African swine fever is a viral disease with a very high mortality rate, not harmful to humans. Synonyms – Montgomery disease, African fever, South African swine fever, ASF. Pathology is very dangerous, spreads rapidly and leads to large economic losses. Clinical symptoms are mild, laboratory diagnosis can confirm the final diagnosis.Sick animals are not subject to treatment today, they take preventive measures to prevent it.
- Etiology of the disease
- Epidemiology
- Pathogenesis of the disease
- Clinic of African plague
- Pathological changes and diagnosis
- Treatment and prevention
- Activities in the outbreak
- How to prevent the virus from entering the household

frikanskaya swine fever
The etiology of the disease
What is African swine pathogen and how it is caused. The cause of the pathology is a virus, the genetic material of which is contained in DNA, from the Asfaviride family, the genus Asphivirus.This virus has amazing resistance to various adverse environmental influences:
- survives at a pH of 2 to 13 units (both in acidic and alkaline environments);
- in pickles and smoked meats remain active for weeks, or even months;
- at a temperature of 5 ° C, survives for 7 years;
- at a temperature of 18-20 ° C – 18 months;
- at a temperature of 37 ° C – 30 days;
- during pasteurization at a temperature of 60 ° C it survives 10 minutes;
- lives in pork corpses from 17 days to 10 weeks;
- in feces – 160 days, in urine – up to 60 days;
- in soil on Under the strain of the summer-autumn period it can be stored up to 112 days, in winter and spring – up to 200 days.
Due to such high resistance of the virus, African swine fever and the pathogen can be transported over very long distances. It can only be destroyed by burning the corpses of pigs using high doses of disinfectants (hydrated lime, formaldehyde, etc.). In addition, the virus is extremely virulent, even small doses can cause an acute illness.
Epidemiology
The first cases of the disease were recorded at the beginning of the twentieth century in South Africa, from where it spread to Portugal, Spain, other countries of southern Europe. In the 70-80 years, pathology was recorded in South and North America, the USSR. Now the disease is a serious threat, because of it pigs are almost not raised in Africa, their number is declining in Europe and America.An outbreak was recorded in Georgia in 2007, in Ukraine in 2015, and African plague has been reported regularly in the European part of Russia since 2008, as reported by veterinary services.
The source of the pathology is sick pigs and virus carriers. Even if the animal recovers, it continues to secrete the pathogen until the end of life, therefore, in the focus of epizootics, the entire population is destroyed. The natural focus is African species of pigs, especially wild ones. In them, the infection proceeds in a latent and chronic form, very rarely in acute. Domestic pigs are more susceptible to the virus, especially European breeds. Even among wild boars in Europe, mortality is at the same level as among domesticated ones.
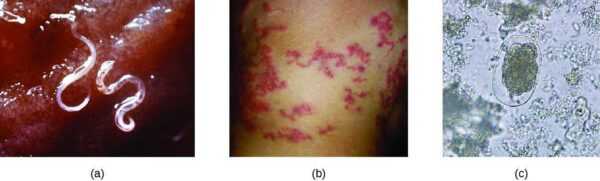
The virus of African swine fever is transmitted by airborne, alimentary route. The main objects and things through which pigs are infected are water and food (especially feeds that use animal meat), care items, and infected litter. The virus can be carried with the clothes and shoes of people caring for sick pigs. Often the virus enters the bloodstream through ticks, which are its natural reservoir. Flies and other insects that suck blood can carry the infection. Often, domestic birds and rodents are distributed mechanically by the pathogen.
Pathogenesis of the disease
The susceptibility of domestic pigs to the virus is very high, because the disease is so dangerous.The pathogen enters the body through the mucous membranes and the skin, even with microscopic injuries, sometimes penetrates the blood when insect bites. From the point of entry, the virus enters the cells of the immune system (macrophages, neutrophils, monocytes), as well as into the endothelial cells of blood vessels. In these structures, the pathogen multiplies.
After replication, the virus leaves the cells, destroying them. In the vessels and lymph nodes, foci of necrosis occur. Vascular permeability increases sharply, blood clots form in their lumen, inflammation develops around damaged structures. In various organs, anesthetized lymph nodes are found. Due to damage to the immune system, the pig’s ability to protect and resist other diseases is sharply reduced. Symptoms of African plague manifest quickly leading to the death of the animal.
Clinic of African plague
The incubation period lasts 5-10 days. The disease of pigs viral African plague can occur in three forms: fulminant, acute and chronic. In the first case, it lasts 2-3 days and ends in death in 100%. The first symptoms and signs of African plague in pigs in such cases do not have time to develop. The farmer can find the herd quite healthy in the evening dead in the morning.
In the second case, the clinical manifestations are more pronounced.
