Ascariasis of pigs is not a deadly disease, but it causes a slowdown in young growth and leads to economic losses in pig production.
- Etiology of ascariasis
- Epizootology of ascariasis
- Clinical signs and consequences
- Acute stage of development
- Chronic stage
- Diagnosis and treatment
- Preventive measures

Swine ascariasis
Etiology of ascariasis
Ascariasis refers to chronic diseases associated with the presence of round helminths from the family a in animals carid.
The causative agents of the disease settle in the small intestine of pigs, sometimes localized in the bile ducts in the liver.
Swine ascariasis occurs in almost all farms both in our country and abroad The exception is only some regions of the Far North. Infected animal meat cannot be eaten.
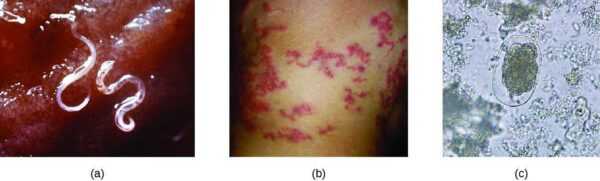
The causative agents of the disease are nematodes, white with a pink hue, which in females can be up to 40 cm long, in males up to 25 cm. You can see how helminths look in the photo . The parasite leaves an oval dark brown egg with a tuberous membrane.
At risk for ascaridosis, the population is from 2 to 6 months old.
Roundworms in pigs can undergo development without an intermediate host, spreading in the body of piglets daily up to 200 eggs secreted by animals along with feces. In the environment, ascaris eggs retain their activity for up to a month at average temperatures of 25 ° C, and in sandy soils can live up to 2.5 years.
Epizootology of ascaridosis
Among the main causes of the disease, there are:
- ingestion of larvae and eggs when eating food or with drinking water,
- the pathogen enters through eating the earth in cases of mineral starvation,
- distribution by milk feeding piglets through the udder of the sow.
The most common Tests for infecting piglets are walking places and a pigsty.
The pattern of entry and spread of roundworm larvae and eggs includes:
- entry into the intestinal area of the animal,
- the introduction of larvae into the intestinal mucous membranes,
- movement with blood flow into the liver and the right atrium,
- spread towards the lung tissue of pigs, settling in the bronchi and bronchioles,
- localization in small capillaries.
Ascaris larvae that enter the intestinal cavity grow for up to 2.5 months to state ence maturity and can live in the body of a pig from 4 to 10 months.
Among the factors that contribute to the spread of the disease are the placement of pigsties in damp lowlands and on sandstones, poor sanitary conditions for animals.
Clinical signs and consequences
Ascaris disease in pigs can occur in various forms.
Acute stage of development
The symptoms of the acute course are:
- allergic reactions ,
- nervous disorders in the form of convulsive states and tremors in the limbs,
- impaired coordination,
- dry appearance go cough, turning into a wet state and bronchopneumonia,
- increase in general body temperature.
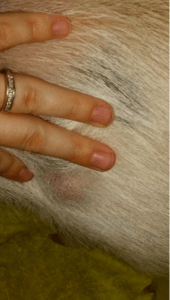
On the skin of piglets infected with ascariasis, rashes with papules may appear to the size of the grain, gradually turning after 5-6 days in scabs with brown or black fringing.
Chronic stage
With a diagnosed chronic development, a decrease in animal appetite is clearly expressed. Symptoms of the disease can be disorders of the gastrointestinal tract both in the form of diarrhea and constipation.
Adult individuals do not show symptoms of development in a chronic form. Infected pigs stop at their pace of development and lose weight, losing weight significantly.
Infection of pigs with ascariasis disease leads to various consequences:
- inflammatory processes in organs and tissues begin due to a mechanical violation of the integrity of the vessels during the movement of ascaris larvae;
- allergic reactions occur due to toxicity of the larvae in the animal’s body, which release metabolic products during development;
- due to mechanical damage to the intestinal walls, frequent breaks occur, leading to tissue atrophy;
- I in the hepatic ducts of ascaris in pigs cause complications in the outflow of bile,
- spotted changes are observed in the liver, and lung tissue undergoes hemorrhages and become covered with foci of pneumonia.
The most serious consequence ascariasis disease is the development of pneumonia.
Diagnosis and treatment
A laboratory test of feces for the presence of roundworm larvae and eggs with simultaneous clinical analysis is used as the main diagnostic method for ascariasis in pigs Sim volumes and signs of the disease, then treatment is prescribed.
The diagnosis of ascariasis can be supplied by the research to the antigen, which is made from ascarids and is found in pigs ear. A positive reaction can be judged by the manifestation after 5 minutes at the injection site of the red rim, which does not disappear after an hour.
In the treatment of pigs from the described disease, anthelmintic drugs and their salts are used. Among the most common means for treatment, piperazine is allocated, which is prescribed to animals twice a day in the morning and evening when feeding. In this case, a single dose for piglets weighing up to 50 kg is 0.3 g of the drug per 1 kg of body weight. For adults, the dose of piperazine is 15 g of the active substance per kilogram of weight.
Piperazine treatment is carried out by the group method, for which the necessary amount of substance is calculated for the entire livestock in the pigsty and mixed with feed. Weakened animals are treated in small groups of up to 30 animals.
For the treatment of ascariasis, medicinal feeds containing piperazine salts can be used, which are fed at the rate of 2 kg per head per day as the main power supply.
Preventive measures
In pig breeding, as a prophylaxis, mandatory deworming is carried out without fail, for sows this is done a month before farrowing, for the whole herd as a whole – in the autumn and before moving m livestock per stall.
Resistance of pigs to ascaridosis develops with the age of animals. Immune bodies appear after vaccination on days 5-10 and last for 3-4 months.
The cycle of prophylactic deworming of young animals depends on the time of the event:
- If this is done before mid-winter (until December), medications are given to piglets at the age of 35-40 days for initial prevention, the second stage occurs at the age of 80 days.
- If the dehelm events ntizatsii fall beyond December to May, the initial phase between the ages of piglets 50-55 days, and the second – on the 90-day period.
Prevention of ascariasis also involves the disinfestation of rooms where the livestock of pigs is kept, which can be used for:
- ash liquor,
- 5 percent sodium solution (70-80 ° C),
- 10% xylonaphtha emulsion in water (70-80 ° C).
In order to prevent floors in the pigsty and on walking grounds, they are made with a coating of hard material, the premises are cleaned of manure daily, followed by thermal sterilization.