Pigs are considered highly productive farm animals. With one individual, you can get 100 kg of selected meat. However, before selling a meat and greasy product, the animal must be cut. The carcass of a pig or adult pig has similar methods of butchering. The price of meat cuts depends on the breed of the animal and the quality of the cut.
- Types of claw-cutting patterns
- Grade of meat
- Cutting cuts of pork carcasses and their use
- Pork <
- Scapular-cervical girdle
- Shoulder <
- Spine-lumbar cut
- Abdominal
- Korean
- Sacrum
- Pig’s head
- Conclusion <

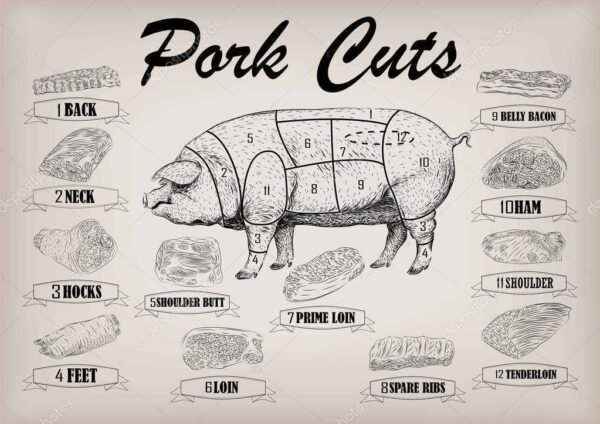
Pork parts carcasses
If the carcass of the pig was not cut for sale correctly, then such a product will be less In order to correctly separate the parts of the first-class pork carcass from the second-class, you should use special schemes.
Types of cloven-carved meat cutting schemes
First of all, you should decide what the parts will go for pigs Cutting artiodactyls depends on the final sale of products. There are several options:
- for cooking at home;
- for sale on the market;
- for salting or smoking;
- for lard.
If the meat goes to the market, the slices should be even, in addition, a certificate from a veterinarian is required to confirm the safety of the product. For consumption at home, you can carve artiodactyl less carefully.
There are four common schemes for carving carcasses:
- German;
- English;
- American;
- Moscow.
The German pork carcass is divided into 2 equal parts, after which they are divided into 8 cuts, depending on the type of meat. The classification of parts according to the German scheme looks like this:
- First grade – ham from the hind limbs, lumbar, patty.
- Second grade – ham from the forelimbs, sternum, scapular .
- The third grade is the stomach.
- The fourth grade is the limbs, the head.
Cutting the artiodactyl in English involves cutting into 4 parts of the carcass of a pig . Each piece is named according to location:
- head;
- front cut;
- central cut;
- back cut.
The American method involves dividing the carcass into 2 longitudinal parts of the pig, after which each major part is divided into 6 pieces:
- head;
- front ham;
- sides;
- back ham;
- notch with back of the portion;
- shoulder blades, shoulder part.
Also, the cutting and deboning of pork carcasses in American style distributes the meat for the purpose of cooking. The shoulder blade is divided into meat and greasy tenderloin. The vertebral and lumbar regions are distributed the same way, and the side is divided into ribs and meat.
In the CIS, pork carcasses are divided according to the Moscow scheme.Artiodactyls are cut into 8 cuts, which bear such names:
- head;
- cutlet portion – cut from the back;
- scapular portion;
- sternum;
- legs from the first joint to the second;
- hooves;
- back ham;
- cervical part.
Meat grade
In many countries, parts of pork carcasses are evaluated differently. However, the first grade always includes a meat layer along the pig’s spine. The muscle tissue from this place is soft and tender, as artiodactyls do not use these muscles when walking. In addition, first-class pieces of pork include collars. Unlike other farm animals, pigs practically do not move their heads.
There is a general classification of the meat grade used in the culinary industry:
- It is customary to include the cloven-hoofed shoulder girdle, the first grade , sternum, lumbar and ham.
- The second grade includes the head, forearm and shanks.
