Rodent breeding will take place without complications if you know how rabbit teeth grow and what diseases torment a furry animal. How many teeth does a rabbit have, how does it clean it?
- Features of rodent teeth
- Structure of the lower and upper jaw
- Diseases of the teeth of the rabbit
- Diagnosis of the oral cavity in rabbits
The structure of the rodent’s jaw and dental diseases determine the health of the animal. Dental problems can lead to the death of the furry.

Teeth of the rabbit
Physiological factors should be considered for breeding and proper keeping of fluffy animals Breeds of the breed Experienced farmers recommend regularly inspecting the teeth of rabbits to prevent serious pathologies.
Features of the teeth of rodents
The teeth of the rabbit must be strong and strong. The breed of domesticated rodents eats hard coarsely ground vegetables and feeds If the front incisors begin to hurt in fluffy animals, such diseases immediately affect the well-being of the pets. Animals become lethargic, weaken, quickly lose weight and die over time. The teeth of the rabbit need to be inspected once every few weeks, so as not to miss the development of dangerous diseases.
The teeth in the rabbit are different from those found in other breeds of rodents. Scientists distinguish a separate species of hare-like animals, which are similar to rodents, but the structure of their skull is significantly different.The teeth of a rabbit have a different size, which is due to the lifestyle of a fluffy rodent. The pet grows, and in the process of its growth 2 front incisors increase. This is the main chewing mechanism that allows rabbits to eat solid vegetables.
The rabbit’s teeth are divided into a pair of incisors and root teeth, which rodents use to crush solid foods. The reason why the incisors of hares are longer is very simple: they serve to quickly chew nutritious vegetables.
Fluffy animals have 26 teeth in total, unlike rodents with 18 incisors located on the jaws. In young animals, chewing teeth and incisors grow quickly, in just a couple of months, the hare has a full dentition.
After the main teeth have grown, bone growth continues. Such a development of the skeletal system does not bear particularly noticeable changes. In decorative breeds specially bred for home breeding, the dentition is significantly less than that of their relatives living in the natural environment. The reason for the jaw deformation is this: as a result of crossing, breeds of a smaller size and with a weaker immune system were bred. Ornamental types of dental diseases occur quite often, and it is also necessary to treat such animals.
The structure of the lower and upper jaw
The physiological characteristics of rabbits determine the structure of their skull. Herbivores need strong incisors that can withstand heavy loads.The digestive system easily overcooks plant foods, but the task of the dentition of furry animals is to crush vegetables. Grated and “cut” food is quickly absorbed and gives a lot of energy to hares. Only a specialist can remove the teeth of domesticated rodents and only in cases where the problem has no other solution. The absence of at least 1 tooth creates a large load on the remaining incisors.
The structure of the skull of rodents allows you to “cut” the food with incisors, and kill the food with the help of the root teeth. In the winter season, domesticated rabbits eat only dry food and hay, which the root row of teeth can easily cope with. Cutting is done several times a year and only according to the testimony of a veterinarian.
A photo of fluffy animals shows how long teeth can grow in rabbits. Even small breeds have a massive jaw. It is very important, regardless of the lifestyle of rodents, to monitor the health of their oral cavity. Milk teeth (lower and upper) fall out very quickly, but the removal of healthy and permanent incisors is a big problem that should be prevented in all possible ways. Cut the teeth with a mill or other tools that are found in the farmer’s farm. Carrying out such procedures at home can result in damage and deformation of the jaw of the animal.
Even experienced rabbit breeders disagree on how many teeth a rabbit has in its mouth.
The lower and upper jaws of the animal are difficult to examine completely, so the data on the number of incisors and root teeth diverge. Adult fluffy rodents have 22 teeth, but sometimes there are breeds with a full range of 28 incisors and root. Two rows above and below consist of 2 strong incisors. After the incisors, hares have no teeth. Such a space in the oral cavity is called “toothless” and it helps crushed food to enter the esophagus more quickly. The rabbit does not have fangs, like other animals.
Root teeth of rabbits:
- premolar;
- molars.
Rabbits have 12 upper molars at once, which are supported by 10 teeth of the lower row.
You can easily calculate the number of teeth in furry animals: 26 strong teeth that help to grind even the most solid food. During growth, small rodents quickly adapt to hard vegetables. Green lure makes up only a third of the animal feed in the summer and is practically absent in the winter.
Each animal that enters the farmer’s farmyard needs constant inspection and proper maintenance. Proper care of furry rodents will guarantee that the meat of the animal is safe and suitable for human consumption.
