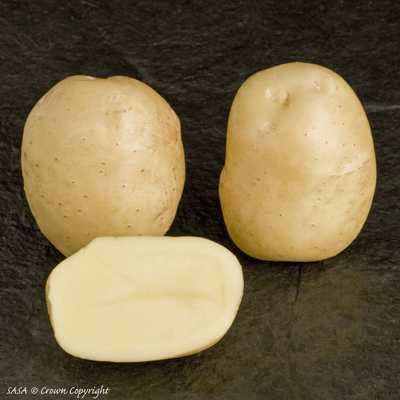
Zorachka potatoes – an early variety of Belarusian selection. Forms tubers in the first half of the growing season. Average productivity, taste excellent, culinary type AB. Unpretentious to soil and weather conditions.
- Features of the
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Planting potatoes
- Soil preparation
- Planting potatoes
- Caring for potatoes
- Watering <
- Fertilizer
- Pest Control
- Conclusion <

Characteristics of Zorohka potato
Features of the variety
Characteristics of potato Zorachka testifies to the mass of its advantages units of other varieties of early selection. The bush is medium-tall, semi-erect, with green intermediate leaves. The variety ripens in just 70-75 days after planting. The first tubers dig already on the 40-45 day of planting, 9-12 pieces are tied under the bite, average weight 90-120 gr.
Description of the tubers:
- oval slightly elongated;
- yellow peel with small glasses;
- light yellow flesh.
The tubers are slightly boiled, their taste is good. They contain about 14% starch and are ideal for salads m and frying.
Advantages and disadvantages
Early ripe Zorachka potatoes are grown for table use.
Its main advantage is early tuberization and the rapid growth of potatoes.Advantages of the variety:
- is resistant to the Dahlem cancer type;
- is almost not affected by the nematode;
- is immune to late blight;
- is well preserved ;
- has taste;
- productivity 250-315 c / s hectare;
- unpretentiousness, gives good productivity on any type of soil and in various climates.
Disadvantages of the variety: it is unstable to the Y-virus, it does not tolerate drought and requires regular watering, in greenhouses it is affected by whiteflies, spider mites. Relatively resistant to mechanical damage.
Potato planting

Tubers germinate before planting
Tubers germinate before planting at temperatures from 4 ° C to 21 ° C. They are scattered with a thin ball in a greenhouse or room and covered with a film. In dry air, the seeds are turned over and sprayed with water, covered from direct sunlight with paper or a white cloth. Vegetable growers recommend that the seed be sanitized with a solution of potassium permanganate every week.
Soil preparation
The site for the crop is selected sunny. This takes into account which plants were grown on it before.
Good predecessors of Zorachka:
- perennial and annual grasses;
- winter crops;
- cereals and legumes;
- in the sand – lupine.
The soil is prepared in the fall. In acidic soil on 1 m² contribute up to 200 gr. lime. Organic fertilizers are added in such quantities:
- in clay soil – a bucket of humus or peat;
- in sandy soil – by a bucket of humus, peat and clay;
- in peat soil – 10 kg of clay, sand and humus.
1 tablespoon is added per 1 m² of land. superphosphate, 150,200 gr. ash, not more than 1 tsp potash fertilizer. Vegetable growers and summer residents do not recommend fertilizing the site with fresh manure. This significantly impairs the taste of the culture. After fertilizing, the soil is deeply dug, choosing weeds and their roots.
Planting potatoes
Seeds are planted in open ground in May, when the sprouts reach a length of 1 cm Before this, they are treated with a solution of phytosporin-M (50 g of the drug is diluted in 3000 ml of water). These measures will protect the plant from late blight.
Potatoes are planted manually or mechanically. The distance between the seeds is 30-35 cm, between the rows – at least 60 cm.
Care for potatoes
The culture requires constant care. Untimely watering or hilling entail a delay in the growth and development of the plant. In this case, it will not work to get a super-early harvest.
The land around the crop should be constantly soft. This will provide unhindered air access to the roots. Loosening is performed every time a crust forms on its surface.
Potato care rules:
- A week after planting potatoes, the soil is loosened with a rake or harrow. If it quickly overgrows with weeds, these measures are repeated in a week.
- After the rows are formed, nightshade is treated with a hoe, destroying weeds.
- A plant 15-15 cm tall is sprinkled with soil so that it does not bent over and did not break in the wind.
Some vegetable growers believe that it is not worthwhile to spud plants in hot, dry summers if it is not possible to provide regular watering. The tubers simply “bake” in the ground. You can’t do this on a hot sunny day when the land is dry.

