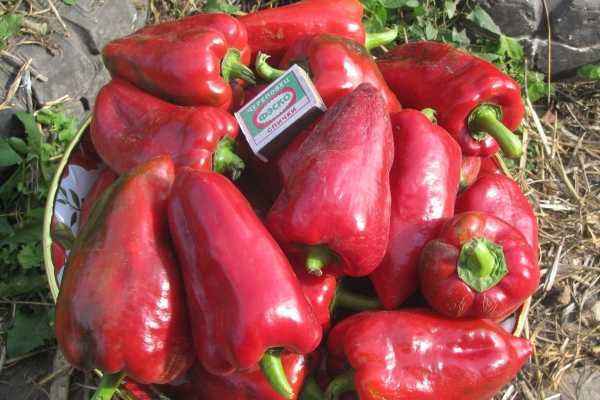
Growing pepper is a troublesome business. However, using little secrets, it is real to grow delicious peppers in the open ground and in the greenhouse. Consider the basic rules of agricultural technology and growing tips.
- General recommendations
- Variety selection
- Seeds <
- Ripening dates
- Preparation of soil and seeds
- Soil soil
- Seeds
- Growing seedlings
- Sowing
- Hardening
- Transplanting seedlings and leaving
- Watering
- Mineral nutrition
- Cultivation under different conditions
- Home conditions
- Greenhouse conditions
- In open ground

Pepper growing rules
General recommendations
Pepper is a lazy vegetable crop. Those wishing to grow pepper need to stick growing technology:
- The vegetable is sensitive to the temperature regime of air and soil. Sprouted seedlings are transplanted with sweet pepper only at a temperature of at least 14 ° C, choosing a place protected from the wind.
- Watering peppers requires plentiful, but infrequent. The soil in which vegetables are grown should not be dry or too wet: this affects the quality of flowering and leads to the fall of flowers and foliage.
- Insufficiency of light affects the process of growth and flowering of the plant, which subsequently affects the yield of the vegetable crop.
- Mulching, which often uses organic matter and protection with covering material, can increase the yield of a vegetable. Do not forget about hilling bushes.
- Peppers are not recommended to be planted on the same bed for 3 consecutive seasons. Adhering to crop rotation, you can not use drugs against plant diseases and pests. Correctly planted pepper is quite stable.
- If the flowers are not pollinated enough, especially when growing pepper on the balcony, on the window or in the greenhouse, curved vegetables of an irregular shape appear. This can be avoided by periodically shaking the plants at the flowering stage. Also, do not plant different varieties nearby, you need to separate the sweet from the bitter, so that the plants do not pollinate among themselves.
Without making mistakes in the cultivation, it is easy to get a good harvest of salad vegetables.
Variety selection
Proper pepper cultivation involves choosing a variety.
Seeds
Today there are varieties and hybrids f1. Their difference lies in the fact that it makes no sense to collect seeds from hybrid vegetables, since they do not convey the characteristics of the parent species during reproduction.Hybrid seeds have to be purchased annually, but they show high yields with large fruits, are more resistant to diseases, show good results when grown hydroponically.
In contrast to hybrids, varietal species can be grown not only for the purpose of obtaining vegetables for consumption for food, but also for the further collection of seeds used as seed in the new garden year.
Ripening dates
Gardeners grow pepper, while planting varieties with different maturity so that both sinter continuous harvest, since the vegetable crop does not differ in good technological keeping quality.
In warm areas, seedlings are grown or using almost all varietal varieties without seedling.
However, plant and grow late-ripe sweet Bulgarian or black with red hot peppers in the northern regions in the open ground on a summer cottage is not possible. For such areas it is recommended to choose early ripe peppers for planting, which fully mature in a short period of time and plant them in a greenhouse. In the northern regions, it is advisable to plant pepper seeds so that the vegetables have time to ripen before the first frost.
When choosing a variety of pepper for growing, you can focus on a table of ripening dates:
| Varieties | Ripening dates |
| Early (Tusk, Eroshka, Aivengo, Pyatitsvet) | 80-100 days |
| Mid-season (Cherry, Purple Othello, Phoenix) | 115-130 days |
| Late (Gladiator, Black cardinal) | 140 days |
Soil and seed preparation
From properly prepared soil and the quality of the seeds depends on the success of the future harvest.
Soil nt
It is recommended to prepare fertile soil for growing peppers. The acidity level should not be large (in the range of 6.2 to 7.0 pH points), however, the vegetable crop can also grow on alkaline soil, therefore the upper limit of the acidity level may be slightly higher.
Bring the level acidity to the required level allows additives:
- with excess acid, ash powder is added to the soil or limestone is mixed with it,
- with excess alkali, needles are mixed into the soil or peat moss is mixed.
The soil is examined for clumps and stones, removing pain Larger in size.
For seedlings use fertile black soil, which is diluted in equal proportions with river sand.By mixing a little vermiculite with it, you can provide the necessary moisture and loose soil for sowing in the summer cottage or at home.
Seeds
If you soak the seeds before sowing in water for 2 -8 hours, until they sink to the bottom, you can speed up the process of their germination, softening the coating. Also, with the aim of disinfecting the seeds, they are soaked in low concentration chamomile tea or in a solution with hydrogen peroxide at the rate of 2 tsp. in a glass of water.