Diseases of the rabbit’s teeth
A large load on the teeth due to hard and dry food leads to the fact that the incisors are erased and the root teeth become weak and begin to hurt. Common pathologies that occur in rodents of different ages are as follows:
- Malocclusion. Such pathologies arise due to a rodent malocclusion. The fluffy grows, and along with the muscle mass, the skeletal system increases. Improper diet of young animals or diseases at an early age can lead to malocclusion. As a result, the upper and lower jaw does not close. Malocclusion prevents rodents from gaining weight and makes them weak.
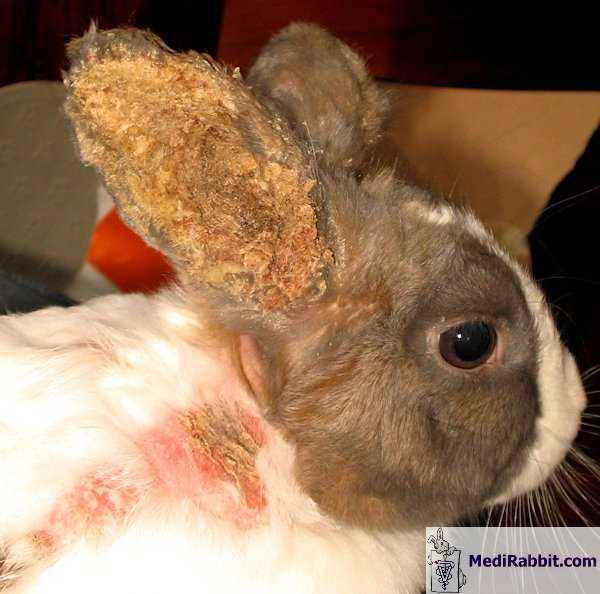
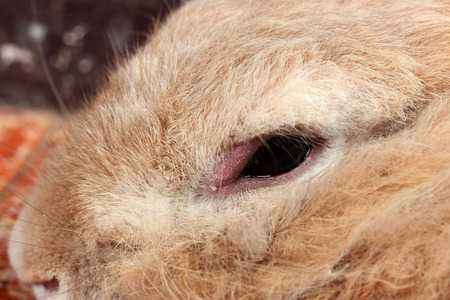
- Deformation of the root of the dentition. Another problem associated with malocclusion leads to serious health consequences for the rodent. Due to the too large size of the root teeth of the rabbit, the incisors bend, hence the rattle. Improper load on the entire dentition leads to diseases with lacrimal canals. The consequences of this deformation are disruption of the eyeballs. More often, the teeth of a small decorative rabbit suffer from this.
- Abscesses. The most dangerous for the health and life of these rodents are suppuration and strong inflammatory processes in the oral cavity of a rodent. To cut teeth while pus is secreted in the animal’s mouth is by no means possible. For a rabbit, such a procedure is severe stress and unbearable pain.There are several ways to solve the problem, including medication. Special preparations prescribed by veterinarians are needed for proper cleaning of the dentition.
The animal world is amazing in the variety of species. Domestic and decorative rodents are a special breed. These are quite dangerous animals, even predators, which are distinguished by vitality and a lively character. To teach these pussies to live at home is easy if you provide the rodents with the necessary care. Curved incisors (rabbit teeth sometimes bend) can cause the death of fluffy. If the farmer hears that the rabbit is grinding its teeth, then the animals should be examined before the onset of severe symptoms of the disease. A disease that causes pain in the jaws provokes the depletion of the rabbit’s body, can cause big problems.
What should I do if rodents sharpen their teeth or they have obvious problems? Creak, cracks in the teeth (the rabbit broke the incisor, molar or molar) are the first signs of the disease. Do not self-medicate, because rash actions can cost a person all the pussies. Only a specialist can help.
Diagnosis of the oral cavity in rabbits
How many times a year do you need to examine the oral cavity of rabbits, do you need to remove a bad tooth?
Timely diagnosis and prevention of diseases will prevent serious diseases. Veterinarians argue that the farmer needs to polish the teeth of rabbits.Such actions are taken if the rodent knocks with incisors or behaves aggressively. Too large incisors need to be trimmed, otherwise the animal can injure itself. A special treatment mixture will help to regularly clean the teeth of rabbits. It is applied to special wooden blocks with soft wood.
What should I do if pus starts to stand out in my rodent’s mouth?To clean the oral cavity from secretions or treat inflammation should only be a specialist who is familiar with the structural features of the rabbit skull. Cleansing pus without treatment for the underlying cause of the disease is inefficient and even life threatening for rodents.