There are such signs of African swine fever:
- fever up to 40-42 ° C;
- cough, piglet begins to choke;
- vomiting with a splash of blood;
- hind legs paralyzes;
- constipation, less commonly bloody diarrhea;
- from the nasal passages and eyelet a clear, purulent or bloody liquid flows;
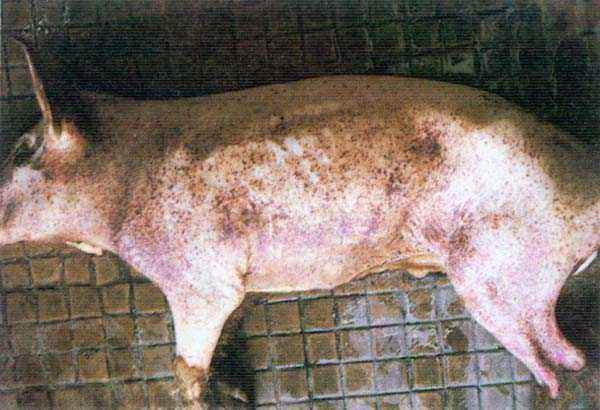
- on the hips from the inside, near the ears, on the stomach, purple spots are visible that do not lighten when pressed;
- bruises are visible on the conjunctiva, sky, tongue;
- purulent pustules and sores may appear in some places.
A sick pig tries to hide in the far corner of the barn, it lies on its side, does not rise to its feet, its tail spins up. Pregnant sows lose piglets when infected. 1-3 days before death, the temperature in animals decreases.
African swine fever in chronic and asymptomatic forms is extremely rare and mild. Such variants are more typical for wild species in the natural foci of the disease. The clinical picture is not expressed, animals with this course of pathology gradually weaken, suffer from constipation, they have minor symptoms of bronchitis. Sometimes, spot hemorrhages or spots are found on the skin and mucous membranes. A chronic disease may end in recovery, but the virus persists in the blood, pigs remain carriers of it forever. When signs of a protracted pathology are found in pigs, laboratory diagnosis is mandatory.
Pathological changes and diagnostics
If you suspect ASF, you must conduct a selective examination of the corpses. Pathological changes and histological signs of African plague are as follows:
- The skin on the abdomen, under the chest, behind the ears, on the inner sides of the thighs is red or dark purple.
- Mouth, nose, trachea filled with pink foam.
- The lymph nodes are greatly enlarged, the picture on the slice is marble, multiple hemorrhages are visible, sometimes the node resembles a continuous hematoma with black clots.
- The spleen is large, with multiple hemorrhages, patches necrosis.
- The kidneys are also enlarged with hemorrhages in the parenchyma e and on the walls of the enlarged renal pelvis.
- The lungs are full of blood, a shade of gray with red, there are multiple bruises in the parenchyma, there are symptoms of pneumonia, fibrous cords (signs of fibrotic inflammation) are found between the alveoli.
- The liver is full of blood, significantly enlarged, gray with a clay shade, uneven.
- The mucous membrane of the intestines and stomach swells, hemorrhages are revealed on them.
- In chronic pathology, bronchitis is found on both sides, enlarged lymph nodes in the lungs.
- With essimptomnoy form visible only changes in the lymph nodes, they have marble pattern
African swine fever has symptoms similar to ordinary plague of this type of animal..In order to distinguish between 2 diseases, laboratory diagnosis is mandatory. The method of PCR, fluorescent antibodies, hemadsorption is used. Biological tests are also carried out, the material of sick animals is administered to pigs vaccinated against ordinary plague. If they show a pathology, the diagnosis is confirmed.
Treatment and prevention
Specific treatment, like the vaccine, has not been invented today. It is not allowed to even try to treat pigs with symptomatic drugs, as they will continue to excrete pathogens. Prevention of African swine fever in pigs consists of measures in the outbreak and prevention of viruses from other places.
Activities in the outbreak
If pigs show even the slightest signs of possible ASF, all the herd is subject to destruction. Preliminary laboratory diagnostics are carried out to confirm the diagnosis. Especially in cases where the clinical picture is not completely clear. Measures taken at the site of confirmed infection consist of the following items:
- Strict quarantine is imposed on yards and farms where African swine fever is found.
- All animals are killed by any bloodless by method.
- All carcasses are burned, but it is impossible to remove them from the place where quarantine is imposed.
- It is advisable to burn corpses together with a pigsty and utility rooms.
- Destruction is also subject to inventory, residues of feed, bedding, clothes of people caring for pigs.
- Ash is mixed with slaked lime and buried to a depth of not less than a meter.
- Rooms that cannot be burned are thoroughly disinfected. Use caustic soda 3% or formaldehyde 2%.
- The same measures are carried out at all pig farms that are within a radius of 25 km from the infected zone, they kill even completely healthy pigs.
- Throughout territories carry out the destruction of ticks and other blood-sucking insects, rodents, stray animals.
- While quarantine lasts (on average 40 days), no products obtained from animals (not necessarily pig meat) can be taken out of the zone and sold.
- For 6 months after the moment the outbreak occurred, it is prohibited to export and sell any plant agricultural products.
- Pigs cannot be bred throughout the year in the entire quarantine territory, all this time there is a danger of a second outbreak.
The measures must be taken Veterinary services, for this there are certain articles of the law in Russia and other countries. Such strict rules and control measures allow at least partially stop the spread of the disease to other regions. Unfortunately, they cause huge economic harm to households. Many countries have developed a material compensation system, but it does not cover all losses. How events are held in the focus of infection, you can watch the video.
Some ask whether African swine fever is dangerous to humans or not? For people, the disease is not dangerous. But along with the products, it can be transmitted to other pigs in the region. Especially in cases where animals are fed with waste from the food industry.Therefore, it is strictly forbidden to export any products from dysfunctional territories, even if no one is going to sell them