Cutting cuts of pork carcass and using them
Boning and cutting pork carcasses into cuts also includes cutting the parts themselves. The following parts of the carcass of a farm pig are distinguished:
- ham;
- shoulder-cervical girdle;
- knuckle;
- dorso-lumbar cut;
- abdominal cavity;
- loin;
- sacrum;
- head.
Gammon
Gammon is a clipping from the cloven-hoofed thighs. Traditionally, ham is sold in a cut. With this cut, you can cut the maximum amount of meat from the bone. A whole ham can often have torn edges, which reduces its cost.
The meat cut from the animal’s thigh is used in the preparation of many meat dishes. The upper part of the ham contains a large percentage of muscle mass, so dishes such as:
- kebab;
- schnitzel;
- boiled pork are cooked from it.
>
The lower part of the ham usually contains less meat, so the jelly is most often prepared from it.
Shoulder-neck belt
Shoulder cut and neck pigs are called the scapular part and the neck. This cut is done in three pieces:
- scapula without bone.
- scapula on bone.
- neck.
The boneless shoulder is used for baking and frying. Also, goulash, sausages and sausage are prepared on the basis of this meat.
The scapular boneless part of pork is drier and stiffer meat, therefore, in the culinary industry, this part is marinated before cooking. Also, the cut is suitable for frying and smoking.
The neck is considered tender meat, because the animal does not use this muscle mass during life. Barbecue, escalope and chops are prepared from it.
Knuckle
The knuckle is the part of the pork that is on the first joint of the front legs. The same cut of the hind limb is called the shank. The knuckle is considered meat of the second grade, since the muscle tissue on the legs is dense. Most often, jelly is prepared from this cut. Due to its high muscle density, the shank is well suited as the basis for meatloaf.
In some countries this cut is smoked, after which the meat is cut thinly from the bone.
Spine lumbar cut
This part of the pig carcass is also called carbonate. The lumbar cut in all schemes is considered first-class meat, due to its high palatability. In the Moscow scheme, this part is called cutlet. The quality of the lumbar cut depends on how many concentrates the animal consumed.
Cutting along the spine is the most expensive part of the carcass. It is used to prepare the following dishes:
- escalope;
- chops;
- steaks.
Meat from the lumbar department after heat treatment is baked or smoked. Also, sausages and sausages are prepared from this cut.
Abdominal section
This cut includes such parts of the artiodactyl body:
- sternum.
- underscores.
- abdominal part.
The sternum is the thick edge of the abdominal part in the lumbar region. There is a high percentage of fat in such meat, so it is better suited for baking and smoking.
The thin edge of the peritoneum is called flank. This part is closer to the ham and is suitable for making rolls.
Undercall is called lard with meat veins. Such a greasy layer is much more appreciated than a pure product. Undercuts are suitable for baking and smoking.
Loin
There are 2 types of this part of the carcass:
- loin on the bone;
- loin without bones.
The meat on the bone is cut from the back along with the base of the ribs. This muscle mass has good taste, so the loin is often used for baking and served on the bones. Clean ribs are suitable for jellied meat and broths.
A boneless loin is a clean piece of meat that is cut from a cloven-hoofed lumbar belt. A similar portion is used for steaks.
Sacrum
This cut is located at the end of the animal’s back belt. The sacrum has the smallest percentage of body fat. The lean portion of meat is primarily suitable for cooking or barbecue. Since the muscle mass from the sacrum is lean, it can be used by people with diseases of the pancreas and liver.
Pig’s head
This cut has a low taste, however, due to its cheapness , many culinary specialists prefer to take this part for cooking various dishes. Most often, the head is used for aspic and broth. They make an aspic from the tongue of a pig.
An animal’s brain, when properly cooked, is considered a delicacy. Artiodactyl cheeks have a good fat layer and are suitable for baking. Pork ears are fried in Asian countries, marinated first in mustard.
Conclusion
There are several schemes by which you can cut the pig.The cost of cuts depends on the quality of the cut and deboning.
Pig meat is classified by grades, depending on taste. The cloven-hoofed cuttering scheme is selected depending on which breed is grown on the farm and in which area the final product will be used.