Plants need good care
In the northern latitudes, where the summers are cool and it often rains, it is necessary to cultivate the culture. This will protect the plant from frost and rid of weeds.
Watering
Timely watering is a prerequisite for a high crop yield. Watering the plant is necessary depending on weather conditions, region and soil moisture. If it rains frequently, you can forget about this event before the flowering of the crop.
For the entire growing season, three plentiful irrigation is enough:
- during the first emergence;
- at the beginning of flowering;
- after flowering.
Zorachka variety is sensitive to drought, in such weather it requires regular watering.Withered leaves – a signal for urgent watering. Do this in the late afternoon, pour at least 3 liters of water under each bush. Watering methods:
- in the holes or furrows:
- by sprinkling.
It is better to use the first method, since the second can cause fungal diseases . The earth around the culture must be manually cultivated every other day.
Fertilizer
The culture is fed three times during the entire growing season. The first time fertilizers are applied 3-4 weeks after planting. In the southern latitudes this is done in May, in the northern – in June. About 1 g of urea, 20 g of superphosphate and 10 g of potassium sulfate are taken per 1 m2. Fertilizers are dissolved in water and water the crop. If there is drip irrigation, it is enough to sprinkle fertilizer along the aisles. The lush and dark green tops indicate an excess of nitrogen. In this case, mineral fertilizers can be replaced with bird droppings (per 1 m2 – 200 g of litter).
- The second dressing is carried out after the buds appear, the third – after the plant has blossomed.
- 2-3 times spend foliar top dressing. The bushes are sprayed with a 2% solution of a mixture of superphosphate, potassium chloride and Bordeaux liquid.
- This will not only fertilize the plants, but also protect them from painful conditions and pests.
Pest Control
Pests and disease states lie in wait for crops everywhere, and to prevent this from affecting crop yields, you need to know how to deal with them.
Pests and methods of dealing with them:
- Medvedka eats tubers of a young plant. You can identify it by the “moves”, which are clearly visible. Pest control measures: during the planting of crops on 1 m2 lay a branch of needles; fill the passages with a solution of laundry soap; fall asleep moves. The pest leaves the site and leaves.
- Potato moth affects plants in the southern latitudes, where they are grown 2 times a year. Caterpillars that eat leaves are dangerous. They are treated with drugs “Bankol”, “Fosbezid” according to the instructions.
- A spider mite populates the back of the leaves, they turn yellow and fall off. Preventive measures: harvesting from the soil the remains of previous plants, disinfection of greenhouses.
- The Colorado potato beetle eats leaves, flowers and stems of a plant. Biological pest control measures: plants regularly inspect, collect beetles, their eggs, larvae and destroy. Chemical methods: cultures are treated with the preparations “Mospilan”, “Killer”, “Stop bug”.
In addition, tubers sometimes rot. The cause is late blight, common scab or dry rot. These painful conditions are easily prevented by proper planting and picking of tubers.
Grow good the harvest is easy. You need to take preventative measures and monitor pests in a timely manner.
Conclusion
Zorohka is an early table variety that is resistant to most diseases conditions, unpretentious to soil and weather conditions.High yield and good taste, short ripening period allowed it to occupy a worthy niche among other early types of potatoes.