Growing seedlings
Fill the tanks with seedlings with prepared soil. As such a container, simple storefront plastic containers are suitable, in the bottom of which it is necessary to make holes. Drainage is poured into the bottom of the tank: pebbles or small stones – and only then mix soil.
Sowing
Seeds are sown at a distance of 1.5 to 2 cm in pre-cut grooves spilled with warm water. Sprinkle the sown seeds with the same soil mixture, from above the ground is abundantly sprayed with water from the spray gun. The container with planted seeds is covered with a film.
The temperature of seedling cultivation is from 24 ° C to 26 ° C.
To accelerate the process of seed germination, you can put a container with sowing under light lamp with a power of 40-80 watts. Extra lighting is especially required when there is not enough sunlight in an enclosed area. The lamp is placed at a distance of 8-10 cm from the surface of the soil mixture.
Hardening
With the first seedlings that appear after 5-6 days, the seedlings are placed in a cooler place, lowering the degree of the environment to 14-16 ° C. First, this is done for several hours a day, gradually increasing the amount of time spent. This allows you to strengthen the root system of the plant and harden the young shoots. after a week of hardening, the temperature degree begins to gradually rise to a level of 23-25 ° C.
Transplanting seedlings and leaving
2 pairs of leaves that have grown in young seedlings are a sign of the pepper’s readiness seedlings for transplanting to a permanent place of cultivation.
If you plan to continue to grow pepper at home, each bush can be transplanted into a separate container. Most often, small shrubby pepper is grown at home in pots, hanging baskets, plastic bottles or buckets. When transplanting seedlings in open soil, keep a distance of 25-40 cm between the bushes.
Watering
The main care for pepper, Bulgarian sweet or red bitter red requires regular watering, first once it is carried out immediately after transplanting the seedlings to its permanent place. The second watering procedure is carried out after 4-5 days.
The regularity of watering in open soil depends also on weather conditions. On hot and dry days, watering peppers is required once every 7 days. This frequency is maintained until the formation of the ovaries.Bushes stop watering at the stage of active fruiting.
Mineral nutrition
If at the stage of growing seedlings of peppers mineral nutrition is not required, fertilizer is applied at least 3 times for the transplanted plant. The first bait is carried out 2 weeks after the plant is transplanted to a permanent place of cultivation. Secondary fertilizer is applied at the stage of fruit formation. The third bait is produced after 2-3 weeks after the second.
Peppers respond favorably to foliar nutrition in the form of spraying.
Cultivation under different conditions

Growing is possible in a greenhouse and in open ground
depending on where you intend to grow vegetables, you must adhere to the rules of cultivation.
Home conditions
To grow a good sweet or hot pepper, you can do the following: sow the seeds in small containers, covering them from above with a film or glass. After 5-7 days, when the first sprouts appear, seedlings are dived into separate pots. Further care comes down to timely watering and making mineral nutrition.
For the cultivation of hot and ornamental varieties of pepper, the windowsill is often adapted. Harvesting is possible all year round.
Screens with a reflective surface are often used to create proper lighting when growing peppers at home. They are placed from the side of the room. In the dark winter time, phytolamps help to provide light. When it is not possible to create additional artificial lighting, the seeds are recommended to be planted no earlier than the last days of February or early March, when daylight hours increase.
Greenhouse conditions
Growing sweet Bulgarian and hot pepper in the greenhouse is the most acceptable option. Features of such cultivation of vegetable crops and care for it:
- proper irrigation, carried out in the morning with water heated to 18-20 ° C,
- regular ventilation of the greenhouse,
- maintaining the temperature of the soil at the level of 18-22 ° С, air – at least 25 ° С,
- additional illumination,
- introduction of nitrogen-containing complexes at the stage of active growth, fertilizing with superphosphate at the stage of budding and top dressing with mineral compounds during the formation of ovaries and the appearance of fruits.
In the open ground
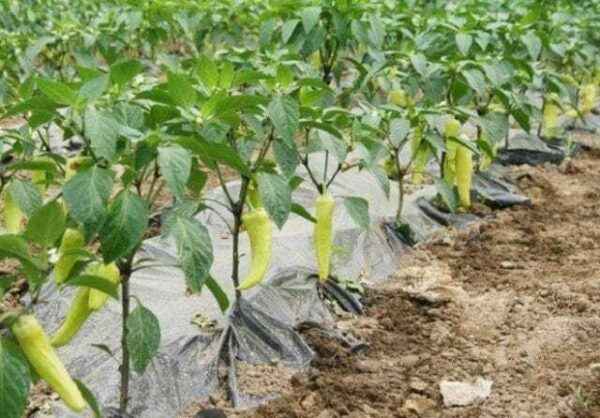
You can grow pepper in the garden if you protect the plantings from temperature extremes using a black non-woven covering film material. Germinated seedlings are planted, depending on the region, but in any case, when all the frosts end.
The largest, largest in size and healthy vegetables grow in a sunny area.
In order to protect plantings on unprotected soil, gardeners use small tricks: against the winds they plant a live damper in the form of corn, tall flowers and other plants that exceed the size of pepper bushes.